
Cabaret Voltaire were an English music group formed in Sheffield in 1973 and initially composed of Stephen Mallinder, Richard H. Kirk, and Chris Watson. Named for the Zürich nightclub that fostered the early Dada movement, the band are often characterized as among the most innovative and influential electronic acts of their era.

The secretary of state for housing, communities and local government is a secretary of state in the Government of the United Kingdom, and Cabinet minister, responsible for the overall leadership and strategic direction of the Ministry of Housing, Communities and Local Government (MHCLG). They are responsible for local government in England.

The Proliferation Security Initiative (PSI) is a global effort that aims to stop trafficking of weapons of mass destruction (WMD), their delivery systems, and related materials to and from states and non-state actors of proliferation concern. Launched by United States President, George W. Bush in May 2003 at a meeting in Kraków, Poland, the PSI has now grown to include the endorsement of 105 nations around the world, including Russia, Canada, the United Kingdom, Australia, France, Germany, Italy, Argentina, Japan, the Netherlands, Poland, Singapore, New Zealand, Republic of Korea and Norway.

Dennis George Mortimer is an English former footballer who played as a midfielder and captained Aston Villa. He made nearly 600 appearances in the Football League playing for Coventry City, Aston Villa, Sheffield United, Brighton & Hove Albion and Birmingham City.

Margaret Osborn, known professionally as Alice Glass, is a Canadian singer and songwriter. She is the co-founder and former frontwoman of the electronic band Crystal Castles. In 2014, she embarked on a solo career. She released her eponymous debut EP in 2017. Her solo debut album, Prey//IV, was released in February 2022.

Tatiana Yadira Suarez Padilla is an American professional mixed martial artist and former wrestler who currently competes in the women’s Strawweight division of the Ultimate Fighting Championship (UFC). She was the strawweight tournament winner in the 23rd season of The Ultimate Fighter reality show. As of April 16, 2024, she is #1 in the UFC women's strawweight rankings and #9 in the UFC women's pound-for-pound rankings.

David Lloyd Wolper was an American television and film producer, responsible for shows such as Roots, The Thorn Birds, and North and South, and the theatrically-released films Willy Wonka & the Chocolate Factory (1971) and L.A. Confidential. He was awarded the Jean Hersholt Humanitarian Award at the 57th Academy Awards in 1985 for his work producing the opening and closing ceremonies of the 1984 Summer Olympics in Los Angeles, as well as helping to bring the games there. His 1971 film about the study of insects, The Hellstrom Chronicle, won an Academy Award.

A direct-administered municipality is a city of China that is directly affiliated with the central government and is not placed under any provinces. There are four municipalities in China: Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai, and Chongqing.

In mathematical logic and computer science, homotopy type theory (HoTT) refers to various lines of development of intuitionistic type theory, based on the interpretation of types as objects to which the intuition of (abstract) homotopy theory applies.

The Republican Right group, formerly the Union for a Popular Movement group from 2003 and 2015 and The Republicans group from 2015 to 2024, is a parliamentary group in the National Assembly including representatives of The Republicans (LR), formerly the Union for a Popular Movement.

Lotta Hintsa is a Finnish model, mountaineer and beauty pageant titleholder who was crowned Miss Finland 2013 and represented her country at Miss Universe 2013.

Century Pacific Food, Inc. (CNPF) is a Philippine multinational food processing company headquartered in Ortigas Center, Pasig. It is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Century Pacific Group, Inc.
Vigiland is a Swedish house duo consisting of Claes Remmered Persson and Otto Pettersson from the Swedish community Västervik, Sweden. Their first single "Bouncer" became popular on Spotify when it was released in late 2013. Upon releasing their Melbourne Bounce-influenced single "UFO", it made the top 10 of Spotify's most played songs. With the release of their single "Shots & Squats", Vigiland achieved number-ones in Scandinavia over summer and autumn 2015. "Shots & Squats" also became popular in Latin America due to Vine and after it was used as the theme for the MTV series SuperShore. In 2016, Vigiland released "Pong Dance", which reached number 2 in Sweden.
Greek basketball clubs in European and worldwide competitions is the performance record of men's professional basketball clubs from Greece's top-tier level league, the Greek Basket League, in international competitions.

Kim Chung-ha, known mononymously as Chungha, is a South Korean pop singer, dancer and choreographer. She finished fourth in Mnet's girl group survival show Produce 101, becoming a member of the resulting girl group I.O.I. Following the dissolution of I.O.I in 2017, Chungha debuted as a solo artist with the extended play Hands on Me.
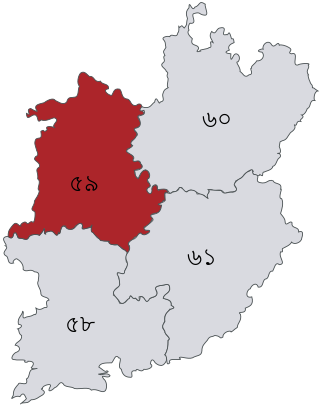
Natore-2 is a constituency represented in the Jatiya Sangsad of Bangladesh since 2014 by Md. Shafiqul Islam Shimul of the Awami League.
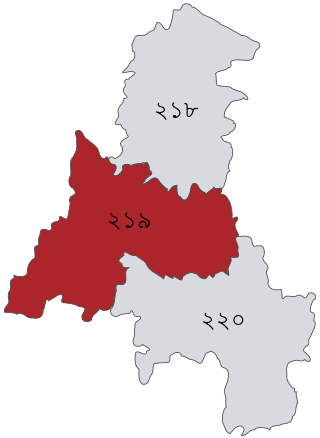
Madaripur-2 is a constituency represented in the Jatiya Sangsad of Bangladesh since 1986 by Shajahan Khan of the Awami League.

Mymensingh-2 is a constituency represented in the Jatiya Sangsad of Bangladesh since 2014 by Sharif Ahmed of the Awami League.

Rasmus Mathias Lindh is a Swedish racing car driver who competed in Indy NXT in 2023 for Juncos Hollinger Racing in the #76 car, after switching from HMD Motorsports with Dale Coyne Racing. Lindh previously competed in the then Indy Lights for Juncos.

Ancient Apocalypse is a 2022 Netflix series, where the British writer Graham Hancock presents his pseudoarchaeological theories about the existence of an advanced civilization active during the last ice age. Academic archeologists describe many of the claims made as easily disproven.


















