Three-tier system may refer to:
A capital requirement is the amount of capital a bank or other financial institution has to have as required by its financial regulator. This is usually expressed as a capital adequacy ratio of equity as a percentage of risk-weighted assets. These requirements are put into place to ensure that these institutions do not take on excess leverage and risk becoming insolvent. Capital requirements govern the ratio of equity to debt, recorded on the liabilities and equity side of a firm's balance sheet. They should not be confused with reserve requirements, which govern the assets side of a bank's balance sheet—in particular, the proportion of its assets it must hold in cash or highly-liquid assets. Capital is a source of funds not a use of funds.

Naomi Kathleen Cavaday is a British former professional tennis player from Sidcup, Kent. She retired in April 2011 to take up a coaching role with the Lawn Tennis Association. At the time of her retirement, she was the British No. 6, with a ranking of world No. 231. Her career-high ranking was 174, achieved in May 2010. She won three ITF singles titles and two ITF doubles titles. Her coach at retirement was Rob Smith. She was formerly coached by David Felgate, the long-time coach of Tim Henman.
The WTA Tier II tournaments were Women's Tennis Association tennis second-level tournaments held from 1990 until the end of the 2008 season. The line-up of events varied over the years, with tournaments being promoted, demoted or cancelled.
Basel III is a global, voluntary regulatory framework on bank capital adequacy, stress testing, and market liquidity risk. This third installment of the Basel Accords was developed in response to the deficiencies in financial regulation revealed by the financial crisis of 2007–08. It is intended to strengthen bank capital requirements by increasing bank liquidity and decreasing bank leverage.
Tier 1 or Tier One may refer to:

The COVID-19 pandemic is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus reached the United Kingdom in late January 2020. As of 24 March 2021, there have been 4.3 million cases confirmed and 126,172 deaths overall among people who had recently tested positive – the world's eleventh-highest death rate by population and the highest death toll in Europe. There have been 151,313 deaths where the death certificate mentioned COVID by 2 April 2021, with around 90% giving it as the main cause. There has been some disparity between the outbreak's severity in each of the four countries. Health in the UK is devolved, with England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland each having their own publicly-funded healthcare systems and governments.

The COVID-19 pandemic was first confirmed to have spread to England with two cases among Chinese nationals staying in a hotel in York on 31 January 2020. The two main public bodies responsible for health in England are NHS England and Public Health England. NHS England oversees the budget, planning, delivery and day-to-day operation of the commissioning side of the NHS in England while PHE's mission is "to protect and improve the nation’s health and to address inequalities". As of 7 April 2021, there have been 3,818,665 total cases and 111,666 deaths in England. In January 2021 it was estimated around 22% of people in England have had coronavirus.
The 2021 Wimbledon Championships is a planned Grand Slam tennis tournament that is scheduled to take place at the All England Lawn Tennis and Croquet Club in Wimbledon, London, United Kingdom. Novak Djokovic and Simona Halep are the defending singles champions.
This article contains a list of primary and secondary legislation enacted by the Parliament of the United Kingdom in connection with the COVID-19 pandemic.
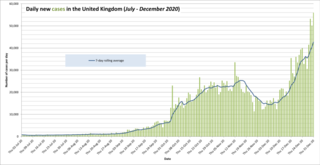
The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom from July 2020 to December 2020. There are significant differences in the legislation and the reporting between the countries of the UK: England, Scotland, Northern Ireland, and Wales. The numbers of cases and deaths are reported on a government Web site updated daily during the pandemic. The UK-wide COVID Symptom Study based on surveys of four million participants, endorsed by authorities in Scotland and Wales, run by health science company ZOE, and analysed by King's College London researchers, publishes daily estimates of the number of new and total current COVID-19 infections in UK regions, without restriction to only laboratory-confirmed cases.

On 14 October 2020, the UK Government abandoned its attempts to control the spread of SARS-CoV-2 by means of piecemeal local regulations and introduced a three-tier approach across England, with legal restrictions varying according to government-defined tiers. Tier 1 restrictions are referred to as 'Local COVID Alert Level Medium', with tier 2 being 'Local COVID Alert Level High' and tier 3 'Local COVID Alert Level Very High'. The restrictions were enforced by three English statutory instruments, as follows:

The Health Protection (England) Regulations 2020 is an English statutory instrument (SI) made on 3 November 2020 by the Secretary of State for Health and Social Care, Matt Hancock, in response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
COVID-19 tier regulations in England may refer to:

The Health Protection (England) Regulations 2020 is an English emergency statutory instrument that replaced the second lockdown regulations from 2 December 2020. As initially made, it brought back the three-tier legal framework first introduced by the first COVID-19 tier regulations in England, but with changes to the restrictions within each tier.

A substantial meal or table meal is a term of art in British law regarding the application of alcohol licensing laws. It was also used in reference to the closure of pubs, restaurants and cafés due to the COVID-19 pandemic, with those serving "substantial meals" being protected.
Tier 4 or Tier four may refer to:
The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in England from July 2020 to December 2020. There are significant differences in the legislation and the reporting between the countries of the UK: England, Scotland, Northern Ireland, and Wales.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.






