Related Research Articles

The citric acid cycle (CAC)—also known as the Krebs cycle or the TCA cycle —is a series of chemical reactions to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. The Krebs cycle is used by organisms that respire to generate energy, either by anaerobic respiration or aerobic respiration. In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids, as well as the reducing agent NADH, that are used in numerous other reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest components of metabolism and may have originated abiogenically. Even though it is branded as a 'cycle', it is not necessary for metabolites to follow only one specific route; at least three alternative segments of the citric acid cycle have been recognized.

Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose, into pyruvic acid. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). Glycolysis is a sequence of ten reactions catalyzed by enzymes.

A mitochondrion is a double-membrane-bound organelle found in most eukaryotic organisms. Mitochondria use aerobic respiration to generate most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is subsequently used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1857 in the voluntary muscles of insects. The term mitochondrion was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. The mitochondrion is popularly nicknamed the "powerhouse of the cell", a phrase coined by Philip Siekevitz in a 1957 article of the same name.

In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second recessive. This state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new or inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes (autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child. Since there is only one copy of the Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, there are other forms of dominance such as incomplete dominance, in which a gene variant has a partial effect compared to when it is present on both chromosomes, and co-dominance, in which different variants on each chromosome both show their associated traits.
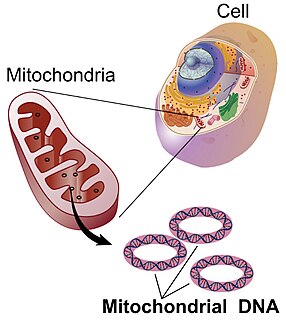
Mitochondrial DNA is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is only a small portion of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell; most of the DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and, in plants and algae, also in plastids such as chloroplasts.

The enzyme cytochrome c oxidase or Complex IV, EC 1.9.3.1, is a large transmembrane protein complex found in bacteria, archaea, and mitochondria of eukaryotes.
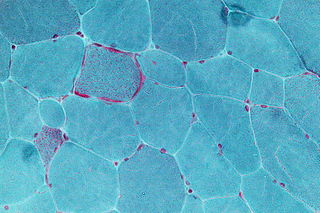
Mitochondrial disease is a group of disorders caused by mitochondrial dysfunction. Mitochondria are the organelles that generate energy for the cell and are found in every cell of the human body except red blood cells. They convert the energy of food molecules into the ATP that powers most cell functions.
A genetic screen or mutagenesis screen is an experimental technique used to identify and select for individuals who possess a phenotype of interest in a mutagenized population. Hence a genetic screen is a type of phenotypic screen. Genetic screens can provide important information on gene function as well as the molecular events that underlie a biological process or pathway. While genome projects have identified an extensive inventory of genes in many different organisms, genetic screens can provide valuable insight as to how those genes function.

Leigh syndrome is an inherited neurometabolic disorder that affects the central nervous system. It is named after Archibald Denis Leigh, a British neuropsychiatrist who first described the condition in 1951. Normal levels of thiamine, thiamine monophosphate, and thiamine diphosphate are commonly found but there is a reduced or absent level of thiamine triphosphate. This is thought to be caused by a blockage in the enzyme thiamine-diphosphate kinase, and therefore treatment in some patients would be to take thiamine triphosphate daily.
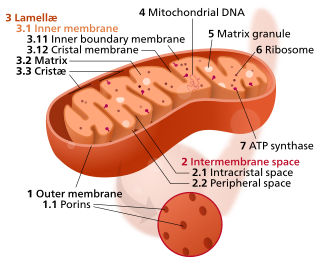
In the mitochondrion, the matrix is the space within the inner membrane. The word "matrix" stems from the fact that this space is viscous, compared to the relatively aqueous cytoplasm. The mitochondrial matrix contains the mitochondrial DNA, ribosomes, soluble enzymes, small organic molecules, nucleotide cofactors, and inorganic ions.[1] The enzymes in the matrix facilitate reactions responsible for the production of ATP, such as the citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, oxidation of pyruvate, and the beta oxidation of fatty acids.

Homoplasmy is a term used in genetics to describe a eukaryotic cell whose copies of mitochondrial DNA are all identical. In normal and healthy tissues, all cells are homoplasmic. Homoplasmic mitochondrial DNA copies may be normal or mutated; however, most mutations are heteroplasmic. It has been discovered, though, that homoplasmic mitochondrial DNA mutations may be found in human tumors.

Human mitochondrial genetics is the study of the genetics of human mitochondrial DNA. The human mitochondrial genome is the entirety of hereditary information contained in human mitochondria. Mitochondria are small structures in cells that generate energy for the cell to use, and are hence referred to as the "powerhouses" of the cell.
Kearns–Sayre syndrome (KSS), oculocraniosomatic disorder or oculocranionsomatic neuromuscular disorder with ragged red fibers is a mitochondrial myopathy with a typical onset before 20 years of age. KSS is a more severe syndromic variant of chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia, a syndrome that is characterized by isolated involvement of the muscles controlling movement of the eyelid and eye. This results in ptosis and ophthalmoplegia respectively. KSS involves a combination of the already described CPEO as well as pigmentary retinopathy in both eyes and cardiac conduction abnormalities. Other symptoms may include cerebellar ataxia, proximal muscle weakness, deafness, diabetes mellitus, growth hormone deficiency, hypoparathyroidism, and other endocrinopathies. In both of these diseases, muscle involvement may begin unilaterally but always develops into a bilateral deficit, and the course is progressive. This discussion is limited specifically to the more severe and systemically involved variant.
petite (ρ–) is a mutant first discovered in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Due to the defect in the respiratory chain, 'petite' yeast are unable to grow on media containing only non-fermentable carbon sources and form small colonies when grown in the presence of fermentable carbon sources. The petite phenotype can be caused by the absence of, or mutations in, mitochondrial DNA, or by mutations in nuclear-encoded genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation. A neutral petite produces all wild type progeny when crossed with wild type.
NUMT, pronounced "new might," is an acronym for "nuclear mitochondrial DNA" segment coined by evolutionary geneticist, Jose V. Lopez, which describes a transposition of any type of cytoplasmic mitochondrial DNA into the nuclear genome of eukaryotic organisms.
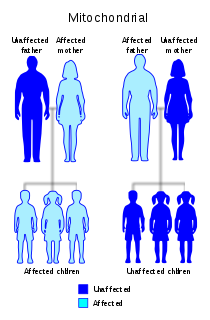
Diabetes and deafness (DAD) or maternally inherited diabetes and deafness (MIDD) or mitochondrial diabetes is a subtype of diabetes which is caused from a point mutation at position 3243 in human mitochondrial DNA, which consists of a circular genome. This affects the gene encoding tRNALeu. Because mitochondrial DNA is contributed to the embryo by the oocyte and not by spermatozoa, this disease is inherited from maternal family members only. As indicated by the name, MIDD is characterized by diabetes and sensorineural hearing loss.
MT-ATP6 is a mitochondrial gene with the full name 'mitochondrially encoded ATP synthase membrane subunit 6' that encodes the ATP synthase Fo subunit 6. This subunit belongs to the Fo complex of the large, transmembrane F-type ATP synthase. This enzyme, which is also known as complex V, is responsible for the final step of oxidative phosphorylation in the electron transport chain. Specifically, one segment of ATP synthase allows positively charged ions, called protons, to flow across a specialized membrane inside mitochondria. Another segment of the enzyme uses the energy created by this proton flow to convert a molecule called adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to ATP. Mutations in the MT-ATP6 gene have been found in approximately 10 to 20 percent of people with Leigh syndrome.

Cytochrome c oxidase I (COX1) also known as mitochondrially encoded cytochrome c oxidase I (MT-CO1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MT-CO1 gene. In other eukaryotes, the gene is called COX1, CO1, or COI. Cytochrome c oxidase I is the main subunit of the cytochrome c oxidase complex. Mutations in MT-CO1 have been associated with Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON), acquired idiopathic sideroblastic anemia, Complex IV deficiency, colorectal cancer, sensorineural deafness, and recurrent myoglobinuria.
The term proofreading is used in genetics to refer to the error-correcting processes, first proposed by John Hopfield and Jacques Ninio, involved in DNA replication, immune system specificity, enzyme-substrate recognition among many other processes that require enhanced specificity. The proofreading mechanisms of Hopfield and Ninio are non-equilibrium active processes that consume ATP to enhance specificity of various biochemical reactions.
The citrate-malate shuttle is a series of chemical reactions – commonly referred to as a biochemical cycle or system – that transports acetyl-CoA in the mitochondrial matrix across the inner and outer mitochondrial membrane for fatty acid synthesis. Mitochondria, also known as the powerhouse of a cell, is enclosed in a double membrane. As the inner mitochondrial membrane is impermeable to acetyl-CoA, the shuttle system is essential to fatty acid synthesis in the cytosol. It plays an important role in the generation of lipids in the liver.
References
- 1 2 Craven L, Alston CL, Taylor RW, Turnbull DM (August 2017). "Recent Advances in Mitochondrial Disease". Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics. 18 (1): 257–275. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-091416-035426 . PMID 28415858.
- 1 2 Rossignol R, Faustin B, Rocher C, Malgat M, Mazat JP, Letellier T (March 2003). "Mitochondrial threshold effects". The Biochemical Journal. 370 (Pt 3): 751–62. doi:10.1042/bj20021594. PMC 1223225 . PMID 12467494.