The Aimaq or Chahar Aimaq, also transliterated as Aymaq, Aimagh, Aimak and Aymak, are a collection of Sunni and mostly Persian-speaking nomadic and semi-nomadic tribes. They live mostly in the central and western highlands of Afghanistan, especially in Ghor and Badghis. Aimaqs were originally known as chahar ("four") Aymaqs: Jamshidi, Aimaq Hazara, Firozkohi and Taymani. The Timuri, which is a separate tribe but is sometimes included among Aimaqs, which is known as Aimaq-e digar.

The Hazaras are an ethnic group and a principal component of the population of Afghanistan, native to Afghanistan, Pakistan, and Iran. They are one of the largest ethnic groups in Afghanistan and primarily residing in the Hazaristan (Hazarajat) region in central Afghanistan, as well as a significant minority groups mainly in Quetta, Pakistan and Mashhad, Iran. They speak the Dari and Hazaragi dialects of Persian. Dari, also known as Dari Persian, is one of two official languages of Afghanistan.
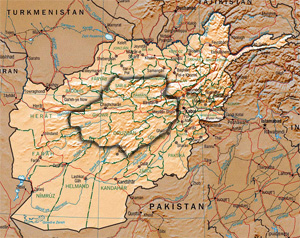
Hazarajat, also known as Hazaristan, is a mostly mountainous region in the central highlands of Afghanistan, among the Kuh-e Baba mountains in the western extremities of the Hindu Kush. It is the homeland of the Hazara people who make up the majority of its population. Hazarajat denotes an ethnic and religious zone.
Lal wa Sarjangal, is a district in the north-east of Ghor province in central Afghanistan. The district center is the town of La'l.

Afghanistan is a multiethnic and mostly tribal society. The population of the country consists of numerous ethnolinguistic groups: mainly the Pashtun, Tajik, Hazara, and Uzbek and minorities of Aimaq, Turkmen, Baloch, Pashai, Nuristani, Gujjar, Brahui, Qizilbash, Pamiri, Kyrgyz, Sadat, and others. Altogether they make up the Afghan people.
Behsudi or Behsud are one of the major tribes of the Hazaras in Afghanistan.
The Hazara Democratic Party (HDP) : is a political party of the Hazara people in Pakistan. It is mainly active in Quetta city, where up to half a million Hazara currently reside.

The Hazaras have long been the subjects of persecution in Afghanistan. The Hazaras are mostly from Afghanistan, primarily from the central regions of Afghanistan, known as Hazarajat. Significant communities of Hazara people also live in Quetta, Pakistan, and in Mashad, Iran, as part of the Hazara and Afghan diasporas.
The Hazara people are an ethnic group who are mostly from Afghanistan, primarily from the central regions of Afghanistan, known as Hazarajat, they established a large diaspora that consists of many communities in different countries around the world as part of the later Afghan diaspora. There are currently a million Hazara who live in the Balochistan province of Pakistan mostly in Quetta, many of whom have been settled in the country for generations and are now Pakistani citizens. A similarly large Hazara community is also present in Mashhad, Iran, as part of the Hazara and Afghan diaspora.
Hazara cuisine or Hazaragi cuisine refers to the food and cuisine of the Hazara people in Afghanistan and western Pakistan. The food of the Hazara people is strongly influenced by Central Asian, South Asian cuisines and shares similarities with neighboring regional cuisines in Afghanistan and Central Asia. However, there are certain dishes, culinary methods and styles of cooking that are unique to the Hazara people.
Hazara culture refers to the culture and tradition of the Hazara people, who live primarily in the Hazarajat region of central Afghanistan, the Balochistan province of Pakistan, and elsewhere around the world where the Hazara diaspora is settled as part of the wider Afghan diaspora.

On 23 July 2016, a twin bombing occurred in the vicinity of Deh Mazang square in Kabul, capital of Afghanistan, when Enlightenment Movement protesters, mostly from the Hazara ethnic group, were marching against a decision to bypass their region in the development of the TUTAP mega power project. At least 97 people were killed and 260 injured. The terrorist group Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant claimed responsibility, however the same group later on refused it. Some Hazara protestors allege that Afghan president Ashraf Ghani was behind the attack. They believe that Ashraf Ghani government was abetting the terrorists who were responsible for the attack. They also allege that the government officials were preventing the wounded from being shifted to the hospital.

The 1888–1893 Hazara uprisings or genocide and displacement of Hazaras occurred in the aftermath of the Second Anglo-Afghan War when the Afghan Emirate signed the Treaty of Gandamak. Afghan Amir Abdur Rahman set out to bring the Turkistan, Hazaristan, and Kafiristan regions under his control. He launched several campaigns in the Hazarajat due to resistance to oppression from the Hazaras, culminating in the Battle of Uruzgan and he conducted a widespread genocidal campaign against its population.
Hazara nationalism is a movement that claims the Hazara people, an ethnic group native to the Hazaristan region of Afghanistan, are a distinct nation and deserve a nation-state of their own. The movement propagates the view that Muslims are not a nation and that ethnic loyalty must surpass religious loyalty, though this view has been challenged by both the 1890s independence uprisings of Hazaristan and the systematic discrimination many Hazaras have historically faced within Afghanistan.
Hazara Australians or Australian Hazaras are Australians who have Hazara ancestry. The Hazaras are an ethnic group native to, and primarily residing in, the mountainous region of Hazarajat in central Afghanistan. Many Hazara Australians have also migrated from Pakistan. The Hazara Council of Australia is an organization formed by the Hazara community of Australia. Hazaras constitute one of the largest ethnic groups of asylum seekers in Australia
On 8 May 2021, a car bombing, followed by two more improvised explosive device (IED) blasts, occurred in front of Sayed al-Shuhada school in Dashte Barchi, a predominantly Shia Hazara area in western Kabul, Afghanistan, leaving at least 90 people dead and 240 injured. The majority of the casualties were girls between 11 and 15 years old. The attack took place in a neighborhood that has frequently been attacked by militants belonging to the regional Islamic State – Khorasan Province (IS-K) over the years.
The Enlightenment Movement or Junbesh-e Roshnayi is a grassroots civil disobedience movement of Hazaras created in 2016 in Afghanistan in response to the Afghan government's change in routing plans for proposed international electricity networking, which was perceived as continuing historical anti-Hazara discrimination. The group organised major protests in Afghanistan and internationally during 2016 and 2017, protesting against discrimination. The group's youthful leadership challenged traditional Hazara leaders for representativity of the community.








