Related Research Articles

Telehealth is the distribution of health-related services and information via electronic information and telecommunication technologies. It allows long-distance patient and clinician contact, care, advice, reminders, education, intervention, monitoring, and remote admissions. Telemedicine is sometimes used as a synonym, or is used in a more limited sense to describe remote clinical services, such as diagnosis and monitoring. When rural settings, lack of transport, a lack of mobility, conditions due to outbreaks, epidemics or pandemics, decreased funding, or a lack of staff restrict access to care, telehealth may bridge the gap as well as provide distance-learning; meetings, supervision, and presentations between practitioners; online information and health data management and healthcare system integration. Telehealth could include two clinicians discussing a case over video conference; a robotic surgery occurring through remote access; physical therapy done via digital monitoring instruments, live feed and application combinations; tests being forwarded between facilities for interpretation by a higher specialist; home monitoring through continuous sending of patient health data; client to practitioner online conference; or even videophone interpretation during a consult.
eHealth describes healthcare services which are supported by digital processes, communication or technology such as electronic prescribing, Telehealth, or Electronic Health Records (EHRs). The term "eHealth" originated in the 1990s, initially conceived as "Internet medicine," but has since evolved to have a broader range of technologies and innovations aimed at enhancing healthcare delivery and accessibility. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), eHealth encompasses not only internet-based healthcare services but also modern advancements such as artificial intelligence, mHealth, and telehealth, which collectively aim to improve accessibility and efficiency in healthcare delivery. Usage of the term varies widely. A study in 2005 found 51 unique definitions of eHealth, reflecting its diverse applications and interpretations. While some argue that it is interchangeable with health informatics as a broad term covering electronic/digital processes in health, others use it in the narrower sense of healthcare practice specifically facilitated by the Internet. It also includes health applications and links on mobile phones, referred to as mHealth or m-Health.. Key components of eHealth include electronic health records (EHRs), telemedicine, health information exchange, mobile health applications, wearable devices, and online health information. For example, diabetes monitoring apps allow patients to track health metrics in real time, bridging the gap between home and clinical care. These technologies enable healthcare providers, patients, and other stakeholders to access, manage, and exchange health information more effectively, leading to improved communication, decision-making, and overall healthcare outcomes.
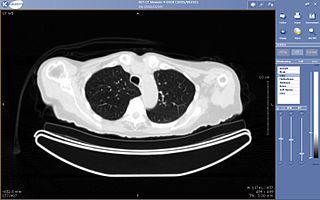
Teleradiology is the transmission of radiological patient images from procedures such as x-rays photographs, Computed tomography (CT), and MRI imaging, from one location to another for the purposes of sharing studies with other radiologists and physicians. Teleradiology allows radiologists to provide services without actually having to be at the location of the patient. This is particularly important when a sub-specialist such as an MRI radiologist, neuroradiologist, pediatric radiologist, or musculoskeletal radiologist is needed, since these professionals are generally only located in large metropolitan areas working during daytime hours. Teleradiology allows for specialists to be available at all times.
Health advocacy or health activism encompasses direct service to the individual or family as well as activities that promote health and access to health care in communities and the larger public. Advocates support and promote the rights of the patient in the health care arena, help build capacity to improve community health and enhance health policy initiatives focused on available, safe and quality care. Health advocates are best suited to address the challenge of patient-centered care in our complex healthcare system. The Institute of Medicine (IOM) defines patient-centered care as: Health care that establishes a partnership among practitioners, patients, and their families to ensure that decisions respect patients' wants, needs, and preferences and that patients have the education and support they need to make decisions and participate in their own care. Patient-centered care is also one of the overreaching goals of health advocacy, in addition to safer medical systems, and greater patient involvement in healthcare delivery and design.

The New England Hospital for Women and Children was founded by Marie Zakrzewska on July 1, 1862. The hospital's goal was to provide patients with competent female physicians, educate women in the study of medicine, and train nurses to care for the sick. Until 1951, the hospital remained dedicated to women, it was then renamed to New England Hospital to include male patients. The hospital was renamed again to the Dimock Community Health Center in 1969. At present, that institution provides a range of healthcare services including adult & pediatric primary care, women's healthcare, and HIV/AIDS specialty care.

mHealth is an abbreviation for mobile health, a term used for the practice of medicine and public health supported by mobile devices. The term is most commonly used in reference to using mobile communication devices, such as mobile phones, tablet computers and personal digital assistants (PDAs), and wearable devices such as smart watches, for health services, information, and data collection. The mHealth field has emerged as a sub-segment of eHealth, the use of information and communication technology (ICT), such as computers, mobile phones, communications satellite, patient monitors, etc., for health services and information. mHealth applications include the use of mobile devices in collecting community and clinical health data, delivery/sharing of healthcare information for practitioners, researchers and patients, real-time monitoring of patient vital signs, the direct provision of care as well as training and collaboration of health workers.
Connected health is a socio-technical model for healthcare management and delivery by using technology to provide healthcare services remotely. Connected health, also known as technology enabled care (TEC) aims to maximize healthcare resources and provide increased, flexible opportunities for consumers to engage with clinicians and better self-manage their care. It uses readily available consumer technologies to deliver patient care outside of the hospital or doctor's office. Connected health encompasses programs in telehealth, remote care, and disease and lifestyle management. It often leverages existing technologies, such as connected devices using cellular networks, and is associated with efforts to improve chronic care. However, there is an increasing blur between software capabilities and healthcare needs whereby technologists are now providing the solutions to support consumer wellness and provide the connectivity between patient data, information and decisions. This calls for new techniques to guide Connected Health solutions such as "design thinking" to support software developers in clearly identifying healthcare requirements, and extend and enrich traditional software requirements gathering techniques.
Virtual Hospital is an international non-government organization that operates as part of Virtual Healthcare Limited. Virtual Hospital uses telemedicine to deliver medical care to the developing world.
The Lopez Family Foundation is an American nonprofit organization founded by sisters, Jennifer Lopez and Lynda Lopez in 2009. Although the sisters had wanted to create a charitable foundation for years, it wasn't until Jennifer's daughter Emme experienced a medical scare when they did. At the age of three weeks, a bump was discovered on Emme's head. Although she was okay, Jennifer felt that there are mothers and children who didn't have proper medical care and access to health systems. The sisters then partnered with Children's Hospital Los Angeles and the Telemedicine program to develop 'The Maribel Foundation'. It was named after Jennifer's then-husband Marc Anthony's sister Maribel, who died due to a brain cancer at age 8. While also partnering with companies such as Samsung and Best Buy, the foundation works to increase the availability of health care and health education to the less fortunate. As of 2012, its name has been changed to The Lopez Family Foundation. The foundation's slogan is Where children are concerned, there is no time to lose.

Neel Shah is an American physician, Harvard University assistant professor, Chief Medical Officer of Maven Clinic, and founder of the nonprofit organizations Costs of Care and March for Moms. Shah is married to MIT Professor Julie Shah.
Digital health is a discipline that includes digital care programs, technologies with health, healthcare, living, and society to enhance the efficiency of healthcare delivery and to make medicine more personalized and precise. It uses information and communication technologies to facilitate understanding of health problems and challenges faced by people receiving medical treatment and social prescribing in more personalised and precise ways. The definitions of digital health and its remits overlap in many ways with those of health and medical informatics.
Electronic consultation is an aspect of telemedicine which involves remote communication between patients and clinicians, or between clinicians and specialists.
American Well Corporation, doing business as Amwell, is a telemedicine company based in Boston, Massachusetts, that connects patients with doctors over secure video. Amwell sells its platform as a subscription service to healthcare providers to put their medical professionals online and its proprietary software development kits, APIs, and system integrations enable clients to embed telehealth into existing workflows utilized by providers and patients.
Pager, Inc. is a virtual care platform that offers a variety of services to guide patients and health plan members through the healthcare journey. Pager offers virtual nurse chat and triage, appointment scheduling with assistance from care coordinators, telemedicine, aftercare follow-up, and more while implementing artificial intelligence on its platform.
Daniel Carlin is the founder and CEO of the connected care telemedicine practice WorldClinic. He is a former U.S. Navy chief medical officer who has served as a refugee camp physician on the Afghanistan–Pakistan frontier. Carlin is board certified in Emergency Medicine and holds a consultant-staff appointment at Lahey Hospital and Medical Center in suburban Boston. He has been in practice for 29 years.

Teladoc Health, Inc. is a multinational telemedicine and virtual healthcare company headquartered in the United States. Primary services include telehealth, medical opinions, AI and analytics, telehealth devices and licensable platform services. In particular, Teladoc Health uses telephone and videoconferencing software as well as mobile apps to provide on-demand remote medical care.
Satmed is a satellite-based eHealth communications platform, in particular for provision of eHealth to remote, resource-poor areas of emerging and developing countries. It aims to provide services to non-governmental organisations (NGOs) that provide healthcare, education or health management services, governmental organisations that support regional development programs and humanitarian operations, and institutions such as medical universities, hospitals and health management institutions.
Dara Kass is an emergency medicine physician and a consultant in healthcare policy and impact. She is also an advocate for advancing the careers of women in medicine. She is a longtime advocate for advancing the careers of women in medicine. While treating patients during the Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic, Kass became infected and shared her disease course, becoming a public health messenger in the process. Since the Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization supreme court decision, she has focused on healthcare policy and advocacy related to reproductive healthcare, specifically on the care patients receive in Emergency Departments.

Rumi Chunara is a computer scientist who is an associate professor of biostatistics at the New York University School of Global Public Health. She develops computational and statistical approaches to acquire, integrate and make use of data improve population-level public health.

Dr. Véronique Inès Thouvenot is a medical doctor, scientific director, and specialist in public and humanitarian health with a focus in eHealth and Telemedicine since 2002. She was named in BBC's 100 women, as one of the 100 inspiring and influential women from around the world for 2019. She is co-founder of Zero Mothers Die and Fundación Millenia2025 focused on women empowerment and equality, and has held senior positions at the United Nations and the World Health Organization.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "Ting Shih". Cartier Women's Initiative. Cartier Women's Initiative. Retrieved 4 November 2016.
- 1 2 "Ting Shih, 'Saving People' through Innovative ClickMedix". Asian Fortune News. Asian Fortune News. Retrieved 4 November 2016.
- 1 2 3 Cegielski, Emily. "Entrepreneur wants to bring "one-click health care" to the world". The New York Times. Retrieved 4 November 2016.
- 1 2 "ClickMedix: enabling women to become the virtual eyes and ears of doctors". The Guardian. Retrieved 4 November 2016.
- ↑ "Toyota Mothers of Invention: Ting Shih". Toyota Mothers of Invention. Toyota Mothers of Invention. Retrieved 4 November 2016.