
The Order of Preachers, commonly known as the Dominican Order, is a Catholic mendicant order of pontifical right that was founded in France by a Castilian priest named Dominic de Guzmán. It was approved by Pope Honorius III via the papal bull Religiosam vitam on 22 December 1216. Members of the order, who are referred to as Dominicans, generally display the letters OP after their names, standing for Ordinis Praedicatorum, meaning 'of the Order of Preachers'. Membership in the order includes friars, nuns, active sisters, and lay or secular Dominicans. More recently, there have been a growing number of associates of the religious sisters who are unrelated to the tertiaries.

Scholasticism was a medieval school of philosophy that employed a critical organic method of philosophical analysis predicated upon Aristotelianism and the Ten Categories. Christian scholasticism emerged within the monastic schools that translated scholastic Judeo-Islamic philosophies, and "rediscovered" the collected works of Aristotle. Endeavoring to harmonize his metaphysics and its account of a prime mover with the Latin Catholic dogmatic trinitarian theology, these monastic schools became the basis of the earliest European medieval universities, and thus became the bedrock for the development of modern science and philosophy in the Western world. Scholasticism dominated education in Europe from about 1100 to 1700. The rise of scholasticism was closely associated with these schools that flourished in Italy, France, Portugal, Spain and England.

Jacques Maritain was a French Catholic philosopher. Raised as a Protestant, he was agnostic before converting to Catholicism in 1906. An author of more than 60 books, he helped to revive Thomas Aquinas for modern times, and was influential in the development and drafting of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. Pope Paul VI presented his "Message to Men of Thought and of Science" at the close of Vatican II to Maritain, his long-time friend and mentor. The same pope had seriously considered making him a lay cardinal, but Maritain rejected it. Maritain's interest and works spanned many aspects of philosophy, including aesthetics, political theory, philosophy of science, metaphysics, the nature of education, liturgy and ecclesiology.

Thomism is the philosophical and theological school which arose as a legacy of the work and thought of Thomas Aquinas (1225–1274), the Dominican philosopher, theologian, and Doctor of the Church.
A Pontifical University or Athenaeum is an ecclesiastical university established or approved directly by the Holy See, composed of three main ecclesiastical faculties and at least one other faculty. These academic institutes deal specifically with Christian revelation and related disciplines, and the Church's mission of spreading the Gospel, as proclaimed in the apostolic constitution Sapientiachristiana. As of 2018, they are governed by the apostolic constitution Veritatis gaudium issued by Pope Francis on 8 December 2017.

Sir Roger Vernon Scruton, was an English philosopher, writer, and social critic who specialised in aesthetics and political philosophy, particularly in the furtherance of traditionalist conservative views.
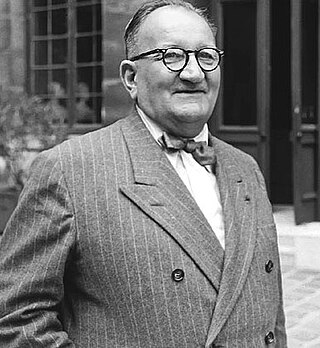
Étienne Henri Gilson was a French philosopher and historian of philosophy. A scholar of medieval philosophy, he originally specialised in the thought of Descartes; he also philosophized in the tradition of Thomas Aquinas, although he did not consider himself a neo-Thomist philosopher. In 1946 he attained the distinction of being elected an "Immortal" (member) of the Académie française. He was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature.

Tommaso Maria Zigliara, OP was a Corsican priest of the Catholic Church, a member of the Dominicans, a theologian, philosopher and a cardinal.

The Pontifical University of Saint Thomas Aquinas (PUST), also known as the Angelicum in honor of its patron the Doctor Angelicus Thomas Aquinas, is a pontifical university located in the historic center of Rome, Italy. The Angelicum is administered by the Dominican Order and is the order's central locus of Thomist theology and philosophy.

The Dominican University College was a bilingual university located in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. From 2012 to 2024, Dominican University College was an affiliated college of Carleton University.
Cornelio Fabro CSS was an Italian Catholic priest of the Stigmatine Order and a scholastic Thomist philosopher. He was the founder of the Institute for Higher Studies on Unbelief, Religion and Cultures.
Aeterni Patris was an encyclical issued by Pope Leo XIII in August 1879. It was subtitled "On the Restoration of Christian Philosophy in Catholic Schools in the Spirit of the Angelic Doctor, St. Thomas Aquinas". The aim of the encyclical was to advance the revival of Scholastic philosophy.

Neo-scholasticism is a revival and development of medieval scholasticism in Catholic theology and philosophy which began in the second half of the 19th century.

Réginald Marie Garrigou-Lagrange was a French Dominican friar, philosopher and theologian. Garrigou-Lagrange was a neo-Thomist theologian, recognized along with Édouard Hugon and Martin Grabmann as distinguished theologians of the 20th century. As professor at the Pontifical University of Saint Thomas Aquinas, he taught dogmatic and spiritual theology in Rome from 1909 to 1959. There he wrote The Three Ages of the Interior Life in 1938.

The Dominican House of Studies is a Catholic institution in Washington, DC, housing both the Priory of the Immaculate Conception, a community of the Province of St. Joseph of the Order of Preachers (Dominicans), and the Pontifical Faculty of the Immaculate Conception, an ecclesiastical faculty of theology.

The Pontifical Academy of Saint Thomas Aquinas is a pontifical academy established on 15 October 1879 by Pope Leo XIII. The academy is one of the pontifical academies housed along with the academies of science at Casina Pio IV in Vatican City, Rome.

Mario Luigi Ciappi, O.P. was an Italian Cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church who served as personal theologian to five popes from 1955 to 1989, and was elevated to the cardinalate in 1977.
John Joseph Haldane is a British philosopher, commentator and broadcaster. He is a former papal adviser to the Vatican. He is credited with coining the term 'analytical Thomism' and is himself a Thomist in the analytic tradition. Haldane is associated with The Veritas Forum and is the current chair of the Royal Institute of Philosophy.
Benedict M. Ashley, O.P., was an American theologian and philosopher who had a major influence on 20th century Catholic theology and ethics in America through his writing, teaching, and consulting with the United States Conference of Catholic Bishops. Author of 19 books, Ashley was a major exponent of the River Forest Thomism. Health Care Ethics, which he co-authored in 1975 and now in its fifth edition, continues to be a fundamental text in the field of Catholic Medical Ethics. Ashley taught at numerous institutions and was an active teacher, consultant, and author. He was a faculty member of the Institute for Advanced Physics, a physics research and educational organization reintegrating the foundational principles given directly through our senses into the heart of modern science, from 2003 till his death. He called the Institute for Advanced Physics "the first and only institution addressing this problem [the disintegration of secular and religious culture] at its core by integrating the proper philosophical depth into the heart of modern science."
The John Paul II Center for Interreligious Dialogue is an academic center that serves to build bridges between religious traditions, particularly between Catholic Christian and Jewish pastoral and academic leaders. The Center is a partnership between the Russell Berrie Foundation and the Pontifical University of Saint Thomas Aquinas (Angelicum). It operates as part of the Section for Ecumenism and Dialogue in the Theology Faculty of the Angelicum in Rome.













