Related Research Articles

A grimoire is a textbook of magic, typically including instructions on how to create magical objects like talismans and amulets, how to perform magical spells, charms, and divination, and how to summon or invoke supernatural entities such as angels, spirits, deities, and demons. In many cases, the books themselves are believed to be imbued with magical powers. The only contents found in a grimoire would be information on spells, rituals, the preparation of magical tools, and lists of ingredients and their magical correspondences. In this manner, while all books on magic could be thought of as grimoires, not all magical books should be thought of as grimoires.

An athame or athamé is a ceremonial blade, generally with a black handle. It is the main ritual implement or magical tool among several used in ceremonial magic traditions, and by other neopagans, witchcraft, as well as satanic traditions. A black-handled knife called an arthame appears in certain versions of the Key of Solomon, a grimoire dating to the Renaissance.
Belief in magic exists in all societies, regardless of whether they have organized religious hierarchy including formal clergy or more informal systems. Such concepts tend to appear more frequently in cultures based in polytheism, animism, or shamanism. Religion and magic became conceptually separated in the West where the distinction arose between supernatural events sanctioned by approved religious doctrine versus magic rooted in other religious sources. With the rise of Christianity this became characterised with the contrast between divine miracles versus folk religion, superstition, or occult speculation.

Ceremonial magic encompasses a wide variety of rituals of magic. The works included are characterized by ceremony and numerous requisite accessories to aid the practitioner. It can be seen as an extension of ritual magic, and in most cases synonymous with it. Popularized by the Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn, it draws on such schools of philosophical and occult thought as Hermetic Qabalah, Enochian magic, Thelema, and the magic of various grimoires. Ceremonial magic is part of Hermeticism and Western esotericism.
The Lesser Key of Solomon, also known by its Latin title Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis or simply the Lemegeton, is an anonymously authored grimoire on sorcery, mysticism and magic. It was compiled in the mid-17th century, mostly from materials several centuries older. It is divided into five books: the Ars Goetia, Ars Theurgia-Goetia, Ars Paulina, Ars Almadel, and Ars Notoria. It is based on the Testament of Solomon and the ring mentioned within it that he used to seal demons.
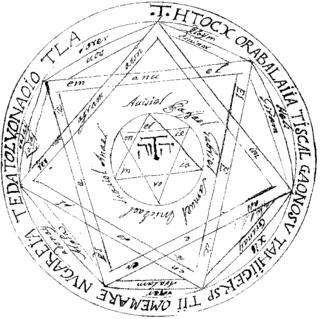
The Key of Solomon, also known as the Greater Key of Solomon, is a pseudepigraphical grimoire attributed to King Solomon. It probably dates back to the 14th or 15th century Italian Renaissance. It presents a typical example of Renaissance magic.

Enochian magic is a system of Renaissance magic developed by John Dee and Edward Kelley and adopted by more modern practitioners. The origins of this esoteric tradition are rooted in documented collaborations between Dee and Kelley, encompassing the revelation of the Enochian language and script, which Dee wrote were delivered to them directly by various angels during their mystical interactions. Central to the practice is the invocation and command of various spiritual beings.
A guardian angel is a type of angel that is assigned to protect and guide a particular person, group or nation. Belief in tutelary beings can be traced throughout all antiquity. The idea of angels that guard over people played a major role in Ancient Judaism. In Christianity, the hierarchy of angels was extensively developed in the 5th century by Pseudo-Dionysius the Areopagite. The theology of angels and tutelary spirits has undergone many changes since the 5th century. The belief is that guardian angels serve to protect whichever person God assigns them to. The Memorial of the Holy Guardian Angels is celebrated on 2 October.
The Bornless Ritual, also known as the Preliminary Invocation of the Goetia or simply Preliminary Invocation, originates from the Graeco-Egyptian Papyri Graecae Magicae (PGM), a collection of ancient spells, invocations, and hymns compiled between the 2nd century BCE and the 5th century CE. Initially used for exorcism and healing, the ritual invokes the "Headless One". In modern times this entity has been re-interpreted as the "Bornless One" without beginning or end, who symbolizes the unity of the divine and the practitioner. Some interpretations suggest that the ritual may have connections with the Egyptian god Set. It is also called the "Headless Rite" or the "Invocation of the Bornless One".

The Book of Abramelin tells the story of an Egyptian mage named Abraham, or Abra-Melin, who taught a system of magic to Abraham of Worms, a Jew from Worms, Germany, presumed to have lived from c. 1362 to c. 1458. The system of magic from this book regained popularity in the 19th and 20th centuries partly due to Samuel Liddell MacGregor Mathers' translation, The Book of the Sacred Magic of Abramelin the Mage.
The Book of the Penitence of Adam is a manuscript dealing with Kabbalistic traditions, all of which are embodied in the allegory it contains.

The angel Jophiel, also called Iophiel, Iofiel, Jofiel, Yofiel, Youfiel, Zophiel and Zuriel, is an archangel in Christian and Jewish angelology. Jophiel is associated with beauty, art, and wisdom.

Sefer HaRazim is a Jewish magical text supposedly given to Noah by the angel Raziel, and passed down throughout Biblical history until it ended up in the possession of Solomon, for whom it was a great source of his wisdom and purported magical powers. This is not the same work as the Sefer Raziel HaMalakh, which was given to Adam by the same angel, although both works stem from the same tradition, and large parts of Sefer HaRazim were incorporated into the Sefer Raziel under its original title.

The Arbatel De Magia Veterum is a Latin grimoire of Renaissance ceremonial magic published in 1575 in Switzerland.

Babalon is a goddess found in the occult system of Thelema, which was established in 1904 with the writing of The Book of the Law by English author and occultist Aleister Crowley. The spelling of the name as "Babalon" was revealed to Crowley in The Vision and the Voice. Her name and imagery feature prominently in Crowley's "Liber Cheth vel Vallum Abiegni".

Moses Gaster was a Romanian, later British scholar, the Hakham of the Spanish and Portuguese Jewish congregation, London, and a Hebrew and Romanian linguist. Moses Gaster was an active Zionist in Romania as well as in England, where in 1899 he helped establish the English Zionist Federation.
Practical Kabbalah in historical Judaism, is a branch of the Jewish mystical tradition that concerns the use of magic. It was considered permitted white magic by its practitioners, reserved for the elite, who could separate its spiritual source from qlippoth realms of evil if performed under circumstances that were holy (Q-D-Š) and pure, tumah and taharah. The concern of overstepping Judaism's strong prohibitions of impure magic ensured it remained a minor tradition in Jewish history. Its teachings include the use of Divine and angelic names for amulets and incantations.
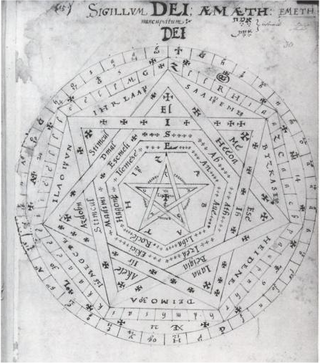
The Sigillum Dei is a magical diagram, composed of two circles, a pentagram, two heptagons, and one heptagram, and is labeled with the names of God and its angels. It is an angelic magic seal with the magical function that, according to one of the oldest sources, allowed a destined intended magician to have the power to possess the Spirit of God and when activated can become the Living God; or The Lord God itself; amongst humanity and all creation itself, communicate with spirits as well as angels and archangels, control all elements, control every creature's holy spirit on the planet including the Spirit of God itself; all except for the Archangels, and to control light itself. The intended user also possesses the true benefic vision of God.

The Sword of Moses is a 2013 mystery detective thriller novel by the English historian and journalist Dominic Selwood. It is part one of the Ava Curzon trilogy.

The Magical Treatise of Solomon, also known as the Hygromanteia or Solomonikê, is a collection of late Byzantine-era grimoires written in medieval Greek. A pseudepigraphon, the book purports to contain Solomon's instructions to his son Rehoboam on various magical techniques and tools to summon and control different spirits and their powers, astrological beliefs, select charms, different means of divination, and the magical uses of herbs. The Magical Treatise survives in fragments from a number of manuscripts dating from the 15th century CE. The book has been important for the history of European magic, serving as a link between the earlier Greek magical practices and the later grimoires of Western Europe. During the early modern period, the book begun to be translated in Latin, becoming the source for future European grimoires, most notably the Key of Solomon.
References
- ↑ "Interview with Yuval Harari- Jewish Magic before the Rise of Kabbalah". 4 June 2017.
- ↑ Harari, Yuval (2012). "The Sword of Moses (Ḥarba de-Moshe): A New Translation and Introduction". Magic, Ritual, and Witchcraft. 7 (1): 68–69. doi:10.1353/mrw.2012.0008. S2CID 162236993.
- ↑ Harari, The Sword of Moses
- ↑ Amazon page for the book