
Gloria Fowles, known professionally as Gloria Gaynor, is an American singer, best known for the disco era hits "I Will Survive" (1978), "Let Me Know " (1979), "I Am What I Am" (1983), and her version of "Never Can Say Goodbye" (1974).

Fury is a 1936 American crime film directed by Fritz Lang that tells the story of an innocent man who narrowly escapes being burned to death by a lynch mob and the revenge he then seeks. The film was released by Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer and stars Sylvia Sidney and Tracy, with a supporting cast featuring Walter Abel, Bruce Cabot, Edward Ellis and Walter Brennan. Loosely based on the events surrounding the Brooke Hart murder in San Jose, California, the film was adapted by Bartlett Cormack and Lang from the story Mob Rule by Norman Krasna. Fury was Lang's first American film.

The Last Picture Show is a 1971 American coming-of-age drama film directed by Peter Bogdanovich and co-written by Bogdanovich and Larry McMurtry, adapted from the 1966 semi-autobiographical novel by McMurtry. The film's ensemble cast includes Timothy Bottoms, Jeff Bridges, Ellen Burstyn, Ben Johnson, Cloris Leachman, and Cybill Shepherd. Set in a small town in northern Texas from November 1951 to October 1952, it is a story of two high school seniors and long-time friends, Sonny Crawford (Bottoms) and Duane Jackson (Bridges).

The Poor Little Rich Girl is a 1917 American comedy-drama film directed by Maurice Tourneur. Adapted by Frances Marion from the 1913 play by Eleanor Gates. The Broadway play actually starred future screen actress Viola Dana. The film stars Mary Pickford, Madlaine Traverse, Charles Wellesley, Gladys Fairbanks and Frank McGlynn Sr.

Dances With Wolves is a 1990 American epic Western film starring, directed, and produced by Kevin Costner in his feature directorial debut. It is a film adaptation of the 1988 novel Dances With Wolves, by Michael Blake, that tells the story of Union Army Lieutenant John J. Dunbar (Costner), who travels to the American frontier to find a military post, and who meets a group of Lakota.

Wild and Woolly is a 1917 American silent Western comedy film which tells the story of one man's personal odyssey from cowboy-obsessed Easterner to Western tough guy. It stars Douglas Fairbanks, Eileen Percy, Walter Bytell and Sam De Grasse. The film was adapted by Anita Loos from a story by Horace B. Carpenter and was directed by John Emerson.

El Mariachi is a 1992 Spanish language American independent neo-Western action film and the first part of the saga that came to be known as Robert Rodriguez's Mexico Trilogy. It marked the feature-length debut of Rodriguez as writer and director. The Spanish language film was shot with a mainly amateur cast in the northern Mexican border town of Ciudad Acuña, Coahuila, Mexico across from Del Rio, Texas, the home town of leading actor Carlos Gallardo as the title character. The US$7,225 production was originally intended for the Mexican home-video market, but executives at Columbia Pictures liked the film and bought the American distribution rights. Columbia eventually spent $200,000 to transfer the print to film, to remix the sound, and on other post-production work, then spent millions more on marketing and distribution.
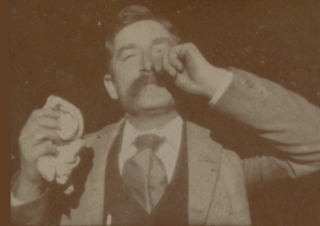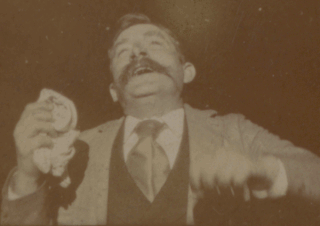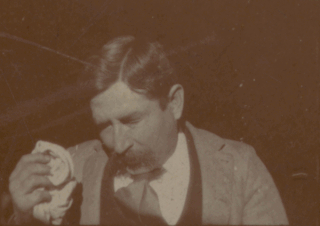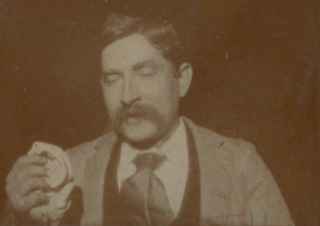
Fred Ott's Sneeze is an 1894 short, black-and-white silent film shot by William K.L. Dickson and featuring Fred Ott. According to the Library of Congress, it is the second oldest surviving U.S. motion picture to be copyrighted, although it is now in the public domain.

King of Jazz is a 1930 American pre-Code color musical film starring Paul Whiteman and his orchestra. The film title refers to Whiteman's popular cultural appellation. At the time the film was made, "jazz", to the general public, meant jazz-influenced syncopated dance music heard on phonograph records, on radio broadcasts, and in dance halls. In the 1920s Whiteman signed and featured white jazz musicians including Joe Venuti and Eddie Lang, Bix Beiderbecke, Frank Trumbauer, and others.

A lost film is a feature or short film in which the original negative or copies are not known to exist in any studio archive, private collection, or public archive. Films can be wholly or partially lost for a number of reasons. Early films were not thought to have value beyond their theatrical run, so many were discarded afterward. Nitrate film used in early pictures was highly flammable and susceptible to degradation. The Library of Congress began acquiring copies of American films in 1909, but not all were kept. Due to improvements in film technology and recordkeeping, few films produced in the 1950s or beyond have been lost.

Mom and Dad is a 1945 American sexploitation film directed by William Beaudine, and largely produced by the exploitation film maker and presenter Kroger Babb. Mom and Dad is considered the most successful film within its genre of "sex hygiene" films. Although it faced numerous legal challenges and was condemned by the National Legion of Decency, it became one of the highest-grossing films of the 1940s.

The Iron Horse is a 1924 American silent epic Western film directed by John Ford and produced by Fox Film. It was a major milestone in Ford's career, and his lifelong connection to the Western film genre. It was Ford's first major film, in part because the hastily planned production went over budget, as Fox was making a hurried response to the success of another studio's western. In 2011, this film was deemed "culturally, historically, or aesthetically significant" by the United States Library of Congress and selected for preservation in the National Film Registry.

The Music Man is a 1962 American musical film directed and produced by Morton DaCosta, based on Meredith Willson's 1957 Broadway musical of the same name, which DaCosta also directed. Robert Preston reprises the title role from the stage version, starring alongside Shirley Jones, Buddy Hackett, Hermione Gingold, Ronny Howard, and Paul Ford.

Sheldon Dick (1906–1950) was an American publisher, literary agent, photographer, and filmmaker. He was a member of a wealthy and well-connected industrialist family, and was able to support himself while funding a series of literary and artistic endeavors. He published a book by poet Edgar Lee Masters, and made a documentary about mining that has been of interest to scholars. Dick is best known for the photographs he took on behalf of the Farm Security Administration during the Great Depression, and for the violent circumstances of his death.

The BFI National Archive is a department of the British Film Institute, and one of the largest film archives in the world. It was founded as the National Film Library in 1935; its first curator was Ernest Lindgren. In 1955, its name became the National Film Archive, and, in 1992, the National Film and Television Archive. It was renamed BFI National Archive in 2006.
The Texas Archive of the Moving Image (TAMI) is an independent 501(c)(3) organization founded in 2002 by film archivist and University of Texas at Austin professor Caroline Frick, PhD. TAMI's mission is to preserve, study, and exhibit Texas film heritage. The organization has three main projects: the TAMI Online Collection, the Texas Film Round-Up, and Teach Texas. Its offices are located in Austin, Texas.

Lonesome is a 1928 American sound part-talkie comedy drama film directed by Paul Fejös, and starring Barbara Kent and Glenn Tryon. Although containing a few sequences with audible dialog, the majority of the film had a synchronized musical score with sound effects with English intertitles. The film was released in both sound-on-disc and sound-on-film formats. Its plot follows two working-class residents of New York City over a 24-hour-period, during which they have a chance meeting at Coney Island during the Independence Day weekend and swiftly fall in love with one another. It was produced and distributed by Universal Pictures.
Melton Barker was an itinerant filmmaker who produced and directed numerous films with his company, Melton Barker Juvenile Productions, from the 1930s though the 1970s. These films were shot across the United States with casts of children who each paid a fee for the opportunity to star in the two-reel shorts.
Herbert Lee Waters (1902–1997) was an American photographer and filmmaker. Waters was born in Caroleen, North Carolina. He worked as a studio photographer in Lexington, North Carolina. Waters also created over 252 short films that make up a series, Movies of Local People, depicting life in small towns in North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, and Virginia. Waters arranged screenings of the short films at local cinemas. They were usually played before the feature film of the screening. Waters made the films profitable for himself through admission prices and contributions from local businesses that wished to appear in the films.

Beginning in the early days of silent films Itinerant filmmakers traveled across the US to make their movies on location with "home talent." They capitalized on the public's desire to see themselves and/or their children in the movies. The filmmakers hoped to cash in on the vanity of politicians, high-society types and prominent businessmen and their families. They would pay a small fee to be in the movie and townspeople would pay to watch their neighbors in the film. It was also common for the local chamber of commerce to pay the production expenses and choose the backdrop and locations for filming. Many times it was promised that the film would be shown around the country, enticing the viewers to come and visit the places they saw. The film would then be returned to the Chamber after its run. They often filmed the same characters in the same story over and over, only changing the cast in each city. Sometimes the title would change leading people to think their particular film was unique. These itinerant films were popular in the silent era, but in some cases they were still operating into the 1970s. Several people made careers out of making itinerant films.
















