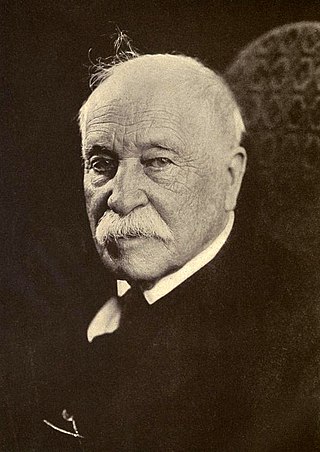Paul Laurence Dunbar was an American poet, novelist, and short story writer of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Born in Dayton, Ohio, to parents who had been enslaved in Kentucky before the American Civil War, Dunbar began writing stories and verse when he was a child. He published his first poems at the age of 16 in a Dayton newspaper, and served as president of his high school's literary society.

Joel Chandler Harris was an American journalist and folklorist best known for his collection of Uncle Remus stories. Born in Eatonton, Georgia, where he served as an apprentice on a plantation during his teenage years, Harris spent most of his adult life in Atlanta working as an associate editor at The Atlanta Constitution.

Charles Waddell Chesnutt was an American author, essayist, political activist, and lawyer, best known for his novels and short stories exploring complex issues of racial and social identity in the post-Civil War South. Two of his books were adapted as silent films in 1926 and 1927 by the African-American director and producer Oscar Micheaux. Following the Civil Rights Movement during the 20th century, interest in the works of Chesnutt was revived. Several of his books were published in new editions, and he received formal recognition. A commemorative stamp was printed in 2008.
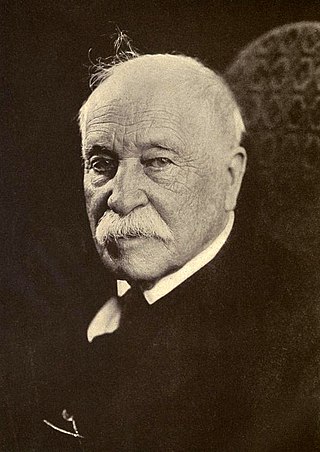
William Dean Howells was an American realist novelist, literary critic, and playwright, nicknamed "The Dean of American Letters". He was particularly known for his tenure as editor of The Atlantic Monthly, as well as for the novels The Rise of Silas Lapham and A Traveler from Altruria, and the Christmas story "Christmas Every Day," which was adapted into a 1996 film of the same name.

Thomas Bailey Aldrich was an American writer, poet, critic, and editor. He is notable for his long editorship of The Atlantic Monthly, during which he published writers including Charles W. Chesnutt. He was also known for his semi-autobiographical book The Story of a Bad Boy, which established the "bad boy's book" subgenre in nineteenth-century American literature, and for his poetry.

The Marrow of Tradition (1901) is a novel by the African-American author Charles W. Chesnutt, portraying a fictional account of the Wilmington Insurrection of 1898 in Wilmington, North Carolina, an event that had just recently occurred.
The tragic mulatto is a stereotypical fictional character that appeared in American literature during the 19th and 20th centuries, starting in 1837. The "tragic mulatto" is a stereotypical mixed-race person, who is assumed to be depressed, or even suicidal, because they fail to completely fit into the "white world" or the "black world". As such, the "tragic mulatto" is depicted as the victim of the society that is divided by race, where there is no place for one who is neither completely "black" nor "white".

Horace Elisha Scudder was an American man of letters and editor.
The House Behind the Cedars is a 1927 silent race film directed, written, produced and distributed by the noted director Oscar Micheaux. It was loosely adapted from the 1900 novel of the same name by African-American writer Charles W. Chesnutt, who explored issues of race, class and identity in the post-Civil War South. No print of the film is known to exist, and it is considered lost. Micheaux remade the film in 1932 under the title Veiled Aristocrats.

Veiled Aristocrats is a 1932 American pre-Code race film written, directed, produced and distributed by Oscar Micheaux. The film deals with the theme of "passing" by mixed-race African Americans to avoid racial discrimination. It is a remake of The House Behind the Cedars (1927), based on a novel by the same name published in 1900 by Charles W. Chesnutt. Micheaux may have borrowed the new title from a 1923 novel by Gertrude Sanborn.
The Bethel Literary and Historical Society was an organization founded in 1881 by African Methodist Episcopal Church Bishop Daniel Payne and continued at least until 1915. It represented a highly significant development in African-American society in Washington, D.C. Most of its early members were members of the Metropolitan AME Church where its meetings were held, while maintaining an open invitation for black Washingtonians from across the city. It immediately developed into the preeminent debating society and forum for racial issues in Washington, D.C. The prospect of a separation of schools for black children was heatedly debated in 1881–82 as were the ideas of Booker T. Washington and W. E. B. Du Bois in 1903. It was one of the stops of ʻAbdu'l-Bahá's journeys to the West.
According to The Norton Anthology of American Literature, the term Americanization was coined in the early 1900s and "referred to a concerted movement to turn immigrants into Americans, including classes, programs, and ceremonies focused on American speech, ideals, traditions, and customs, but it was also a broader term used in debates about national identity and a person’s general fitness for citizenship”.

The Conjure Woman is a collection of short stories by African-American fiction writer, essayist, and activist Charles W. Chesnutt. First published in 1899, The Conjure Woman is considered a seminal work of African-American literature composed of seven short stories, set in Patesville, North Carolina. A film adaptation, The Conjure Woman (film) was made by Oscar Micheaux.

The Colonel's Dream is a novel written by the African-American author Charles W. Chesnutt. The novel is published by Doubleday, Page, & Co. in 1905. The Colonel's Dream portrays the continuing oppression and racial violence prominent in the Southern United States after the American Civil War.

Evelyn's Husband is a novel published by the University of Mississippi in 2005 from an unpublished manuscript by African American author Charles W. Chesnutt which was edited by Matthew Wilson and Marjan Van Schaik. In addition to being an author, Chesnutt was an educator, lawyer and political activist who was involved in the early works of the NAACP.

The House Behind the Cedars is the first published novel by American author Charles W. Chesnutt. It was published in 1900 by Houghton, Mifflin and Company. The story occurs in the southern American states of North and South Carolina a few years following the American Civil War. Rena Walden, a young woman of mixed white and black ancestry, leaves home to join her brother, who has migrated to a new city, where he lives as a white man. Following her brother's lead, Rena begins living as a white woman. The secret of her identity leads to conflict when she falls in love with a white aristocrat who learns the truth of her heredity. The ensuing drama emphasizes themes of interracial relations and depicted the intricacies of racial identity in the American south.

A Business Career is a novel by African-American author Charles Chesnutt that features the life of a "new woman" of the late 19th century; she enters the world of business instead of embracing the traditional roles of women. It explores a failed romance between two successful upper-class members. A family’s vendetta against the man who allegedly destroyed the family's fortune is revealed to be mistaken. The novel was unusual for its time as Chesnutt wrote only about white society.

"The Passing of Grandison" is a short story written by Charles W. Chesnutt and published in the collection The Wife of His Youth and Other Stories of the Color-Line (1899). The story takes place in the United States in the early 1850s, at the time of anti-slavery sentiment and the abolitionist movement in the Northern United States, and after the passage of the Fugitive Slave Law of 1850.

The Negro Problem is a collection of seven essays by prominent Black American writers, such as W. E. B. Du Bois and Paul Laurence Dunbar, edited by Booker T. Washington, and published in 1903. It covers law, education, disenfranchisement, and Black Americans' place in American society.
William Leake Andrews is an American Professor Emeritus of English at The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and a scholar of early African-American literature. With books such as To Tell a Free Story: The First Century of Afro-American Autobiography, 1760–1865 (1986), Andrews helped establish the academic study of African-American literature in the late twentieth century. In 2017, Andrews received the Jay B. Hubbell Medal for Lifetime Achievement in American Literature from the Modern Language Association.