Related Research Articles

John Craig Venter is an American biotechnologist and businessman. He is known for leading one of the first draft sequences of the human genome and assembled the first team to transfect a cell with a synthetic chromosome. Venter founded Celera Genomics, the Institute for Genomic Research (TIGR) and the J. Craig Venter Institute (JCVI). He was the co-founder of Human Longevity Inc. and Synthetic Genomics. He was listed on Time magazine's 2007 and 2008 Time 100 list of the most influential people in the world. In 2010, the British magazine New Statesman listed Craig Venter at 14th in the list of "The World's 50 Most Influential Figures 2010". In 2012, Venter was honored with Dan David Prize for his contribution to genome research. He was elected to the American Philosophical Society in 2013. He is a member of the USA Science and Engineering Festival's advisory board.

The human genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within individual mitochondria. These are usually treated separately as the nuclear genome and the mitochondrial genome. Human genomes include both protein-coding DNA sequences and various types of DNA that does not encode proteins. The latter is a diverse category that includes DNA coding for non-translated RNA, such as that for ribosomal RNA, transfer RNA, ribozymes, small nuclear RNAs, and several types of regulatory RNAs. It also includes promoters and their associated gene-regulatory elements, DNA playing structural and replicatory roles, such as scaffolding regions, telomeres, centromeres, and origins of replication, plus large numbers of transposable elements, inserted viral DNA, non-functional pseudogenes and simple, highly repetitive sequences. Introns make up a large percentage of non-coding DNA. Some of this non-coding DNA is non-functional junk DNA, such as pseudogenes, but there is no firm consensus on the total amount of junk DNA.

BGI Group, formerly Beijing Genomics Institute, is a Chinese genomics company with headquarters in Yantian, Shenzhen. The company was originally formed in 1999 as a genetics research center to participate in the Human Genome Project. It also sequences the genomes of other animals, plants and microorganisms.

In genetics and bioinformatics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently large fraction of the population, many publications do not apply such a frequency threshold.
The Human Genome Organisation (HUGO) is a non-profit organization founded in 1988. HUGO represents an international coordinating scientific body in response to initiatives such as the Human Genome Project. HUGO has four active committees, including the HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC), and the HUGO Committee on Ethics, Law and Society (CELS).
The International HapMap Project was an organization that aimed to develop a haplotype map (HapMap) of the human genome, to describe the common patterns of human genetic variation. HapMap is used to find genetic variants affecting health, disease and responses to drugs and environmental factors. The information produced by the project is made freely available for research.

The Wellcome Sanger Institute, previously known as The Sanger Centre and Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, is a non-profit British genomics and genetics research institute, primarily funded by the Wellcome Trust.

Paleogenetics is the study of the past through the examination of preserved genetic material from the remains of ancient organisms. Emile Zuckerkandl and Linus Pauling introduced the term in 1963, long before the sequencing of DNA, in reference to the possible reconstruction of the corresponding polypeptide sequences of past organisms. The first sequence of ancient DNA, isolated from a museum specimen of the extinct quagga, was published in 1984 by a team led by Allan Wilson.

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences in and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (alleles), a situation called polymorphism.

The Human Genome Project (HGP) was an international scientific research project with the goal of determining the base pairs that make up human DNA, and of identifying, mapping and sequencing all of the genes of the human genome from both a physical and a functional standpoint. It started in 1990 and was completed in 2003. It remains the world's largest collaborative biological project. Planning for the project started after it was adopted in 1984 by the US government, and it officially launched in 1990. It was declared complete on April 14, 2003, and included about 92% of the genome. Level "complete genome" was achieved in May 2021, with only 0.3% of the bases covered by potential issues. The final gapless assembly was finished in January 2022.
Human evolutionary genetics studies how one human genome differs from another human genome, the evolutionary past that gave rise to the human genome, and its current effects. Differences between genomes have anthropological, medical, historical and forensic implications and applications. Genetic data can provide important insights into human evolution.
The Neanderthal genome project is an effort of a group of scientists to sequence the Neanderthal genome, founded in July 2006.

The 1000 Genomes Project (1KGP), taken place from January 2008 to 2015, was an international research effort to establish the most detailed catalogue of human genetic variation at the time. Scientists planned to sequence the genomes of at least one thousand anonymous healthy participants from a number of different ethnic groups within the following three years, using advancements in newly developed technologies. In 2010, the project finished its pilot phase, which was described in detail in a publication in the journal Nature. In 2012, the sequencing of 1092 genomes was announced in a Nature publication. In 2015, two papers in Nature reported results and the completion of the project and opportunities for future research.

Whole genome sequencing (WGS), also known as full genome sequencing, complete genome sequencing, or entire genome sequencing, is the process of determining the entirety, or nearly the entirety, of the DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a single time. This entails sequencing all of an organism's chromosomal DNA as well as DNA contained in the mitochondria and, for plants, in the chloroplast.

A reference genome is a digital nucleic acid sequence database, assembled by scientists as a representative example of the set of genes in one idealized individual organism of a species. As they are assembled from the sequencing of DNA from a number of individual donors, reference genomes do not accurately represent the set of genes of any single individual organism. Instead, a reference provides a haploid mosaic of different DNA sequences from each donor. For example, one of the most recent human reference genomes, assembly GRCh38/hg38, is derived from >60 genomic clone libraries. There are reference genomes for multiple species of viruses, bacteria, fungus, plants, and animals. Reference genomes are typically used as a guide on which new genomes are built, enabling them to be assembled much more quickly and cheaply than the initial Human Genome Project. Reference genomes can be accessed online at several locations, using dedicated browsers such as Ensembl or UCSC Genome Browser.
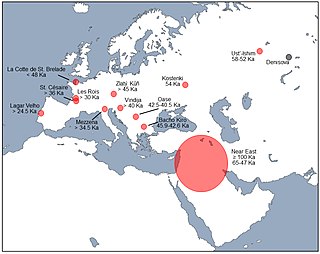
Interbreeding between archaic and modern humans occurred during the Middle Paleolithic and early Upper Paleolithic. The interbreeding happened in several independent events that included Neanderthals and Denisovans, as well as several unidentified hominins.

The horse genome was first sequenced in 2006. The Horse Genome Project mapped 2.7 billion DNA base pairs, and released the full map in 2009. The horse genome is larger than the dog genome, but smaller than the human genome or the bovine genome. It encompasses 31 pairs of autosomes and one sex chromosome pair.

The African Society of Human Genetics (AfSHG) is a learned society and professional membership organization focused on the study of human genetics and genomics in Africans, and open to researchers who are interested in the subject. It has played a role in founding several national genetics societies, and is affiliated with the societies of Cameroon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Mali, Egypt, Rwanda, Senegal, South Africa, and Tanzania.
Ambroise Wonkam is a Cameroonian medical doctor and professor of medical genetics at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine. His research is in sickle cell disease, the genetics of congenital hearing impairment, and ethics in human genetics. He is the current president of the African Society of Human Genetics.
References
- ↑ Schutz, Elna (2 November 2021). "Why Africa urgently needs its own genetic library". BBC News. Archived from the original on 2 November 2021. Retrieved 2 November 2021.
- ↑ "Sequence African genomes for Africa and the world: scientist". Bangkok Post . Agence France-Presse. 11 February 2021. Archived from the original on 2 November 2021. Retrieved 2 November 2021.
- ↑ Wonkam, Ambroise (10 February 2021). "Sequence three million genomes across Africa". Nature (comment). 590 (7845): 209–211. doi: 10.1038/d41586-021-00313-7 . PMC 9979155 . PMID 33568829.