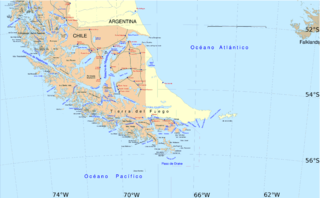
Tierra del Fuego is an archipelago at the southernmost tip of South America, shared between Chile, and Argentina.
Tierra del Fuego may also refer to:
Tierra del Fuego is an archipelago at the southernmost tip of South America, shared between Chile, and Argentina.
Tierra del Fuego may also refer to:

Tierra del Fuego is an archipelago off the southernmost tip of the South American mainland, across the Strait of Magellan.
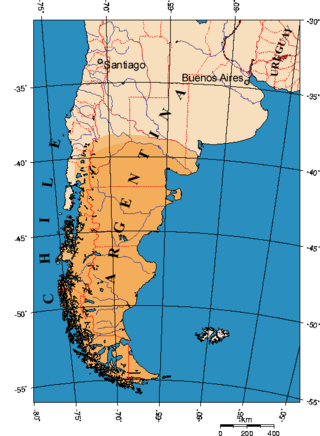
Patagonia is a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes Mountains with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and glaciers in the west and deserts, tablelands, and steppes to the east. Patagonia is bounded by the Pacific Ocean on the west, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, and many bodies of water that connect them, such as the Strait of Magellan, the Beagle Channel, and the Drake Passage to the south.

Ushuaia is the capital of Tierra del Fuego, Antártida e Islas del Atlántico Sur Province, Argentina. With a population of 82,615 and a location below the 54th parallel south latitude, Ushuaia claims the title of world's southernmost city.

Tierra del Fuego, officially the Province of Tierra del Fuego, Antarctica and South Atlantic Islands, is the southernmost, smallest, and least populous Argentine province. The provincial capital city is Ushuaia, from a native word meaning "bay towards the end".

Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego also formerly Isla de Xátiva is an island near the southern tip of South America from which it is separated by the Strait of Magellan. The western portion (61.4%) of the island is in Chile, while the eastern portion is in Argentina. It forms the major landmass in an extended group of islands or archipelago also known as Tierra del Fuego.

Beagle Channel is a strait in the Tierra del Fuego Archipelago, on the extreme southern tip of South America between Chile and Argentina. The channel separates the larger main island of Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego from various smaller islands including the islands of Picton, Lennox and Nueva; Navarino; Hoste; Londonderry; and Stewart. The channel's eastern area forms part of the border between Chile and Argentina and the western area is entirely within Chile.
Santa Inés Island is an island in southern Chile, part of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago and of Punta Arenas municipality, lying south west of the Brunswick Peninsula, from which is separated by the Strait of Magellan and minor islands. It is the largest island of Punta Arenas municipality and the third largest of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago, after Isla Grande and Hoste Island. Its shoreline in this area is part of the Francisco Coloane Marine and Coastal Protected Area. The rest of the island is a part of the Alacalufes National Reserve, equalling that Desolación Island and the Córdova Peninsula. This latter is located in front of the island on the other side of the Strait of Magellan and is a peninsula of Riesco Island. The island belongs to the Tierra del Fuego archipelago.
Sarmiento may refer to:

Tierra del Fuego Province is one of four provinces in the southern Chilean region of Magallanes and Antártica Chilena (XII). It includes the Chilean or western part of the main island of Tierra del Fuego, except for the part south of the Cordillera Darwin, which is in Antártica Chilena Province.

Fagnano Lake, also called Lake Cami, is a lake located on the main island of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago, and shared by Argentina and Chile. The 645 km2 lake runs east–west for about 98 kilometres, of which 72.5 km (606 km2) belong to the Argentine Tierra del Fuego Province, and only 13.5 km (39 km2) belong to the Chilean Magallanes y la Antártica Chilena Region. It has a maximum depth of 449 meters. The southern bank is steep compared to the northern, and expands in a considerably wide and flat piedmont from which both levels of the plateaus can be appreciated. From its western end, the Azopardo River drains towards the Almirantazgo Fjord. On its eastern end is the town of Tolhuin. The lake is located in a pull-apart basin developed along the Magallanes–Fagnano Fault zone.
Tierra del Fuego Province may refer to:
Guanaco is an animal similar to the llama.
The Antarctic Floristic Kingdom, also the Holantarctic Kingdom, is a floristic kingdom that includes most areas of the world south of 40°S latitude. It was first identified by botanist Ronald Good, and later by Armen Takhtajan. The Antarctic Floristic Kingdom is a classification in phytogeography, different from the Antarctic realm classification in biogeography, and from Antarctic flora genera/species classifications in botany.

Tierra del Fuego National Park is a national park on the Argentine part of the island of Tierra del Fuego, within Tierra del Fuego Province in the ecoregion of Patagonic Forest and Altos Andes, a part of the subantarctic forest. Established on 15 October 1960 under the Law 15.554 and expanded in 1966, it was the first shoreline national park to be established in Argentina.

The Selk'nam genocide was the systematic extermination of the Selk'nam people, one of the three indigenous peoples of Tierra del Fuego, from the late 19th to early 20th centuries. Historians estimate that the genocide spanned a period of between ten and fifteen years, and resulted in the decline of the Selk'nam population from approximately 4,000 people during the 1880's to 500 by the early 1900's.

The governments of Chile and Argentina are attempting to eradicate the North American beaver in the Tierra del Fuego area at the southernmost tip of South America. This non-native species was introduced in 1946 as a potential source of commercial fur trading. When the putative fur trade industry failed, the beavers became problematic and the governments agreed to intervene to wipe them out. A June 2011 NPR report stated that the beavers have caused millions of dollars in damages. According to Nature, this plan is the largest eradication project ever attempted.

Between 1883 and 1906 Tierra del Fuego experienced a gold rush attracting many Chileans, Argentines and Europeans to the archipelago, including many Dalmatians. The gold rush led to the formation of the first towns in the archipelago and fueled economic growth in Punta Arenas. After the gold rush was over, most gold miners left the archipelago, while the remaining settlers engaged in sheep farming and fishing. The rush made a major contribution to the genocide of the indigenous Selk'nam people.

The Argentina–Chile border is the longest international border of South America and the third longest in the world after the Canada–United States border and the Kazakhstan–Russia border. With a length of 5,308 kilometres (3,298 mi), it separates Argentina from Chile along the Andes and on the islands of Tierra del Fuego. However, there are some border disputes, particularly around the Southern Patagonian Ice Field. It is the largest border of the two countries, beating the Argentina–Paraguay and Chile–Bolivia, Argentina's and Chile's second largest borders, respectively.

White on White is a 2019 Spanish-Chilean drama film directed by Théo Court. It was screened in the Horizons section at the 76th Venice International Film Festival. At the Venice Film Festival, Théo Court won the award for Best Director in the Horizons section. It was selected as the Chilean entry for the Best International Feature Film at the 94th Academy Awards.

The North American beaver is an invasive species in the southern tip of Patagonia, an area called Tierra del Fuego. Tierra del Fuego is a large island and encompasses land belonging to both Chile and Argentina, and as such, policies and actions to control and eradicate the species has mostly been binational. The beavers were introduced to the area in 1946 due to an effort by the Argentine government to establish a fur trade in the region. Ever since the introduction event, the beavers have spread throughout most of Tierra del Fuego and have even been recently spotted on the Brunswick Peninsula, mainland Chile.