
Cover art by Hanife Hassan
The Mockery Bird is a humorous novel by Gerald Durrell, published in 1981 by William Collins, Sons and Co Ltd. [1] The book, like the other works of the author, contains a strong environmental message.

The Mockery Bird is a humorous novel by Gerald Durrell, published in 1981 by William Collins, Sons and Co Ltd. [1] The book, like the other works of the author, contains a strong environmental message.
The story takes place on a (fictitious) tropical island called Zenkali. The island seems to be populated by the most eccentric people who came there from all around the world, along with the two indigenous tribes, the Fangoua and the Ginka. The Ginkas used to worship a dolphin god, while the Fangouas worshipped a strange avian, the Mockery Bird, which was hunted to extinction by the former French colonizers. Zenkali is ruled by King Tamalawala III, usually referred to as "Kingy" by his people.
Peter Foxglove arrives to Zenkali to be the assistant of Hannibal Oliphant, Kingy's Political Advisor. Zenkali, once a British colony, is about to get self-government. They are also planning to construct a military base, an airport and a power station, and this will mean the flooding of a large, unexplored valley, owned by the villainous businessman, Looja. Peter, along with the beautiful Audrey Damien, visits the valley before it is totally destroyed, and makes a fantastic discovery: a small population of Mockery Birds still live in the valley!
Peter's discovery attracts the attention of the world press, environmentalists, politicians and businessmen from all around the world, and this leads to a couple of adventures. Finally, Professor Droom, a biologist, discovers that the main and only agricultural product of Zenkali, the Amela tree is ecologically linked to the Mockery Birds (explained below), so the flooding of the valley will make the island's economy collapse. Consequently, the construction of the airport is cancelled.
The fictitious bird species of the book, the Mockery Bird is a flightless bird about the size of a goose. It has blue feathers, long legs and a large beak, similar to that of a hornbill. As an example of sexual dimorphism, the male Mockery Birds have a large hump on their beak, while the females have only a small, bony shield. The bird was named after its call, that sounds like laughter (much like the kookaburra's).
The Mockery Bird was worshipped by the native Fangoua people, but was believed to be hunt to extinction. Mysteriously, when the bird was lost, a tree species, the Ombu tree also disappeared. This shows that there was a strong ecological link (symbiosis) between the two species. It means ecological conditions which are congenial for one species are good for the other.
In the book, Professor Droom discovers the nature of this relationship: the bird feeds on the fruit of the tree, and spreads its seeds. Also, the caterpillars of a large species of moth feed on the leaves of the Ombu tree, and this very same moth species pollinates the Amela trees, the main product of Zenkali. So all species on the island, including humans, are linked in an ecological chain.
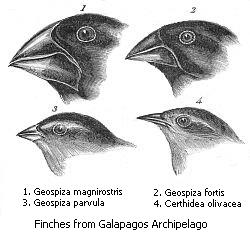
In evolutionary biology, adaptive radiation is a process in which organisms diversify rapidly from an ancestral species into a multitude of new forms, particularly when a change in the environment makes new resources available, alters biotic interactions or opens new environmental niches. Starting with a single ancestor, this process results in the speciation and phenotypic adaptation of an array of species exhibiting different morphological and physiological traits. The prototypical example of adaptive radiation is finch speciation on the Galapagos, but examples are known from around the world.

The dodo is an extinct flightless bird that was endemic to the island of Mauritius, which is east of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean. The dodo's closest relative was the also-extinct and flightless Rodrigues solitaire. The two formed the subfamily Raphinae, a clade of extinct flightless birds that were a part of the family which includes pigeons and doves. The closest living relative of the dodo is the Nicobar pigeon. A white dodo was once thought to have existed on the nearby island of Réunion, but it is now believed that this assumption was merely confusion based on the also-extinct Réunion ibis and paintings of white dodos.

The Beak of the Finch: A Story of Evolution in Our Time (ISBN 0-679-40003-6) is a 1994 nonfiction book about evolutionary biology, written by Jonathan Weiner. It won the 1995 Pulitzer Prize for General Non-Fiction. In 2014, a substantially unchanged 20th-anniversary edition e-book was issued with a preface by the author.

Gerald Malcolm Durrell, was a British naturalist, writer, zookeeper, conservationist, and television presenter. He founded the Durrell Wildlife Conservation Trust and the Jersey Zoo on the Channel Island of Jersey in 1959. He wrote approximately forty books, mainly about his life as an animal collector and enthusiast, the most famous being My Family and Other Animals (1956). Those memoirs of his family's years living in Greece were adapted into two television series and one television film. He was the youngest brother of novelist Lawrence Durrell.

Jersey Zoo is a zoological park established in 1959 on the island of Jersey in the English Channel by naturalist and writer Gerald Durrell (1925–1995). It is operated by the Durrell Wildlife Conservation Trust. It has approximately 169,000 visitors per year.

Darwin's finches are a group of about 18 species of passerine birds. They are well known for their remarkable diversity in beak form and function. They are often classified as the subfamily Geospizinae or tribe Geospizini. They belong to the tanager family and are not closely related to the true finches. The closest known relative of the Galápagos finches is the South American dull-coloured grassquit. They were first collected when the second voyage of the Beagle visited the Galápagos Islands, with Charles Darwin on board as a gentleman naturalist. Apart from the Cocos finch, which is from Cocos Island, the others are found only on the Galápagos Islands.

The huia is an extinct species of New Zealand wattlebird, endemic to the North Island of New Zealand. The last confirmed sighting of a huia was in 1907, although there was another credible sighting in 1924.

The broad-billed parrot or raven parrot is a large extinct parrot in the family Psittaculidae. It was endemic to the Mascarene island of Mauritius. The species was first referred to as the "Indian raven" in Dutch ships' journals from 1598 onwards. Only a few brief contemporary descriptions and three depictions are known. It was first scientifically described from a subfossil mandible in 1866, but this was not linked to the old accounts until the rediscovery of a detailed 1601 sketch that matched both the subfossils and the accounts. It is unclear what other species it was most closely related to, but it has been classified as a member of the tribe Psittaculini, along with other Mascarene parrots. It had similarities with the Rodrigues parrot, and may have been closely related.

Round Island is an uninhabited islet 22.5 kilometres north of Mauritius. It has an area of 1.69 square kilometres and a maximum elevation of 280 metres. The island has been a nature reserve since 1957 and is administered jointly by the National Parks and Conservation Service and the Mauritian Wildlife Foundation. The island has been designated an Important Bird Area (IBA) by BirdLife International.

The hoopoe starling, also known as the Réunion starling or Bourbon crested starling, is a species of starling that lived on the Mascarene island of Réunion and became extinct in the 1850s. Its closest relatives were the also-extinct Rodrigues starling and Mauritius starling from nearby islands, and the three apparently originated in south-east Asia. The bird was first mentioned during the 17th century and was long thought to be related to the hoopoe, from which its name is derived. Some affinities have been proposed, but it was confirmed as a starling in a DNA study.

The Rodrigues parrot or Leguat's parrot is an extinct species of parrot that was endemic to the Mascarene island of Rodrigues. The species is known from subfossil bones and from mentions in contemporary accounts. It is unclear to which other species it is most closely related, but it is classified as a member of the tribe Psittaculini, along with other Mascarene parrots. The Rodrigues parrot bore similarities to the broad-billed parrot of Mauritius, and may have been related. Two additional species have been assigned to its genus, based on descriptions of parrots from the other Mascarene islands, but their identities and validity have been debated.

Livingstone's fruit bat, also called the Comoro flying fox, is a megabat in the genus Pteropus. It is an Old World fruit bat found only in the Anjouan and Mohéli islands in the Union of the Comoros in the western Indian Ocean.

The Kona grosbeak is an extinct species of Hawaiian honeycreeper. The Kona grosbeak was endemic to naio forests on ʻaʻā lava flows at elevations of 1,400–1,500 metres (4,600–4,900 ft) near the Kona District on the island of Hawaii. The species was already very rare when it was first discovered, being found in only about 10 square kilometres (3.9 sq mi), and was last collected in 1894. Reasons for its extinction are not very well known. The genus is known from fossils from Kauai, Oahu and Maui. It was unknown to the Native Hawaiians, and thus a name for it does not exist in the Hawaiian language.

The medium ground finch is a species of bird in the family Thraupidae. It is endemic to the Galapagos Islands. Its primary natural habitat is tropical shrubland. One of Darwin's finches, the species was the first which scientists have observed evolving in real-time.

The Guadeloupe woodpecker or Tapeur is a species of bird in the woodpecker family Picidae belonging to the genus Melanerpes. Endemic to the Guadeloupe archipelago in the Lesser Antilles, it is a medium-sized forest woodpecker with entirely black plumage and red-to-purple reflections on its stomach. It lives mainly in the islands' tropical rainforest areas. The woodpecker has no sexual dimorphism. The species has adapted under the pressure of urbanization to more open forest environments.

The Great Oʻahu crake or Great Oʻahu rail is an extinct bird species that was endemic to the island of Oʻahu in Hawaiʻi. It was one of two flightless rails that had survived on the island until the arrival of people in 200 C.E.

The Māori people have had a strong and changing conservation ethic since their discovery and settlement of New Zealand. This is closely tied to their spiritual beliefs.
Island ecology is the study of island organisms and their interactions with each other and the environment. Islands account for nearly 1/6 of earth’s total land area, yet the ecology of island ecosystems is vastly different from that of mainland communities. Their isolation and high availability of empty niches lead to increased speciation. As a result, island ecosystems comprise 30% of the world’s biodiversity hotspots, 50% of marine tropical diversity, and some of the most unusual and rare species. Many species still remain unknown.
Carl Gwynfe Jones, MBE is a Welsh conservation biologist, who has been employed by Durrell Wildlife Conservation Trust since 1985, and a founding member (1984) and current scientific director of Mauritian Wildlife Foundation (MWF). Additionally he is Chief Scientist at Durrell Wildlife Conservation Trust, and an honorary professor in ecology and conservation biology at the University of East Anglia. Often outspoken on the importance of knowing your species and using intuition, empathy and practical knowledge over dogmatic education, Jones is best known for his work in recovering the Mauritius kestrel from just four individuals in 1974, to an estimated 400. Working in the Mascarene Islands since 1979, Jones has led five successful bird restoration projects where the starting population has numbered less than 12 individuals; as a consequence Mauritius has averted more bird extinctions than any other country. Jones has pioneered the use of ecological or taxon replacements to fill the ecological roles of extinct animals and successfully restored levels of endemic vegetation to previously denuded islets. Jones' work has been highlighted in Douglas Adams and Mark Carwardine's 1990 radio documentary Last Chance to See, along with its accompanying book, as well as David Quammen's 1996 book The Song of the Dodo: Island Biogeography in an Age of Extinctions.

The robust crow or slender-billed crow was a species of large, raven-sized crow that was endemic to the islands of Oahu and Molokai in the Hawaiian Islands during the Holocene. C. viriosus was frugivorous and was adapted for this with a long, slender bill. It was pushed to extinction due to the arrival of people and pests like rats.