Related Research Articles

Sir Michael Foster was an English physiologist. He was instrumental in organizing the Cambridge Biological School and acted as Secretary of the Royal Society.
A gazette is an official journal, a newspaper of record, or simply a newspaper.

Richard Douglas Harries, Baron Harries of Pentregarth, is a retired bishop of the Church of England and former British Army officer. He was the Bishop of Oxford from 1987 to 2006. From 2008 until 2012 he was the Gresham Professor of Divinity.

Immanuel Jakobovits, Baron Jakobovits was the Chief Rabbi of the United Hebrew Congregations of the Commonwealth from 1967 to 1991. Prior to this, he had served as Chief Rabbi of Ireland and as rabbi of the Fifth Avenue Synagogue in New York City. In addition to his official duties he was regarded as an authority in medical ethics from a Jewish standpoint. He was knighted in 1981 and became the first Chief Rabbi to enter the House of Lords in 1988 as Baron Jakobovits.
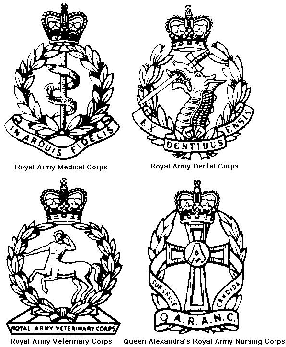
The Army Medical Services (AMS) is the organisation responsible for administering the corps that deliver medical, veterinary, dental and nursing services in the British Army. It is headquartered at the former Staff College, Camberley, near the Royal Military Academy Sandhurst.

The Royal Army Medical Corps (RAMC) is a specialist corps in the British Army which provides medical services to all Army personnel and their families, in war and in peace. The RAMC, the Royal Army Veterinary Corps, the Royal Army Dental Corps and Queen Alexandra's Royal Army Nursing Corps form the Army Medical Services.
The Apothecary to the Household is an officer of the Medical Household of the Royal Household of the Sovereign of the United Kingdom. He has a salaried daily surgery.

Bertrand Edward Dawson, 1st Viscount Dawson of Penn, was a physician to the British Royal Family and President of the Royal College of Physicians from 1931 to 1937. He is known for his responsibility in the death of George V, who under his care was surreptitiously injected with a fatal dose of cocaine and morphine to hasten his death, without obtaining any prior patient consent and in contravention of the law at the time, possibly constituting or amounting to murder.

The Kaisar-i-Hind Medal for Public Service in India was a medal awarded by the Emperor/Empress of India between 1900 and 1947, to "any person without distinction of race, occupation, position, or sex ... who shall have distinguished himself by important and useful service in the advancement of the public interest in India."

Soorjo Coomar Goodeve Chuckerbutty, also spelled Surjo Kumar Chakraborty was the first Indian to pass the examination of the Indian Medical Service (IMS) in 1855 and subsequently became the Professor of Materia Medica at Calcutta Medical College (CMC) in the latter half of the nineteenth century.

Sir Edward Fry, was an English Lord Justice of Appeal (1883–1892) and an arbitrator on the Permanent Court of Arbitration.

The Hospital of St John and St Elizabeth in St John's Wood, London, England, is a Catholic charitable general hospital in north London.

Sir Humphry Davy Rolleston, 1st Baronet, was a prominent English physician.
Colonel Alfred Edward Webb-Johnson, 1st Baron Webb-Johnson, known as Sir Alfred Webb-Johnson, Bt, between 1945 and 1948, was a British surgeon.

Medical Press and Circular was a medical publication from Dublin, Ireland. It was established in 1866 with the merger of the Dublin Medical Press and the Medical Circular. Its masthead featured a Latin language version of the Cicero motto Salus Populi Suprema Lex. It ceased publication in 1961.

Norman Shanks Kerr was a Scottish physician and social reformer who is remembered for his work in the British temperance movement. He originated the Total Abstinence Society and was founder and first president of the Society for the Study and Cure of Inebriety which was founded in 1884.

Sir Dawson Williams was a British physician and the longest serving editor of the British Medical Journal (BMJ).

Edward Hare was a British surgeon and former Director-General of Hospitals in Bengal, India. Hare is best known for his medical work in using quinine for treatment of malaria fevers. He was also a vegetarianism activist.
Lieutenant-colonel Ernest Reinhold Rost O.B.E. was an English physician and Buddhist writer.
References
- ↑ Baker, R.B. (Ed.) (2007). The Codification of Medical Morality: Historical and Philosophical Studies of the Formalization of Western Medical Morality in the Eighteenth and Nineteenth Centuries. Dordrecht: Kluwer. p. 196. ISBN 978-0-585-27444-7.
- ↑ The Medical Times and Gazette. British Library. Retrieved 27 May 2018.