Control theory deals with the control of dynamical systems in engineered processes and machines. The objective is to develop a control model for controlling such systems using a control action in an optimum manner without delay or overshoot and ensuring control stability.
Income is the consumption and saving opportunity gained by an entity within a specified timeframe, which is generally expressed in monetary terms.
A mathematical model is a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed mathematical modeling. Mathematical models are used in the natural sciences and engineering disciplines, as well as in non-physical systems such as the social sciences. Mathematical models are also used in music, linguistics and philosophy.
In general terms, throughput is the rate of production or the rate at which something is processed.
Thermal conduction is the transfer of internal energy by microscopic collisions of particles and movement of electrons within a body. The colliding particles, which include molecules, atoms and electrons, transfer disorganized microscopic kinetic and potential energy, jointly known as internal energy. Conduction takes place in all phases: solid, liquid, and gas. The rate at which energy is conducted as the heat between two bodies depends on the temperature difference between the two bodies and the properties of the conductive interface through which the heat is transferred.

Inventory or stock is the goods and materials that a business holds for the ultimate goal of resale.
The theory of constraints (TOC) is a management paradigm that views any manageable system as being limited in achieving more of its goals by a very small number of constraints. There is always at least one constraint, and TOC uses a focusing process to identify the constraint and restructure the rest of the organization around it. TOC adopts the common idiom "a chain is no stronger than its weakest link". This means that processes, organizations, etc., are vulnerable because the weakest person or part can always damage or break them or at least adversely affect the outcome.

James Edward Meade, was a British economist and winner of the 1977 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences jointly with the Swedish economist Bertil Ohlin for their "pathbreaking contribution to the theory of international trade and international capital movements".
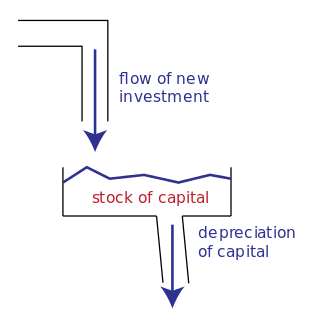
Economics, business, accounting, and related fields often distinguish between quantities that are stocks and those that are flows. These differ in their units of measurement. A stock is measured at one specific time, and represents a quantity existing at that point in time, which may have accumulated in the past. A flow variable is measured over an interval of time. Therefore, a flow would be measured per unit of time. Flow is roughly analogous to rate or speed in this sense.

Throughput accounting (TA) is a principle-based and simplified management accounting approach that provides managers with decision support information for enterprise profitability improvement. TA is relatively new in management accounting. It is an approach that identifies factors that limit an organization from reaching its goal, and then focuses on simple measures that drive behavior in key areas towards reaching organizational goals. TA was proposed by Eliyahu M. Goldratt as an alternative to traditional cost accounting. As such, Throughput Accounting is neither cost accounting nor costing because it is cash focused and does not allocate all costs to products and services sold or provided by an enterprise. Considering the laws of variation, only costs that vary totally with units of output e.g. raw materials, are allocated to products and services which are deducted from sales to determine Throughput. Throughput Accounting is a management accounting technique used as the performance measure in the Theory of Constraints (TOC). It is the business intelligence used for maximizing profits, however, unlike cost accounting that primarily focuses on 'cutting costs' and reducing expenses to make a profit, Throughput Accounting primarily focuses on generating more throughput. Conceptually, Throughput Accounting seeks to increase the speed or rate at which throughput is generated by products and services with respect to an organization's constraint, whether the constraint is internal or external to the organization. Throughput Accounting is the only management accounting methodology that considers constraints as factors limiting the performance of organizations.
Yield management is a variable pricing strategy, based on understanding, anticipating and influencing consumer behavior in order to maximize revenue or profits from a fixed, time-limited resource. As a specific, inventory-focused branch of revenue management, yield management involves strategic control of inventory to sell the right product to the right customer at the right time for the right price. This process can result in price discrimination, in which customers consuming identical goods or services are charged different prices. Yield management is a large revenue generator for several major industries; Robert Crandall, former Chairman and CEO of American Airlines, gave yield management its name and has called it "the single most important technical development in transportation management since we entered deregulation."
A mass balance, also called a material balance, is an application of conservation of mass to the analysis of physical systems. By accounting for material entering and leaving a system, mass flows can be identified which might have been unknown, or difficult to measure without this technique. The exact conservation law used in the analysis of the system depends on the context of the problem, but all revolve around mass conservation, i.e., that matter cannot disappear or be created spontaneously.
Scheduling is the process of arranging, controlling and optimizing work and workloads in a production process or manufacturing process. Scheduling is used to allocate plant and machinery resources, plan human resources, plan production processes and purchase materials.
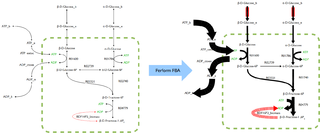
Flux balance analysis (FBA) is a mathematical method for simulating metabolism in genome-scale reconstructions of metabolic networks. In comparison to traditional methods of modeling, FBA is less intensive in terms of the input data required for constructing the model. Simulations performed using FBA are computationally inexpensive and can calculate steady-state metabolic fluxes for large models in a few seconds on modern personal computers.

In accounting, the Inventory turnover is a measure of the number of times inventory is sold or used in a time period such as a year. It is calculated to see if a business has an excessive inventory in comparison to its sales level. The equation for inventory turnover equals the cost of goods sold divided by the average inventory. Inventory turnover is also known as inventory turns, merchandise turnover, stockturn, stock turns, turns, and stock turnover.
A signal-flow graph or signal-flowgraph (SFG), invented by Claude Shannon, but often called a Mason graph after Samuel Jefferson Mason who coined the term, is a specialized flow graph, a directed graph in which nodes represent system variables, and branches represent functional connections between pairs of nodes. Thus, signal-flow graph theory builds on that of directed graphs, which includes as well that of oriented graphs. This mathematical theory of digraphs exists, of course, quite apart from its applications.
In economics, factor payments are the income people receive for supplying the factors of production: land, labor, capital or entrepreneurship.
Industrial process data validation and reconciliation, or more briefly, data validation and reconciliation (DVR), is a technology that uses process information and mathematical methods in order to automatically ensure data validation and reconciliation by correcting measurements in industrial processes. The use of DVR allows for extracting accurate and reliable information about the state of industry processes from raw measurement data and produces a single consistent set of data representing the most likely process operation.
This glossary of economics is a list of definitions of terms and concepts used in economics, its sub-disciplines, and related fields.
Theory of constraints (TOC) is an engineering management technique used to evaluate a manageable procedure, identifying the largest constraint (bottleneck) and strategizing to reduce task time and maximise profit. It assists in determining what to change, when to change it, and how to cause the change. The theory was established by Dr. Eliyahu Goldratt through his 1984 bestselling novel The Goal. Since this time, TOC has continued to develop and evolve and is a primary management tool in the engineering industry. When Applying TOC, powerful tools are used to determine the constraint and reduce its effect on the procedure, including:






