Related Research Articles

A bulletin board system (BBS), also called a computer bulletin board service (CBBS), was a computer server running software that allowed users to connect to the system using a terminal program. Once logged in, the user can perform functions such as uploading and downloading software and data, reading news and bulletins, and exchanging messages with other users through public message boards and sometimes via direct chatting. In the early 1980s, message networks such as FidoNet were developed to provide services such as NetMail, which is similar to internet-based email.
A frequently asked questions (FAQ) list is often used in articles, websites, email lists, and online forums where common questions tend to recur, for example through posts or queries by new users related to common knowledge gaps. The purpose of a FAQ is generally to provide information on frequent questions or concerns; however, the format is a useful means of organizing information, and text consisting of questions and their answers may thus be called a FAQ regardless of whether the questions are actually frequently asked.
The Gopher protocol is a communication protocol designed for distributing, searching, and retrieving documents in Internet Protocol networks. The design of the Gopher protocol and user interface is menu-driven, and presented an alternative to the World Wide Web in its early stages, but ultimately fell into disfavor, yielding to HTTP. The Gopher ecosystem is often regarded as the effective predecessor of the World Wide Web.
Joyce Kathleen Reynolds was an American computer scientist who played a significant role in developing protocols underlying the Internet. She authored or co-authored many RFCs, most notably those introducing and specifying the Telnet, FTP, and POP protocols.

Lynx is a customizable text-based web browser for use on cursor-addressable character cell terminals. As of 2024, it is the oldest web browser still being maintained, having started in 1992.
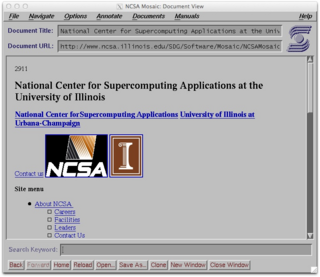
NCSA Mosaic is a discontinued web browser, and one of the first to be widely available. It was instrumental in popularizing the World Wide Web and the general Internet by integrating multimedia such as text and graphics. It was named for its support of multiple Internet protocols, such as Hypertext Transfer Protocol, File Transfer Protocol, Network News Transfer Protocol, and Gopher. Its intuitive interface, reliability, personal computer support, and simple installation all contributed to its popularity within the web. Mosaic is the first browser to display images inline with text instead of in a separate window. It is often described as the first graphical web browser, though it was preceded by WorldWideWeb, the lesser-known Erwise, and ViolaWWW.

Cello is an early, discontinued graphical web browser for Windows 3.1; it was developed by Thomas R. Bruce of the Legal Information Institute at Cornell Law School. It was released as shareware in 1993. While other browsers ran on various Unix machines, Cello was the first web browser for Microsoft Windows, using the winsock system to access the Internet. In addition to the basic Windows, Cello worked on Windows NT 3.5 and with small modifications on OS/2.

Archie is a tool for indexing FTP archives, allowing users to more easily identify specific files. It is considered the first Internet search engine. The original implementation was written in 1990 by Alan Emtage, then a postgraduate student at McGill University in Montreal, Canada.
Interpedia was the first-proposed online encyclopedia which would allow anyone to contribute by writing articles and submitting them to the central catalogue of all Interpedia pages.
Veronica was a search engine system for the Gopher protocol, released in November 1992 by Steven Foster and Fred Barrie at the University of Nevada, Reno.
cURL is a computer software project providing a library (libcurl) and command-line tool (curl) for transferring data using various network protocols. The name stands for "Client for URL".
The Line Mode Browser is the second web browser ever created. The browser was the first demonstrated to be portable to several different operating systems. Operated from a simple command-line interface, it could be widely used on many computers and computer terminals throughout the Internet. The browser was developed starting in 1990, and then supported by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) as an example and test application for the libwww library.

FTP Software, Inc., was an American software company incorporated in 1986 by James van Bokkelen, John Romkey, Nancy Connor, Roxanne van Bokkelen, Dave Bridgham, and several other founding shareholders, who met at Toscanini's in Central Square after an email went out over the Bandykin mailing list looking for people interested in starting a company. Their main product was PC/TCP, a full-featured, standards-compliant TCP/IP package for DOS. The company was based in Andover, Massachusetts. It also had a number of offices throughout the United States and overseas.
Rick Gates is an Internet pioneer mostly known for organizing The Internet Hunt and developing the concept of Interpedia. He studied at the Graduate Library School at the University of Arizona.
A search engine is a software system that provides hyperlinks to web pages and other relevant information on the Web in response to a user's query. The query is typically done within a web browser or a mobile app, and the search results are presented as a list of hyperlinks, accompanied by textual summaries and images.
An Internet scavenger hunt or CyberHunt is an educational lesson which introduces the Internet to students. It is often used as tool for teaching students how to search the Internet and how to use the resources and information available on the Internet. It is an online activity in the form of a scavenger hunt that focuses on gathering information from web sites to answer questions or to support a concept on a particular theme or content area. The intent is to hunt for facts or information to add details for the answer to the question. The questions themselves may vary from the simple fact or statement to the more complex, depending upon the age and skill level of the student. By completing CyberHunts, students learn how to navigate a web site, scan a page for detailed information, and then apply the facts or ideas to the question. A CyberHunt is an excellent way to teach beginning internet researching skills.
BITNET was a co-operative U.S. university computer network founded in 1981 by Ira Fuchs at the City University of New York (CUNY) and Greydon Freeman at Yale University. The first network link was between CUNY and Yale.
InterCon Systems Corporation was founded in April 1988 by Kurt D. Baumann and Mikki Barry to produce software to connect Macintosh computers in environments that were not Macintosh-exclusive. At the time, there was no real concept of the Internet and there was still a question of whether the TCP/IP protocols or OSI protocols would be adopted widely. Over the next 9 years, the company grew from three employees to over 100 and sold software in the US, Europe and Japan.
Emissary was a popular early commercial internet suite from Attachmate for Windows. It featured a web browser, FTP support, e-mail program, a newsreader program, and an HTML editor.
References
- 1 2 3 Gates, Rick (1992-08-31). "A CHALLENGE FOR ALL INTERNET USERS". Newsgroup: bit.listserv.libref-l. Retrieved 15 October 2020.
- ↑ Greim, Lisa (11 May 1997). "Sat-type test measures net skill". Rocky Mountain News . Archived from the original on 19 November 2018. Retrieved 14 September 2012– via HighBeam Research.
- ↑ Silicon Snake Oil, Clifford Stoll, Doubleday, 1995, pp189–190
- ↑ Bruckman, Amy (1 July 1994). "King of the Hunt". Wired. Retrieved 15 October 2020.
Issue 2.07, July, 1994 p33
- ↑ Gates, Rick (1993-12-01). "The November 93 Hunt Results "K-12 ONLY HUNT"". Edtech. Retrieved 15 October 2020.
- ↑ Gates, Rick (1993-09-01). "September Hunt Questions: THE INTERNET HUNT, for September, 1993 - A BEGINNER'S HUNT". Discussion of Library Reference Issues (LIBREF-L). Archived from the original on 2003-06-13. Retrieved 15 October 2020.
- ↑ 1993 October Internet Hunt "The October Internet Hunt required use of netfind, finger, whois, vrfy, CSO, X.500, Usenet Addresses, and numerous local databases to find people on the nets."
- ↑ "LM_NET 01/06/94: January Internet Hunt". Archived from the original on 2020-10-15.