Career
Early Employment
After graduating from Cornell University in 1956, and completing his ROTC commitment, Slater settled in Atlanta, Georgia he was hired by a division of Textron to sell polyethylene products in five southeastern states.
Slater moved to New Orleans in late 1957 and joined Uarco, Inc., a company that manufactured carbon-free business forms for invoices, shipping documentation, and other record keeping forms where duplication was necessary. His sales region included the Southern states.
In 1959, Slater founded Gulf Poly Plastics, which fabricated customized fabrication of industrial Plexiglas, Teflon, polyester and fiberglass to the Louisiana "oil patch" and shipping industries. The distribution company was located in a warehouse on Tchoupitoulas Street.
Given Slater’s experience and knowledge with plastics, he started a new company called "Sea Foam" in 1962. Sea Foam was sprayed as a precise mixture of synthetic resin and hardener which expanded into foam in the hollow structure of oil drilling rigs to keep the structure afloat should the sub-surface rig become punctured or cracked.
Because of the inherent operating risks of working in ship yards and off-shore, Slater discontinued his work with sea foam in 1969 and became a business broker specializing in helping companies find buyers and sellers for many small and medium-sized family businesses that provided goods and services in the growing petroleum industry.
Slater is a lifelong student of the financial markets and became fascinated with the commodity markets and the use of graphical technical analysis tools to analyze them. He drew a large number of financial charts by hand and subscribed to a number of charting services for those markets he could not follow on a day-to-day basis. Updating the charts was a laborious task and trying to calculate technical studies and apply these to the charts was even more difficult. Therefore, Slater used acetate slides to overlay studies onto the charts to identify trend movements.
In 1979, with the acquisition of a Texas Instruments TI-59 programmable calculator which was capable of holding 5000 program steps and a magnetic card reader for data storage, Slater was able to program the device to calculate basic technical analysis computations. [1] The problem of drawing the charts by hand which was time consuming and prone to error, remained.
Kaf Trac Newsletter
Slater knew the limitation of the small calculator would not keep up with the growing number of technical analysis studies that were being shared and developed, such as the Relative Strength Index, Stochastic oscillator, Exponential Moving Average, and other momentum-based technical analysis indicators. In 1972, Slater began to use the shared computer facilities at Tulane University, and working with a number of computer science graduate students, began to produce tables of daily, weekly and monthly, closing market prices along with their corresponding technical analysis study. Subsequently, Slater began publishing a weekly newsletter on Fridays called, “Kaf-Trac” which focused on gold mining stock and the spot and futures market. The weekly letter consisted mainly of closing prices and technical analysis data presented in a tabular format. The circulation never exceeded 200.
CompuTrac
The CompuTrac program began its early development in 1977 when Slater realized that the Apple II computer, could read large amounts of data, calculate the technical indicators and display graphics on its 10-inch monochrome green screen. However, with no programming experience, Slater was led to the computer science department at Loyola University of New Orleans and met Professor James Schmit. With Tim’s understanding of the commodity markets and Jim’s knowledge of the BASIC programming language for the personal Computer, they planned, programmed, and completed the first commercial CompuTrac version 1.0 in July 1977. [2]
The first office was set up in Slater’s home in the Garden District, New Orleans. Schmit transitioned from university teaching and began to manage a small part-time team of programmers drawn mostly from among his students. Slater handled marketing, sales, and contributed to product strategy by consulting with a growing pool of other traders and technical analysts who took a keen interest in the CompuTrac software by contributing to its library of technical analysis studies and tools.
To help finance the very early development of Compu Trac, Slater approached three fellow market technicians who were following his early progress in commercializing the first version. Walter Bressert, Jim Sibbett, Richard L. Redmont along with Tim Slater, its founder, were the original "members" of the TAG group. The company was incorporated as the "Technical Analysis Group" or TAG for short. Shares were issued to Slater, Schmit and the group's early investors.
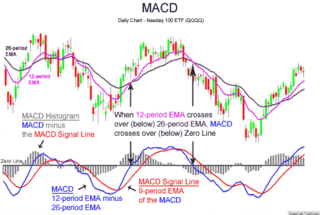
Many of the technical indicators and studies used today were first implemented and popularized in CompuTrac. The Stochastic oscillator study, for example was programmed from the work of George Lane and Ralph Dystant. The indicator's lines were named "%K" and %D" but Slater needed a single name which was more accessible and the word "stochastic" was written on the paper, so he gave the study that name, and it has persisted. [3] Another example is the Moving Average Convergence/Divergence (MACD) study by Gerald Appel. [4]
TAG Seminars
Slater realized that the collective knowledge of technicians across the United States was important for the future development of CompuTrac and it proved to be a successful marketing tool to establish the company as innovators in the industry by educating traders on the technical analysis tools that exist to understand market trends. The seminars also had a “cult” following because it gathered together the pioneers of the industry and allowed technical analysts to network and share trading ideas. [4]
CompuTrac conducted 22 seminars in the United States. The events were called TAG for “Technical Analysis Group” (TAG) Seminars. The first TAG conference was held in New Orleans in 1979 and the final TAG XXII was held in Las Vegas in 1999.
At each event CompuTrac recorded, on cassette tape, all the speaker presentations. Over the years CompuTrac built an archive of over 400 recordings from all twenty two events. Subsequently, CompuTrac members could acquire the tapes and documentation and allow self-study. The TAG events were instrumental in helping to educate individual and institutional traders to the advances of technical analysis and continue to increase sales of the CompuTrac software. [5]
Technical Analysis Group Seminar (TAG) I – New Orleans, Louisiana 1980 Technical Analysis Group Seminar (TAG)I I – New Orleans, Louisiana 1981 Technical Analysis Group Seminar (TAG)III – Toronto, Canada 1982 Technical Analysis Group Seminar (TAG) IV – San Francisco, California 1983 Technical Analysis Group Seminar (TAG) V – New Orleans, Louisiana 1984 Technical Analysis Group Seminar (TAG) VI – New Orleans, Louisiana 1985 Technical Analysis Group Seminar (TAG) VII –Boston, Massachusetts 1985 Technical Analysis Group Seminar (TAG) VIII – New Orleans, Louisiana 1986 Technical Analysis Group Seminar (TAG) IX – San Francisco, California 1987 Technical Analysis Group Seminar (TAG) X – Washington D.C. 1988 Technical Analysis Group Seminar (TAG) XI – New Orleans, Louisiana 1989 Technical Analysis Group Seminar (TAG) XII – Los Angeles, California 1990 Technical Analysis Group Seminar (TAG) XIII – Washington D.C. 1991 Technical Analysis Group Seminar (TAG) XIV – New Orleans, Louisiana 1992 Technical Analysis Group Seminar (TAG) XV – Las Vegas, Nevada 1993 Technical Analysis Group Seminar (TAG) XVI – Las Vegas, Nevada 1994 Technical Analysis Group Seminar (TAG) XVII – Las Vegas, Nevada 1995 Technical Analysis Group Seminar (TAG) XVIII – New Orleans, Louisiana 1996 Technical Analysis Group Seminar (TAG) XIX – Las Vegas, Nevada 1997 Technical Analysis Group Seminar (TAG) XX – Las Vegas, Nevada 1998
Telerate acquires CompuTrac
In June 1986 CompuTrac launched the "Teletrac" charting and analysis system which operated using real-time data and used a proprietary hardware platform designed by Schmit and his engineering group. Leverage Telerate's large domestic and international institutional subscriber base, the product covered, charting for commodities, indices, the spot foreign exchange and fixed income markets. Teletrac offered 32 technical analysis indicators, intra-day charting time frames of 5 minute, hourly, daily, weekly and monthly and the ability to perform algorithmic system testing. [6]
In order to grow the company further and maximize the success of Teletrac, Slater knew that real-time data would be required to market the software to financial institutions. After declining to sell CompuTrac to Reuters, Slater approached Telerate, a real-time financial information company that was affiliated with Cantor-Fitzgerald, a primary U.S. Treasuries brokerage firm. CompuTrac was acquired by Telerate in October 1985 and re-branded as "TeleTrac". [6]
In 1987, Kyodo News Service, which was the Japanese distributor for Telerate's market data services, formed the "Value-Added Sales Team", headed by Peter Jaeger, and began marketing TeleTrac in Tokyo.
Dow Jones Seminars
Dow Jones & Company purchased the remaining shares of Telerate on September 22, 1989 [7] and CompuTrac was transferred to its new owners. The business continued to grow very well for the Teletrac product, however, sales of CompuTrac began to slow. Dow Jones decided to end the support and development of Compu Trac on April 25, 1994. [8] Slater was asked to remain with Dow Jones Telerate and continue his leadership with the TAG events which was growing into larger, multi-stream conferences in the United States, Europe and Asia. With the cooperation of Dow Jones, Slater set up a separate division called, Dow Jones Seminars and assumed the role of President of the division. In 1999 Slater organized his last seminar for Dow Jones and retired.
Personal life
Tim Slater was born to Louis Charles Slater (December 26, 1898 – November 10, 1958) and D. Slater (November 26, 1910 – November 10, 1958). In 1937, Louis Slater accepted a job as Sales Manager for the Southern Region with the Fulton Bag and Cotton Mills and moved the family to New Orleans, Louisiana from Milwaukee, Wisconsin. The family first moved to a house at 2607 Coliseum Street in the Garden District. In 1942 Louis and Dorothy moved to 1745 Arabella Street and then built a new home in the Garden District in 1957 where Slater currently resides with his wife.
Slater attended Choate Rosemary Hall preparatory school in from 1946 to 1950, however, he graduated from Isidore Newman School, in New Orleans in 1952. He attended Cornell University in Ithaca, New York. As a freshman, he planned to earn a degree in mechanical engineering, however he switched to Economics in his second year. He was a member of the Seal and Serpent fraternity and enlisted in the universities ROTC program.
After graduation in 1956, he completed his ROTC commitments with the United States Army reserve in Fort Lee, New Jersey and was discharged in 1963 from the U.S. Army Reserves with the rank of Second Lieutenant.