The history of North Macedonia encompasses the history of the territory of the modern state of North Macedonia.

Saint Helena is one of the three constituent parts of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha, a British overseas territory located in the South Atlantic Ocean. Saint Helena is a remote volcanic tropical island 1,950 km (1,210 mi) west of the coast of south-western Africa, and 4,000 km (2,500 mi) east of Rio de Janeiro in South America.

Helena is the capital city of the U.S. state of Montana and the seat of Lewis and Clark County.
Forum or The Forum may refer to:

"Denes nad Makedonija" is the national anthem of North Macedonia. Todor Skalovski composed the music and Vlado Maleski wrote the lyrics of the song in the early 1940s. It was adopted as the national anthem in 1992, almost a year after the state's independence from Yugoslavia. Before its adoption as a national anthem, it was used as the regional anthem of the Socialist Republic of Macedonia, a constituent state of Yugoslavia, before it became the national anthem of the Republic of North Macedonia.

The White Tower of Thessaloniki is a monument and museum on the waterfront of the city of Thessaloniki, capital of the region of Macedonia in northern Greece. The present tower replaced an old Byzantine fortification, known to have been mentioned around the 12th century, that the Ottoman Empire reconstructed to fortify the city's fortress some time after Sultan Murad II captured Thessaloniki in 1430. During the period of Ottoman rule, the tower became a notorious prison and the scene of numerous mass executions, most famously of the Janissaries who revolted during the reign of Mahmud II.
Macedonia most commonly refers to:

Antigonus III Doson was king of Macedon from 229 BC to 221 BC. He was a member of the Antigonid dynasty. He was called Euergetes, Soter and Guardian (ἐπίτροπος) as he was the guardian of Philip V of Macedon.
Arkansas is a Southern state of the United States. Arkansas's musical heritage includes country music and various related styles like bluegrass and rockabilly.

North Macedonia has participated in the Eurovision Song Contest 21 times since its official debut in 1998. The country had attempted to participate in 1996, but failed to qualify from the audio-only qualifying round. The current Head of Delegation is Meri Popova.
Skopje Fest, officially Festival na zabavni melodii Skopje, is one of the main musical events in North Macedonia, and formerly in Yugoslavia. The show, organized by national broadcaster Macedonian Radio Television (MRT), involves some of North Macedonia's most popular performers, singing original tracks usually accompanied by the orchestra of MRT.
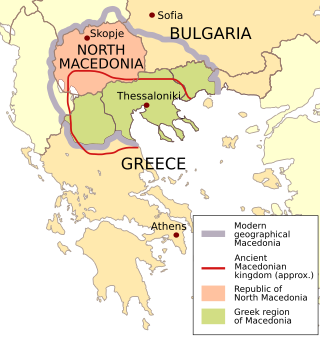
The use of the country name "Macedonia" was disputed between Greece and the Republic of Macedonia between 1991 and 2019. The dispute was a source of instability in the Western Balkans for 25 years. It was resolved through negotiations between Athens and Skopje, mediated by the United Nations, resulting in the Prespa agreement, which was signed on 17 June 2018. Pertinent to its background is an early 20th-century multifaceted dispute and armed conflict that formed part of the background to the Balkan Wars. The specific naming dispute, although an existing issue in Yugoslav–Greek relations since World War II, was reignited after the breakup of Yugoslavia and the newly-gained independence of the former Socialist Republic of Macedonia in 1991. Since then, it was an ongoing issue in bilateral and international relations until it was settled with the Prespa agreement in June 2018, the subsequent ratification by the Macedonian and Greek parliaments in late 2018 and early 2019 respectively, and the official renaming of Macedonia to North Macedonia in February 2019.

The Constitution of the Republic of North Macedonia is a codified constitution outlining North Macedonia's system of government and basic human rights. It was adopted in the Parliament of the then-Republic of Macedonia on 17 November 1991.

Alexis Tsipras is a Greek politician who served as Prime Minister of Greece from 2015 to 2019.

The accession of North Macedonia to the European Union has been on the current agenda for future enlargement of the EU since 2005, when it became an official candidate for accession. The Republic of Macedonia submitted its membership application in 2004, thirteen years after its independence from Yugoslavia. It is one of nine current EU candidate countries, together with Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Georgia, Moldova, Montenegro, Serbia, Turkey and Ukraine.

North Macedonia is a member state of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). In 1995, the country joined the Partnership for Peace. It then began taking part in various NATO missions, including the International Security Assistance Force and the Resolute Support Mission in Afghanistan. At the 2008 Bucharest summit, Greece vetoed the country's invitation to join; however, NATO member states agreed that the country would receive an invitation upon resolution of the Macedonia naming dispute. Following an agreement in June 2018 to rename the country, representatives of NATO member states signed a protocol on the accession of North Macedonia to NATO on 6 February 2019. Over the next thirteen months, all of NATO's 29 member states ratified the protocol. The accession protocol entered into force on 19 March 2020, allowing North Macedonia to deposit its instrument of accession and thereby become NATO's 30th member state on 27 March 2020.

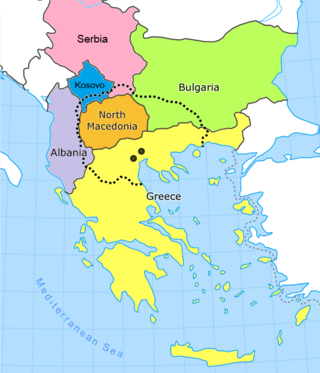
North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe. It shares land borders with Kosovo to the northwest, Serbia to the north, Bulgaria to the east, Greece to the south, and Albania to the west. It constitutes approximately the northern third of the larger geographical region of Macedonia. Skopje, the capital and largest city, is home to a quarter of the country's 1.83 million people. The majority of the residents are ethnic Macedonians, a South Slavic people. Albanians form a significant minority at around 25%, followed by Turks, Roma, Serbs, Bosniaks, Aromanians and a few other minorities.

The Prespa Agreement, also known as the Treaty of Prespa, the Prespes deal or the Prespa accord, is an agreement reached in 2018 between Greece and the then-Republic of Macedonia, under the auspices of the United Nations, resolving a long-standing dispute between the two countries. Apart from resolving the terminological differences, the agreement also covers areas of cooperation between the two countries in order to establish a strategic partnership.

Early parliamentary elections were held in North Macedonia on 15 July 2020. It was originally scheduled for November 2020, but Prime Minister Zoran Zaev called early elections after the European Council failed to come to an agreement on starting talks with North Macedonia on joining the European Union in October 2019. The election date was set for 12 April, but was postponed until July due to the COVID-19 pandemic in North Macedonia.

Albania–North Macedonia relations are diplomatic relations between the Republic of Albania and the Republic of North Macedonia. Both countries are full members of the Council of Europe and of the NATO. Both began European Union accession negotiations in March 2020. The Albanian language is an official language in Albania, while also being an official language in Macedonia on a municipal level, if the ethnic Albanian population exceeds 20%, and ethnic Albanians make up the second largest community in North Macedonia.















