In organic chemistry, allenes are organic compounds in which one carbon atom has double bonds with each of its two adjacent carbon atoms. Allenes are classified as cumulated dienes. The parent compound of this class is propadiene, which is itself also called allene. A group of the structure R2C=C=CR− is called allenyl, while a substituent attached to an allene is referred to as an allenic substituent. In analogy to allylic and propargylic, a substituent attached to a saturated carbon α to an allene is referred to as an allenylic substituent. While allenes have two consecutive ('cumulated') double bonds, compounds with three or more cumulated double bonds are called cumulenes.
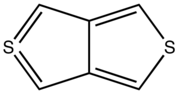
Thiophene is a heterocyclic compound with the formula C4H4S. Consisting of a planar five-membered ring, it is aromatic as indicated by its extensive substitution reactions. It is a colorless liquid with a benzene-like odor. In most of its reactions, it resembles benzene. Compounds analogous to thiophene include furan (C4H4O), selenophene (C4H4Se) and pyrrole (C4H4NH), which each vary by the heteroatom in the ring.
Furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. Chemical compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans.

Benzothiophene is an aromatic organic compound with a molecular formula C8H6S and an odor similar to naphthalene (mothballs). It occurs naturally as a constituent of petroleum-related deposits such as lignite tar. Benzothiophene has no household use. In addition to benzo[b]thiophene, a second isomer is known: benzo[c]thiophene.
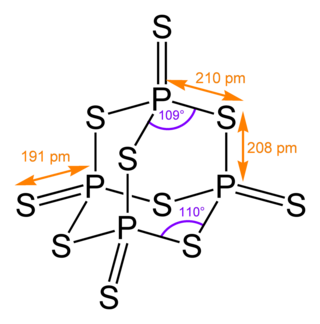
Phosphorus pentasulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula P2S5 (empirical) or P4S10 (molecular). This yellow solid is the one of two phosphorus sulfides of commercial value. Samples often appear greenish-gray due to impurities. It is soluble in carbon disulfide but reacts with many other solvents such as alcohols, DMSO, and DMF.
The Curtin–Hammett principle is a principle in chemical kinetics proposed by David Yarrow Curtin and Louis Plack Hammett. It states that, for a reaction that has a pair of reactive intermediates or reactants that interconvert rapidly, each going irreversibly to a different product, the product ratio will depend both on the difference in energy between the two conformers and the energy barriers from each of the rapidly equilibrating isomers to their respective products. Stated another way, the product distribution reflects the difference in energy between the two rate-limiting transition states. As a result, the product distribution will not necessarily reflect the equilibrium distribution of the two intermediates. The Curtin–Hammett principle has been invoked to explain selectivity in a variety of stereo- and regioselective reactions. The relationship between the (apparent) rate constants and equilibrium constant is known as the Winstein-Holness equation.
Tetrahydrothiophene is an organosulfur compound with the formula (CH2)4S. The molecule consists of a five-membered saturated ring with four methylene groups and a sulfur atom. It is the saturated analog of thiophene or the sulfur analog of THF. It is a volatile, colorless liquid with an intensely unpleasant odor. It is also known as thiophane, thiolane, or THT.
In organic chemistry, the Paal–Knorr synthesis is a reaction used to synthesize substituted furans, pyrroles, or thiophenes from 1,4-diketones. It is a synthetically valuable method for obtaining substituted furans and pyrroles, which are common structural components of many natural products. It was initially reported independently by German chemists Carl Paal and Ludwig Knorr in 1884 as a method for the preparation of furans, and has been adapted for pyrroles and thiophenes. Although the Paal–Knorr synthesis has seen widespread use, the mechanism wasn't fully understood until it was elucidated by V. Amarnath et al. in the 1990s.
Xylidine can refer to any of the six isomers of xylene amine, or any mixture of them.

2,5-Dimethoxy-3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine is a lesser-known psychedelic drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and was described in his book PiHKAL. Shulgin listed the dosage as 30–75 mg and the duration as 6–8 hours. He reported DMMDA as producing LSD-like images, mydriasis, ataxia, and time dilation. DMMDA isn't mentioned much in literature outside PiHKAL unlike 2C-B.

Sulfolene, or butadiene sulfone is a cyclic organic chemical with a sulfone functional group. It is a white, odorless, crystalline, indefinitely storable solid, which dissolves in water and many organic solvents. The compound is used as a source of butadiene.

Dithietanes are saturated heterocyclic compounds that contain two divalent sulfur atoms and two sp3-hybridized carbon centers. Two isomers are possible for this class of organosulfur compounds:

trans-Cyclooctene is a cyclic hydrocarbon with the formula [–(CH2)6CH=CH–], where the two C–C single bonds adjacent to the double bond are on opposite sides of the latter's plane. It is a colorless liquid with a disagreeable odor.
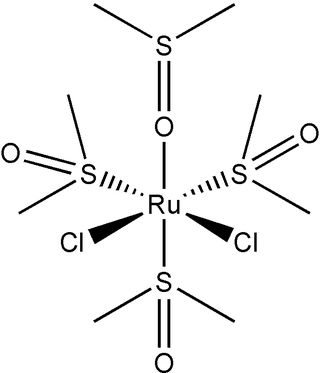
Dichlorotetrakis(dimethyl sulfoxide) ruthenium(II) describes coordination compounds with the formula RuCl2(dmso)4, where DMSO is dimethylsulfoxide. Both cis and trans isomers are known, but the cis isomer is more common. The cis isomer is a yellow, air-stable solid that is soluble in some organic solvents. These sulfoxide complexes are used in the synthesis of various ruthenium(ii) complexes. They have also attracted attention as possible anti-cancer drugs.
1-Naphthol, or α-naphthol, is a organic compound with the formula C10H7OH. It is a fluorescent white solid. 1-Naphthol differs from its isomer 2-naphthol by the location of the hydroxyl group on the naphthalene ring. The naphthols are naphthalene homologues of phenol. Both isomers are soluble in simple organic solvents. They are precursors to a variety of useful compounds.
2-Cyclopentenone is the organic compound with the chemical formula (CH2)2(CH)2CO. 2-Cyclopentenone contains two functional groups, a ketone and an alkene. It is a colorless liquid. Its isomer, 3-cyclopentenone is less commonly encountered.

3-Bromofuran is a colorless, organic compound with the molecular formula C4H3BrO. A versatile intermediate product for synthesizing more complex compounds, it used in the syntheses of a variety of economically important drugs.

Pyridyne in chemistry is the pyridine analogue of benzyne. Pyridynes are the class of reactive intermediates derived from pyridine. Two isomers exist, the 2,3-pyridine (2,3-didehydropyridine) and the 3,4-pyridyne (3,4-didehydropyridine). The reaction of 3-bromo-4-chloropyridine with furan and lithium amalgam gives 1,4-epoxy-dihydroquinoline through the 2,3-pyridyne intermediate. The reaction of 4-bromopyridine with sodium in liquid ammonia gives both 3-aminopyridine and 4-aminopyridine through the 3,4-pyridyne intermediate and an E1cB-elimination reaction.
Diimines are organic compounds containing two imine (RCH=NR') groups. Common derivatives are 1,2-diimines and 1,3-diimines. These compounds are used as ligands, but they are also precursors to other organic compounds.
The Fiesselmann thiophene synthesis is a name reaction in organic chemistry that allows for the generation of 3-hydroxy-2-thiophenecarboxylic acid derivatives from α,β-acetylenic esters with thioglycolic acid and its derivatives under the presence of a base. The reaction was developed by Hans Fiesselmann in the 1950s.
![Thieno[3,2-b]thiophene Thieno(3,2-b)thiophene.jpg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d3/Thieno%283%2C2-b%29thiophene.jpg/220px-Thieno%283%2C2-b%29thiophene.jpg)