
Breast reconstruction is the surgical process of rebuilding the shape and look of a breast, most commonly in women who have had surgery to treat breast cancer. It involves using autologous tissue, prosthetic implants, or a combination of both with the goal of reconstructing a natural-looking breast. This process often also includes the rebuilding of the nipple and areola, known as nipple-areola complex (NAC) reconstruction, as one of the final stages.

Plastic surgery is a surgical specialty involving the restoration, reconstruction, or alteration of the human body. It can be divided into two main categories: reconstructive surgery and cosmetic surgery. Reconstructive surgery covers a wide range of specialties, including craniofacial surgery, hand surgery, microsurgery, and the treatment of burns. This category of surgery focuses on restoring a body part or improving its function. In contrast, cosmetic surgery focuses solely on improving the physical appearance of the body. A comprehensive definition of plastic surgery has never been established, because it has no distinct anatomical object and thus overlaps with practically all other surgical specialties. An essential feature of plastic surgery is that it involves the treatment of conditions that require or may require tissue relocation skills.

Mammaplasty refers to a group of surgical procedures, the goal of which is to reshape or otherwise modify the appearance of the breast. There are two main types of mammoplasty:
- Augmentation mammaplasty is commonly performed to increase the size, change the shape, and/or alter the texture of the breasts. This usually involves the surgical implantation of breast implant devices.
- Reduction mammaplasty is commonly performed to reduce the size, change the shape, and/or alter the texture of the breasts. This involves the removal of breast tissue.
Stryker Corporation is an American multinational medical technologies corporation based in Kalamazoo, Michigan. Stryker's products include implants used in joint replacement and trauma surgeries; surgical equipment and surgical navigation systems; endoscopic and communications systems; patient handling and emergency medical equipment; neurosurgical, neurovascular and spinal devices; as well as other medical device products used in a variety of medical specialties.
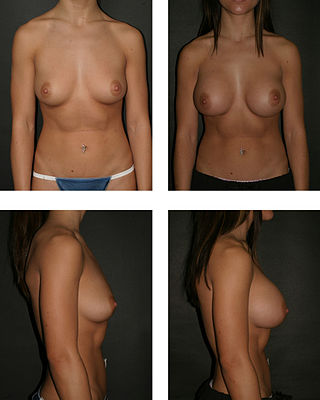
Breast augmentation and augmentation mammoplasty is a cosmetic surgery procedure, which uses breast-implants and/ or fat-graft mammoplasty technique to increase the size, change the shape, and alter the texture of the breasts. Although in some cases augmentation mammoplasty is applied to correct congenital defects of the breasts and the chest wall in other cases it is performed purely for cosmetic reasons.
Medical tourism is the practice of traveling abroad to obtain medical treatment. In the past, this usually referred to those who traveled from less-developed countries to major medical centers in highly developed countries for treatment unavailable at home. However, in recent years it may equally refer to those from developed countries who travel to developing countries for lower-priced medical treatments. With differences between the medical agencies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or the European Medicines Agency (EMA), etc., which decide whether a drug is approved in their country or region, or not, the motivation may be also for medical services unavailable or non-licensed in the home country.

Medtronic plc is an American-Irish medical device company. The company's operational and executive headquarters are in Minneapolis, Minnesota, and its legal headquarters are in Ireland due to its acquisition of Irish-based Covidien in 2015. While it primarily operates in the United States, it operates in more than 150 countries and employs over 90,000 people. It develops and manufactures healthcare technologies and therapies. It is one of the biggest medical tech companies in the world and is currently the largest medical device company in the world by revenue.

Reconstructive surgery is surgery performed to restore normal appearance and function to body parts malformed by a disease or medical condition.
Professor Sir Bruce Edward Keogh, KBE, FMedSci, FRCS, FRCP is a Rhodesian-born British surgeon who specialises in cardiac surgery. He was medical director of the National Health Service in England from 2007 and national medical director of the NHS Commissioning Board from 2013 until his retirement early in 2018. He is chair of Birmingham Women's and Children's NHS Foundation Trust and chairman of The Scar Free Foundation.

A breast implant is a prosthesis used to change the size, shape, and contour of a person's breast. In reconstructive plastic surgery, breast implants can be placed to restore a natural looking breast following a mastectomy, to correct congenital defects and deformities of the chest wall or, cosmetically, to enlarge the appearance of the breast through breast augmentation surgery.
Professor Kefah Mokbel FRCS is currently the chair of breast cancer surgery and the multidisciplinary breast cancer program at the London Breast Institute of the Princess Grace Hospital part of HCA Healthcare, Professor (Honorary) of Breast Cancer Surgery at Brunel University London, an honorary consultant breast surgeon at St George's Hospital. Kefah Mokbel is the founder and current president of Breast Cancer Hope; a UK-based charity "dedicated to improving the quantity and quality of life in women diagnosed with breast cancer". He was appointed as a substantive consultant breast surgeon at St George's Hospital NHS trust in February 2001. He was named in Tatler magazine's Best Doctors Guide as one of the featured "Top Breast Surgeons" in 2006, 2007 and 2013. In November 2010 he was named in the Times magazine's list of Britain's Top Doctors.
The 2010 DePuy Hip Replacement Recall was instituted when DePuy Orthopaedics, Inc., a division of Johnson & Johnson, recalled its ASR XL Acetabular metal-on-metal hip replacement system on August 24, 2010.
Optical Express is a provider of ophthalmology services including laser eye surgery, cataract surgery and lens replacement surgery in the United Kingdom and Europe.
Susan Kolb is a medical doctor in Atlanta, Georgia, and the author of The Naked Truth about Breast Implants: From Harm to Healing. Her area of specialization is plastic and reconstructive surgery. Kolb is a medical authority on the complications arising from breast implants, and has been an active voice in the debate about the safety of breast implant devices since 1996. She has treated over 2,000 women suffering from breast implant disease and related systemic immune disorders.

Poly Implant Prothèse (PIP) was a French company founded in 1991 that produced silicone gel breast implants. The company was preemptively liquidated in 2010 following the revelation that they had been illegally manufacturing and selling breast implants made from cheaper industrial-grade silicone since 2001.

Ted Eisenberg D.O. is a Philadelphia, Pennsylvania based plastic surgeon who specializes in cosmetic breast surgery. He holds a Guinness World Record for the most breast augmentation surgeries performed in a lifetime (male)— 3460.

Jan Stanek is a British cosmetic surgeon, lecturer and broadcaster. He is a Fellow of the Royal College of Surgeons, a member of the British Medical Association, the Royal Society of Medicine and The American Academy of Cosmetic Surgery. He has a private practice in central London.

The Princess Grace Hospital is a private hospital in Marylebone, London, and is part of the international division of HCA, which is the world's largest private healthcare company.
The Iranian Hospital is a non-profit rural general hospital in Dubai is located on the Al Wasl Road in Jumeirah. Inaugurated on 14 April 1972, it was built by and is affiliated to the Iranian Red Crescent Society, and is the oldest known provider of healthcare services in Dubai. Most of the hospital's medical staff are from the Iranian community in the UAE. It is a private hospital and comes under Dubai Health Authority (DHA).
Cosmetic surgery, also referred to as aesthetic surgery, is a surgical procedure which endeavours to improve the physical aspects of one's appearance to become more aesthetically pleasing. The continuously growing field of cosmetic surgery is closely linked with plastic surgery, the difference being, cosmetic surgery is an elective surgery with the sole purpose to enhance the physical features of one's appearance. Plastic surgery is performed in order to rectify defects to reinstate normality to function and appearance. Cosmetic surgical procedures are generally performed on healthy functioning body parts, with the procedure being optional not medically necessary. The inevitable aim of cosmetic surgery is to enhance one's image, encompassing reducing the signs of aging and/or correction of a believed deviation on one's body in turn it is surrounded by controversy. Although the implementation of cosmetic surgery within Australian society is growing, the trade has struggled to find its place within the Australian culture.










