The Aryan race is an obsolete historical race concept that emerged in the late-19th century to describe people of Proto-Indo-European heritage as a racial grouping. The terminology derives from the historical usage of Aryan, used by modern Indo-Iranians as an epithet of "noble". Anthropological, historical, and archaeological evidence does not support the validity of this concept.
Dialectic, also known as the dialectical method, is a discourse between two or more people holding different points of view about a subject but wishing to establish the truth through reasoned argumentation. Dialectic resembles debate, but the concept excludes subjective elements such as emotional appeal and the modern pejorative sense of rhetoric. Dialectic may thus be contrasted with both the eristic, which refers to argument that aims to successfully dispute another's argument, and the didactic method, wherein one side of the conversation teaches the other. Dialectic is alternatively known as minor logic, as opposed to major logic or critique.
ʿIlm al-Kalām, usually foreshortened to Kalām and sometimes called "Islamic scholastic theology" or "speculative theology", is the philosophical study of Islamic doctrine ('aqa'id). It was born out of the need to establish and defend the tenets of the Islamic faith against the philosophical doubters. However, this picture has been increasingly questioned by scholarship that attempts to show that kalām was in fact a demonstrative rather than a dialectical science and was always intellectually creative.

Ian MacDougall Hacking is a Canadian philosopher specializing in the philosophy of science. Throughout his career, he has won numerous awards, such as the Killam Prize for the Humanities and the Balzan Prize, and been a member of many prestigious groups, including the Order of Canada, the Royal Society of Canada and the British Academy.
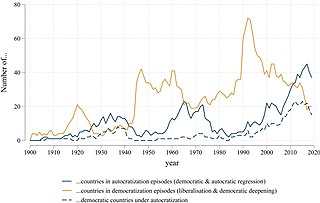
Democratization, or democratisation, is the transition to a more democratic political regime, including substantive political changes moving in a democratic direction. It may be a hybrid regime in transition from an authoritarian regime to a full democracy, a transition from an authoritarian political system to a semi-democracy or transition from a semi-authoritarian political system to a democratic political system.

Eoraptor is a genus of small, lightly built, basal sauropodomorph. One of the earliest-known dinosaurs, it lived approximately 231 to 228 million years ago, during the Late Triassic in Western Gondwana, in the region that is now northwestern Argentina. The type and only species, Eoraptor lunensis, was first described in 1993, and is known from an almost complete and well-preserved skeleton and several fragmentary ones. Eoraptor had multiple tooth shapes, which suggests that it was omnivorous.
The culture of poverty is a concept in social theory that asserts that the values of people experiencing poverty play a significant role in perpetuating their impoverished condition, sustaining a cycle of poverty across generations. It attracted policy attention in the 1970s, and received academic criticism, and made a comeback at the beginning of the 21st century. It offers one way to explain why poverty exists despite anti-poverty programs. Early formations suggest that poor people lack resources and acquire a poverty-perpetuating value system. Critics of the early culture of poverty arguments insist that explanations of poverty must analyze how structural factors interact with and condition individual characteristics. As put by Small, Harding & Lamont (2010), "since human action is both constrained and enabled by the meaning people give to their actions, these dynamics should become central to our understanding of the production and reproduction of poverty and social inequality." Further discourse suggests thats Oscar Lewis’s work was misunderstood.

Afrocentricity is an academic theory and approach to scholarship that seeks to center the experiences and peoples of Africa and the African diaspora within their own historical, cultural, and sociological contexts. First developed as a systematized methodology by Molefi Kete Asante in 1980, he drew inspiration from a number of African and African diaspora intellectuals including Cheikh Anta Diop, George James, Harold Cruse, Ida B. Wells, Langston Hughes, Malcolm X, Marcus Garvey, and W. E. B. Du Bois. The Temple Circle, also known as the Temple School of Thought, Temple Circle of Afrocentricity, or Temple School of Afrocentricity, was an early group of Africologists during the late 1980s and early 1990s that helped to further develop Afrocentricity, which is based on concepts of agency, centeredness, location, and orientation.
Historical institutionalism (HI) is a new institutionalist social science approach that emphasizes how timing, sequences and path dependence affect institutions, and shape social, political, economic behavior and change. Unlike functionalist theories and some rational choice approaches, historical institutionalism tends to emphasize that many outcomes are possible, small events and flukes can have large consequences, actions are hard to reverse once they take place, and that outcomes may be inefficient. A critical juncture may set in motion events that are hard to reverse, because of issues related to path dependency. Historical institutionalists tend to focus on history to understand why specific events happen.
Feminist anthropology is a four-field approach to anthropology that seeks to transform research findings, anthropological hiring practices, and the scholarly production of knowledge, using insights from feminist theory. Simultaneously, feminist anthropology challenges essentialist feminist theories developed in Europe and America. While feminists practiced cultural anthropology since its inception, it was not until the 1970s that feminist anthropology was formally recognized as a subdiscipline of anthropology. Since then, it has developed its own subsection of the American Anthropological Association – the Association for Feminist Anthropology – and its own publication, Feminist Anthropology. Their former journal Voices is now defunct.

Conceptualised by 20th century German director and theatre practitioner Bertolt Brecht (1898-1956), "The Modern Theatre Is the Epic Theatre" is a theoretical framework implemented by Brecht in the 1930s, which challenged and stretched dramaturgical norms in a postmodern style. This framework, written as a set of notes to accompany Brecht's satirical opera, ‘Rise and Fall of the City of Mahagonny’, explores the notion of "refunctioning" and the concept of the Separation of the Elements. This framework was most proficiently characterised by Brecht's nihilistic anti-bourgeois attitudes that “mirrored the profound societal and political turmoil of the Nazi uprising and post WW1 struggles”. Brecht's presentation of this theatrical structure adopts a style that is austere, utilitarian and remains instructional rather than systematically categorising itself as a form that is built towards a more entertaining and aesthetic lens. ‘The Modern Theatre Is the Epic Theatre’ incorporates early formulations of Brechtian conventions and techniques such as Gestus and the V-Effect. It employs an episodic arrangement rather than a traditional linear composition and encourages an audience to see the world as it is regardless of the context. The purpose of this new avant-garde outlook on theatrical performance aimed to “exhort the viewer to greater political vigilance, bringing the Marxist objective of a classless utopia closer to realisation”.

The Ideological Origins of the American Revolution is a 1967 Pulitzer Prize-winning book of history by Bernard Bailyn. It is considered one of the most influential studies of the American Revolution published during the 20th century.

By the end of the 20th century, the theological importance of the Holy Spirit in Johannine literature had been accepted by New Testament scholars, overshadowing the early 20th-century views that minimized its role in the writings of John.
Brian P. Copenhaver is Distinguished Professor Emeritus of Philosophy and History at The University of California, Los Angeles. He teaches and writes about philosophy, religion and science in late medieval and early modern Europe.
Primitive communism is a way of describing the gift economies of hunter-gatherers throughout history, where resources and property hunted or gathered are shared with all members of a group in accordance with individual needs. In political sociology and anthropology, it is also a concept, that describes hunter-gatherer societies as traditionally being based on egalitarian social relations and common ownership. A primary inspiration for both Marx and Engels were Lewis H. Morgan's descriptions of "communism in living" as practised by the Haudenosaunee of North America. In Marx's model of socioeconomic structures, societies with primitive communism had no hierarchical social class structures or capital accumulation.

Dialectical materialism is a philosophy of science, history, and nature developed in Europe and based on the writings of Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. Marxist dialectics, as a materialist philosophy, emphasizes the importance of real-world conditions and the presence of contradictions within things, in relation to but not limited to class, labor, and socioeconomic interactions. This is in contrast to the idealist Hegelian dialectic, which emphasizes the observation that contradictions in material phenomena could be resolved by analyzing them and synthesizing a solution whilst retaining their essence. Marx supposed that the most effective solution to the problems caused by said contradictory phenomena was to address and rearrange the systems of social organization at the root of the problems.
Michael R. Shute was a Canadian scholar and Professor of Religious Studies at Memorial University of Newfoundland. He was known for his research on the works of Bernard Lonergan and moral decision-making. Shute was a co-editor of Journal of Macrodynamic Analysis.

Lonergan's Discovery of the Science of Economics is a 2010 book by Michael Shute, in which the author provides an account of Bernard Lonergan's solution to a fundamental problem in economic theory.
Dutch philosophy is a broad branch of philosophy that discusses the contributions of Dutch philosophers to the discourse of Western philosophy and Renaissance philosophy. The philosophy, as its own entity, arose in the 16th and 17th centuries through the philosophical studies of Desiderius Erasmus and Baruch Spinoza. The adoption of the humanistic perspective by Erasmus, despite his Christian background, and rational but theocentric perspective expounded by Spinoza, supported each of these philosopher's works. In general, the philosophy revolved around acknowledging the reality of human self-determination and rational thought rather than focusing on traditional ideals of fatalism and virtue raised in Christianity. The roots of philosophical frameworks like the mind-body dualism and monism debate can also be traced to Dutch philosophy, which is attributed to 17th century philosopher René Descartes. Descartes was both a mathematician and philosopher during the Dutch Golden Age, despite being from the Kingdom of France. Modern Dutch philosophers like D.H. Th. Vollenhoven provided critical analyses on the dichotomy between dualism and monism.
Joyce E. Salisbury is an American historian. She is professor emerita of humanistic studies (history) at the University of Wisconsin–Green Bay, where she was named Frankenthal Family distinguished professor in 1993.









