
A wire is a flexible, round, bar of metal.
In physics, mean free path is the average distance over which a moving particle travels before substantially changing its direction or energy, typically as a result of one or more successive collisions with other particles.

In physics and electrical engineering, a conductor is an object or type of material that allows the flow of charge in one or more directions. Materials made of metal are common electrical conductors. The flow of negatively charged electrons generates electric current, positively charged holes, and positive or negative ions in some cases.

Shear stress is the component of stress coplanar with a material cross section. It arises from the shear force, the component of force vector parallel to the material cross section. Normal stress, on the other hand, arises from the force vector component perpendicular to the material cross section on which it acts.
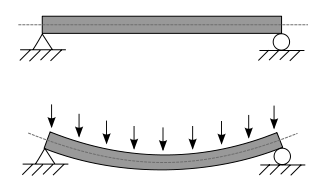
A beam is a structural element that primarily resists loads applied laterally across the beam's axis. Its mode of deflection is primarily by bending, as loads produce reaction forces at the beam's support points and internal bending moments, shear, stresses, strains, and deflections. Beams are characterized by their manner of support, profile, equilibrium conditions, length, and material.

Electron-beam welding (EBW) is a fusion welding process in which a beam of high-velocity electrons is applied to two materials to be joined. The workpieces melt and flow together as the kinetic energy of the electrons is transformed into heat upon impact. EBW is often performed under vacuum conditions to prevent dissipation of the electron beam.

In structural engineering, buckling is the sudden change in shape (deformation) of a structural component under load, such as the bowing of a column under compression or the wrinkling of a plate under shear. If a structure is subjected to a gradually increasing load, when the load reaches a critical level, a member may suddenly change shape and the structure and component is said to have buckled. Euler's critical load and Johnson's parabolic formula are used to determine the buckling stress of a column.

Extrusion is a process used to create objects of a fixed cross-sectional profile by pushing material through a die of the desired cross-section. Its two main advantages over other manufacturing processes are its ability to create very complex cross-sections; and to work materials that are brittle, because the material encounters only compressive and shear stresses. It also creates excellent surface finish and gives considerable freedom of form in the design process.

In applied mechanics, bending characterizes the behavior of a slender structural element subjected to an external load applied perpendicularly to a longitudinal axis of the element.

Framing, in construction, is the fitting together of pieces to give a structure support and shape. Framing materials are usually wood, engineered wood, or structural steel. The alternative to framed construction is generally called mass wall construction, where horizontal layers of stacked materials such as log building, masonry, rammed earth, adobe, etc. are used without framing.

An I-beam is any of various structural members with an I or H-shaped cross-section. Technical terms for similar items include H-beam, w-beam, universal beam (UB), rolled steel joist (RSJ), or double-T. I-beams are typically made of structural steel and serve a wide variety of construction uses.
A flatbow is a bow with non-recurved, flat, relatively wide limbs that are approximately rectangular in cross-section. Because the limbs are relatively wide, flatbows will usually narrow and become deeper at the handle, with a rounded, non-bending handle for easier grip. This design differs from that of a longbow, which has rounded limbs that are circular or D-shaped in cross-section, and is usually widest at the handle. A flatbow can be just as long as a longbow, but can also be very short. Typical lengths would be 68–70 inches (172.5–178 cm) for a flatbow, 70–72 inches (178–183 cm) for an English longbow, and 72–76 inches (183–193 cm) for a warbow-weight English longbow; but these styles may easily overlap each other. Traditional flatbows are usually wooden self bows, though laminated and composite flatbows have been made in ancient and modern times. Modern flatbows commonly use fiberglass.
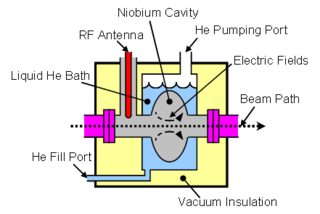
A cryomodule is a section of a modern particle accelerator composed of superconducting RF (SRF) acceleration cavities, which need very low operating temperatures, often around 2 Kelvin). The cryomodule is a complex, state-of-the-art supercooled component in which particle beams are accelerated for scientific research. The superconducting cavities are cooled with liquid helium.
Specific modulus is a materials property consisting of the elastic modulus per mass density of a material. It is also known as the stiffness to weight ratio or specific stiffness. High specific modulus materials find wide application in aerospace applications where minimum structural weight is required. The dimensional analysis yields units of distance squared per time squared. The equation can be written as:
In fluid dynamics, shear flow is the flow induced by a force in a fluid. In solid mechanics, shear flow is the shear stress over a distance in a thin-walled structure.

A box girder or tubular girder is a girder that forms an enclosed tube with multiple walls, as opposed to an I- or H-beam. Originally constructed of wrought iron joined by riveting, they are now made of rolled or welded steel, aluminium extrusions or prestressed concrete.

A deep foundation is a type of foundation that transfers building loads to the earth farther down from the surface than a shallow foundation does to a subsurface layer or a range of depths. A pile or piling is a vertical structural element of a deep foundation, driven or drilled deep into the ground at the building site.
Extrusion is a plastic deformation process in which raw material (billet) is forced to flow by compression through the die opening of a smaller cross-section area. The extrusion process is divided in two basic types: direct extrusion and indirect extrusion. In direct extrusion the billet is pushed through the die with ram pressure, whereas in indirect extrusion a die moves relative to the container.

Diffusion bonding or diffusion welding is a solid-state welding technique used in metalworking, capable of joining similar and dissimilar metals. It operates on the principle of solid-state diffusion, wherein the atoms of two solid, metallic surfaces intersperse themselves over time. This is typically accomplished at an elevated temperature, approximately 50-75% of the absolute melting temperature of the materials. A weak bond can also be achieved at room temperature. Diffusion bonding is usually implemented by applying high pressure, in conjunction with necessarily high temperature, to the materials to be welded; the technique is most commonly used to weld "sandwiches" of alternating layers of thin metal foil, and metal wires or filaments. Currently, the diffusion bonding method is widely used in the joining of high-strength and refractory metals within the aerospace and nuclear industries.
This glossary of structural engineering terms pertains specifically to structural engineering and its sub-disciplines. Please see glossary of engineering for a broad overview of the major concepts of engineering.













