The Grammy Award for Best Classical Contemporary Composition was first awarded in 1961. This award was not presented from 1967 to 1984.

Marin Alsop ['mɛər.ɪn 'æːl.sɑːp] is an American conductor and violinist. She is currently music director of both the Baltimore Symphony Orchestra and the São Paulo State Symphony Orchestra, and chief conductor designate of the Vienna Radio Symphony Orchestra.
Michael Nathaniel Hersch is an American composer and pianist.
Bells for Stokowski for Orchestra and for Symphonic Band by American composer Michael Daugherty, is a 14-minute, single-movement tribute to one of the most prominent 20th century conductors, Leopold Stokowski. Bells for Stokowski for Orchestra (2001) stands alone as a concert piece, however, it is also the last movement of the three-movement work, Philadelphia Stories. Philadelphia Stories was commissioned by the Philadelphia Orchestra in celebration of the Orchestra's centennial under the direction of Wolfgang Sawallisch. The premiere was performed by the Philadelphia Orchestra at the Academy of Music in Philadelphia, under the direction of David Zinman, in November 2001.
Metropolis Symphony for Orchestra (1988–93) by American composer Michael Daugherty is a five-movement symphony inspired by Superman comics. The entire piece was created over the span of five years with separate commissions for each movement. Individual movements may be performed separately; however, it is preferred that the 41 minute symphony be performed in its entirety. MetropolisSymphony was premiered by the Baltimore Symphony Orchestra, David Zinman conducting, in January 1994, at the Meyerhoff Concert Hall in Baltimore, Maryland.
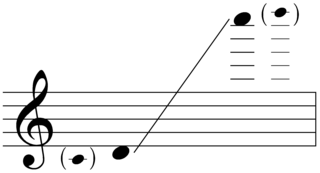
UFO for solo percussion and orchestra (1999) and for solo percussion and symphonic band (2000) by American composer Michael Daugherty, is a composition written for percussionist Evelyn Glennie.
Deus ex Machina is a piano concerto by the American composer Michael Daugherty. The 33-minute work was jointly commissioned by the Charlotte, Nashville, New Jersey, Rochester and Syracuse Symphony Orchestras. It won the 2011 Grammy for Best Classical Contemporary Composition for a recording by soloist Terrance Wilson and the Nashville Symphony Orchestra under the baton of Giancarlo Guerrero.
Route 66 is a single-movement composition for orchestra by the American composer Michael Daugherty. The piece was commissioned by the Kalamazoo Symphony Orchestra and premiered on April 25, 1998 at the Irving S. Gilmore International Keyboard Festival in East Lansing, Michigan under conductor Yoshimi Takeda.
Ghost Ranch is a three-movement orchestral composition by the American composer Michael Daugherty. Inspired by the life and work of artist Georgia O'Keeffe, the title is derived from the name of O'Keeffe's New Mexico summer home, Ghost Ranch. The piece was commissioned by BBC Radio 3, completed in 2005, and premiered February 8, 2006 in Poole, United Kingdom, with the Bournemouth Symphony Orchestra led by conductor Marin Alsop.
Rapture is an orchestral composition in one movement by the American composer Christopher Rouse. The work was commissioned by the Pittsburgh Symphony Orchestra and was completed January 9, 2000. It is dedicated to then Pittsburgh Symphony Orchestra music director Mariss Jansons and premiered in May 2000.
Sunset Strip is an orchestral composition in three movements by the American composer Michael Daugherty. The piece was composed in 1999 and premiered January 7, 2000 at the Ordway Center for the Performing Arts in Saint Paul, Minnesota, with conductor Hugh Wolff leading the Saint Paul Chamber Orchestra.
The Concerto for Orchestra is an orchestral composition by the American composer Christopher Rouse. The work was commissioned by the Cabrillo Festival of Contemporary Music and is dedicated to conductor and frequent Rouse collaborator Marin Alsop. The piece was completed February 24, 2008 and premiered at the festival August 1, 2008, with Marin Alsop leading the Cabrillo Festival Orchestra.
Loose Id is a single-movement composition for brass quintet and percussion—later expanded for orchestra—by the American composer Steven Bryant. The original brass quintet version premiered November 1995 at the University of North Texas and the full orchestral version premiered at Alice Tully Hall, New York City on April 1, 1997, with conductor Jeffrey Milarsky leading the Juilliard Symphony. The piece was Bryant's first composition for orchestra.
Raise the Roof is a one-movement concerto for timpani and orchestra by the American composer Michael Daugherty. The work was commissioned by the Detroit Symphony Orchestra for the opening of the Max M. Fisher Music Center. It was premiered in Detroit, October 16, 2003, with conductor Neeme Järvi leading the Detroit Symphony Orchestra and timpanist Brian Jones. Daugherty later arranged the piece for concert band in 2007; this arrangement was commissioned by the University of Michigan Symphony Band and was premiered under conductor Michael Haithcock at the National Conference of the College Band Directors National Association on March 30, 2007. Raise the Roof is one of Daugherty's most-programmed pieces and has been frequently performed as a concert opener since its publication.
Concerto 4-3 is a concerto for two violins, double bass, and orchestra in three movements by the American composer Jennifer Higdon. The work was commissioned for the string trio Time for Three by the Philadelphia Orchestra, the Pittsburgh Symphony Orchestra, and the Wheeling Symphony Orchestra. It was first performed in Philadelphia on January 10, 2008, by Time for Three and the Philadelphia Orchestra conducted by Christoph Eschenbach.
American Gothic is an orchestral composition by the American composer Michael Daugherty. The approximately 20-minute work is composed in three movements inspired by the paintings of the Iowan artist Grant Wood (1891-1942). Daugherty is a native of Cedar Rapids, Iowa, where the piece premiered on May 4, 2013, at Cedar Rapids' Paramount Theatre, with Timothy Hankewich, conductor.
Masquerade is a single-movement orchestral composition by the British-born composer Anna Clyne. The work was commissioned by the BBC and it was first performed on September 7, 2013 at the Last Night of the Proms by the BBC Symphony Orchestra under conductor Marin Alsop. Clyne dedicated the piece to the Proms' concertgoers colloquially known as the "Prommers".
The Boston Concerto is a concerto for orchestra by the American composer Elliott Carter. The work was commissioned by the Boston Symphony Orchestra, for which the piece is titled. It was first performed in Symphony Hall, Boston, on April 3, 2003 by the Boston Symphony Orchestra under the conductor Ingo Metzmacher. Carter dedicated the concerto to his wife Helen Jones Carter, who died on May 17, 2003.
Berceuse Infinie is an orchestral composition by the American composer Christopher Rouse. The work was commissioned by the Baltimore Symphony Orchestra and was completed on July 1, 2016. It was first performed by the Baltimore Symphony Orchestra under the direction of Marin Alsop at Joseph Meyerhoff Symphony Hall on November 30, 2017. The piece is dedicated to Marin Alsop.
The Percussion Concerto is a composition for solo percussion and orchestra by the Scottish composer Helen Grime. The work was commissioned by the Southbank Centre, the Baltimore Symphony Orchestra, and the Swedish Chamber Orchestra. It was first performed by the percussionist Colin Currie and the London Philharmonic Orchestra conducted by Marin Alsop at the Royal Festival Hall, London, on 16th January 2019.