
Charles XV or Carl was King of Sweden and Norway, there often referred to as Charles IV, from 8 July 1859 until his death in 1872. Charles was the third Swedish monarch from the House of Bernadotte. He was the first one to be born in Sweden, and the first to be raised from birth in the Lutheran faith.

The House of Bourbon is a dynasty that originated in the Kingdom of France as a branch of the Capetian dynasty, the royal House of France. Bourbon kings first ruled France and Navarre in the 16th century. A branch descended from the French Bourbons came to rule Spain in the 18th century and is the current Spanish royal family. Further branches, descended from the Spanish Bourbons, held thrones in Naples, Sicily, and Parma. Today, Spain and Luxembourg have monarchs of the House of Bourbon. The royal Bourbons originated in 1272, when Robert, the youngest son of King Louis IX of France, married the heiress of the lordship of Bourbon. The house continued for three centuries as a cadet branch, serving as nobles under the direct Capetian and Valois kings.

The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the form of government used by the United Kingdom by which a hereditary monarch reigns as the head of state, with their powers regulated by the British Constitution. The term may also refer to the role of the royal family within the UK's broader political structure. The monarch since 8 September 2022 is King Charles III, who ascended the throne on the death of Queen Elizabeth II, his mother.

The Capetian House of Valois was a cadet branch of the Capetian dynasty. They succeeded the House of Capet to the French throne, and were the royal house of France from 1328 to 1589. Junior members of the family founded cadet branches in Orléans, Anjou, Burgundy, and Alençon.

Louis XII, also known as Louis of Orléans, was King of France from 1498 to 1515 and King of Naples from 1501 to 1504. The son of Charles, Duke of Orléans, and Marie of Cleves, he succeeded his second cousin once removed and brother-in-law, Charles VIII, who died childless in 1498.

A pretender is someone who claims to be the rightful ruler of a country although not recognized as such by the current government. The term may often be used to either refer to a descendant of a deposed monarchy or a claim that is not legitimate.
A cadet branch consists of the male-line descendants of a monarch's or patriarch's younger sons (cadets). In the ruling dynasties and noble families of much of Europe and Asia, the family's major assets have historically been passed from a father to his firstborn son in what is known as primogeniture; younger sons, the cadets, inherited less wealth and authority to pass on to future generations of descendants.

Agnatic seniority is a patrilineal principle of inheritance where the order of succession to the throne prefers the monarch's younger brother over the monarch's own sons. A monarch's children succeed only after the males of the elder generation have all been exhausted. Agnatic seniority excludes females of the dynasty and their descendants from the succession. Contrast agnatic primogeniture, where the king's sons stand higher in succession than his brothers.

Ngungunyane, also known as Mdungazwe Ngungunyane Nxumalo, N'gungunhana, or Gungunhana Reinaldo Frederico Gungunhana, was a king of the Gaza Empire and vassal of the Portuguese Empire, who rebelled, was defeated by General Joaquim Mouzinho de Albuquerque and lived out the rest of his life in exile, first in Lisbon, but later on the island of Terceira, in the Azores.

Vukan Nemanjić was the Grand Prince of the Grand Principality of Serbia from 1202 to 1204. He was the Grand Prince of Pomorje from 1195 until his death. He was the eldest, but his father had instead chosen his younger brother Stefan as heir, as soon as his father died, he plotted against his brother, Stefan Nemanjić, and took the throne by force, in a coup assisted by the Kingdom of Hungary. He was defeated two years later, and was pardoned by his third brother, who became Saint Sava, and he continued to rule his appanage of Zeta unpunished.
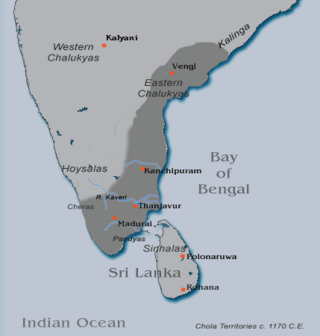
Rajadhiraja Chola II reigned as the Chola emperor succeeding Rajaraja Chola II. Rajaraja Chola II chose Rajadhiraja II, a maternal grandson of Vikrama Chola Because he had no sons. Rajadhiraja II's father was Sangama chola who was the descendant of Virarajendra chola. Hence a century later the real Chola heir ascended the chola throne.

The Greek royal family was the ruling family of the Kingdom of Greece from 1863 to 1924 and again from 1935 to 1973. The family is a branch of the Danish royal family, itself a cadet branch of the House of Glücksburg. The family had replaced the House of Wittelsbach that previously ruled Greece from 1832 to 1862. The first monarch was George I of Greece, the second son of King Christian IX of Denmark. The current head of the family is Pavlos, who assumed the role on 10 January 2023 upon the death of his father, former King Constantine II.

The Barakzai dynasty, also known as the Muhammadzai dynasty, ruled what is now Afghanistan from 1823 to 1978, when the monarchy ended de jure under Musahiban Mohammad Zahir Shah and de facto under his cousin Sardar Mohammad Daoud Khan. The Barakzai dynasty was established by Dost Mohammad Khan after the Durrani dynasty of Ahmad Shah Durrani was removed from power. As the Pahlavi era in Iran, the Muhammadzai era was known for its progressivist modernity, practice of Sufism, peaceful security and neutrality, in which Afghanistan was referred to as the "Switzerland of Asia".

The Kingdom of Serbia, or the Serbian Kingdom, also known as Rascia, was a medieval Serbian kingdom in Southern Europe comprising most of what is today Serbia, Kosovo, and Montenegro, as well as southeastern Bosnia and Herzegovina, parts of coastal Croatia south of the Neretva river, Albania north of the Drin River, North Macedonia, and a small part of western Bulgaria. The medieval Kingdom of Serbia existed from 1217 to 1346 and was ruled by the Nemanjić dynasty. The Grand Principality of Serbia was elevated with the regal coronation of Stefan Nemanjić as king, after the reunification of Serbian lands. In 1219, Serbian Orthodox Church was reorganized as an autocephalous archbishopric, headed by Saint Sava. The kingdom was proclaimed an empire in 1346, but kingship was not abolished as an institution, since the title of a king was used as an official designation for a co-ruler of the emperor.

The House of Urach is a morganatic cadet branch of the formerly royal House of Württemberg. Although the Württemberg dynasty was one of many reigning over small realms in Germany into the 20th century, and despite the fact that marital mésalliances in these dynasties usually disinherited the descendants thereof, the Dukes of Urach unusually managed to elicit consideration for candidacy for the thrones of several European states, viz. the Kingdom of Württemberg, the abortive Kingdom of Lithuania, the Principality of Monaco and even the Principality of Albania. Although none of these prospects came to fruition, they reflected monarchical attempts to accommodate the rapid shifts in national allegiance, regime and international alliances that intensified throughout the 19th century, leading up to and following Europe's Great War of 1914–1918.














