Agesilaus II was king of Sparta from c. 400 to c. 360 BC. Generally considered the most important king in the history of Sparta, Agesilaus was the main actor during the period of Spartan hegemony that followed the Peloponnesian War. Although brave in combat, Agesilaus lacked the diplomatic skills to preserve Sparta's position, especially against the rising power of Thebes, which reduced Sparta to a secondary power after its victory at Leuctra in 371 BC.
Alexander was Tyrant or Despot of Pherae in Thessaly, ruling from 369 to c. 356 BC. Following the assassination of Jason, the tyrant of Pherae and Tagus of Thessaly, in 370 BC, his brother Polyphron ruled for a year, but he was then poisoned by Alexander who assumed power himself. Alexander governed tyrannically and was constantly seeking to control Thessaly and the kingdom of Macedonia. He also engaged in piratical raids on Attica. Alexander was murdered by Tisiphonus, Lycophron and Peitholaus, the brothers of his wife, Thebe, as it was said that she lived in fear of her husband and hated Alexander's cruel and brutal character.

The Peloponnesian War was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided for a long time, until the decisive intervention of the Persian Empire in support of Sparta. Led by Lysander, the Spartan fleet, built with Persian subsidies, finally defeated Athens and started a period of Spartan hegemony over Greece.

Epaminondas was a Greek general and statesman of the 4th century BC who transformed the Ancient Greek city-state of Thebes, leading it out of Spartan subjugation into a pre-eminent position in Greek politics called the Theban Hegemony. In the process, he broke Spartan military power with his victory at Leuctra and liberated the Messenian helots, a group of Peloponnesian Greeks who had been enslaved under Spartan rule for some 230 years following their defeat in the Third Messenian War ending in 600 BC. Epaminondas reshaped the political map of Greece, fragmented old alliances, created new ones, and supervised the construction of entire cities. He was also militarily influential and invented and implemented several important battlefield tactics.

Pelopidas was an important Theban statesman and general in Greece, instrumental in establishing the mid-fourth century Theban hegemony.

Arses, known by his regnal name Artaxerxes II, was King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 405/4 BC to 358 BC. He was the son and successor of Darius II and his mother was Parysatis.
The polis of Sparta was the greatest military land power of classical Greek antiquity. During the Classical period, Sparta governed, dominated or influenced the entire Peloponnese. Additionally, the defeat of the Athenians and the Delian League in the Peloponnesian War in 431–404 BC resulted in a short-lived Spartan dominance of the southern Greek world from 404 to 371 BC. Due to their mistrust of others, Spartans discouraged the creation of records about their internal affairs. The only histories of Sparta are from the writings of Xenophon, Thucydides, Herodotus and Plutarch, none of whom were Spartans. Plutarch was writing several centuries after the period of Spartan hegemony had ceased. This creates difficulties in understanding the Spartan political system, which was distinctly different from any other Greek polis.

Timoleon, son of Timodemus, of Corinth was a Greek statesman and general.

Pharnabazus II was a Persian soldier and statesman, and Satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia. He was the son of Pharnaces II of Phrygia and grandson of Pharnabazus I, and great-grandson of Artabazus I. He and his male ancestors, forming the Pharnacid dynasty, had governed the satrapy of Hellespontine Phrygia from its headquarters at Dascylium since 478 BC. He married Apama, daughter of Artaxerxes II of Persia, and their son Artabazus also became a satrap of Phrygia. According to some accounts, his granddaughter Barsine may have become Alexander the Great's concubine.

The Corinthian War was a conflict in ancient Greece which pitted Sparta against a coalition of city-states comprising Thebes, Athens, Corinth and Argos, backed by the Achaemenid Empire. The war was caused by dissatisfaction with Spartan imperialism in the aftermath of the Peloponnesian War, both from Athens, the defeated side in that conflict, and from Sparta's former allies, Corinth and Thebes, who had not been properly rewarded. Taking advantage of the fact that the Spartan king Agesilaus II was away campaigning in Asia against the Achaemenid Empire, Thebes, Athens, Corinth and Argos forged an alliance in 395 BC with the goal of ending Spartan hegemony over Greece; the allies' war council was located in Corinth, which gave its name to the war. By the end of the conflict, the allies had failed to end Spartan hegemony over Greece, although Sparta was durably weakened by the war.

The Battle of Coronea in 394 BC, also Battle of Coroneia, took place during the Corinthian War, in which the Spartans and their allies under King Agesilaus II defeated a force of Thebans and Argives that was attempting to block their march back into the Peloponnese. It ranks among the deadliest of the Hoplite battles, despite its comparative obscurity, when matched up against more famous battles like the Battle of Delium in 424, and the Battle of Mantinea in 362.

The Battle of Cnidus was a military operation conducted in 394 BC by the Achaemenid Empire against the Spartan naval fleet during the Corinthian War. A fleet under the joint command of Pharnabazus and former Athenian admiral, Conon, destroyed the Spartan fleet led by the inexperienced Peisander, ending Sparta's brief bid for naval supremacy.

Iphicrates was an Athenian general, who flourished in the earlier half of the 4th century BC. He is credited with important infantry reforms that revolutionized ancient Greek warfare by regularizing light-armed peltasts.

The Battle of the Crimissus was fought in 339 BC between a large Carthaginian army commanded by Asdrubal and Hamilcar and an army from Syracuse led by Timoleon. Timoleon attacked the Carthaginian army by surprise near the Crimissus river in western Sicily and won a great victory. When he defeated another much smaller force of Carthaginians shortly afterwards, Carthage sued for peace. The peace allowed the Greek cities on Sicily to recover and began a period of stability. However, another war between Syracuse and Carthage erupted after Timoleon's death, not long after Agathocles seized power in 317 BC.
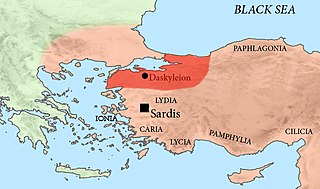
Ariobarzanes, sometimes known as Ariobarzanes I of Cius, was a Persian Satrap of Phrygia and military commander, leader of an independence revolt, and the first known of the line of rulers of the Greek town of Cius who eventually were to stem the kings of Pontus in the 3rd century BCE. Ariobarzanes was apparently a cadet member of the Achaemenid dynasty, possibly son of Pharnabazus II, and part of the Pharnacid dynasty which had settled to hold Dascylium of Hellespont in the 470s BCE. Cius is located near Dascylium, and Cius seemingly was a share of family holdings for the branch of Ariobarzanes.

The Battle of Nemea, also known in ancient Athens as the Battle of Corinth, was a battle in the Corinthian War, between Sparta and the coalition of Argos, Athens, Corinth, and Thebes. The battle was fought in Corinthian territory, at the dry bed of the Nemea River. The battle was a decisive Spartan victory, which, coupled with the Battle of Coronea later in the same year, gave Sparta the advantage in the early fighting on the Greek mainland.

The Second Athenian League was a maritime confederation of Greek city-states that existed from 378 to 355 BC under the leadership (hegemony) of Athens. The alliance represented a partial revival of the Delian League, which had been disbanded in 404 BC following the defeat of Athens in the Peloponnesian War. The new League was centered in the Aegean and included over 60 states, among which were Kos, Mytilene, Rhodes, and Byzantium. It was primarily formed as a defensive alliance against Sparta and secondly the Persian Empire. The new League's main objective was to preserve peace in Greece and counterbalance Sparta's growing hegemony and aggression. The League largely revived Athenian influence in the Greek world, reestablishing it as the strongest naval power in the eastern Mediterranean. This time, Athens made conscious efforts to avoid the strict terms that had eventually rendered the previous Delian League unpopular. The alliance lasted until 355 BC, when most of the allied cities became independent following the Social War that broke out in 357 BC.

The Great Satraps' Revolt, or the Revolts of the Satraps, was a rebellion in the Achaemenid Empire of several satraps in western Anatolia against the authority of the Great King Artaxerxes II. The Satraps who revolted were Datames, Ariobarzanes, Orontes, Autophradates, and Mausolus. The timing of their revolts varied, as did the circumstances that induced them to rebel. Though often portrayed as a general uprising, there was little coordination among them and at no time did they actually threaten Artaxerxes directly. Their efforts were aimed at secession rather than a takeover of the Empire.

The Theban–Spartan War of 378–362 BC was a series of military conflicts fought between Sparta and Thebes for hegemony over Greece. Sparta had emerged victorious from the Peloponnesian War against Athens, and occupied an hegemonic position over Greece. However, the Spartans' violent interventionism upset their former allies, especially Thebes and Corinth. The resulting Corinthian War ended with a difficult Spartan victory, but the Boeotian League headed by Thebes was also disbanded.

The siege of Syracuse from 344 to 343/342 BC was part of a war between the Syracusan general Hicetas and the tyrant of Syracuse, Dionysius II. The conflict became more complex when Carthage and Corinth became involved. The Carthaginians had made an alliance with Hicetas to expand their power in Sicily. Somewhat later, the Corinthian general Timoleon arrived in Sicily to restore democracy to Syracuse. With the assistance of several other Sicilian Greek cities, Timoleon emerged victorious and reinstated a democratic regime in Syracuse. The siege is described by the ancient historians Diodorus Siculus and Plutarch, but there are important differences in their accounts.

















