Related Research Articles

The Battle of Tippecanoe was fought on November 7, 1811, in Battle Ground, Indiana, between American forces led by then Governor William Henry Harrison of the Indiana Territory and tribal forces associated with Shawnee leader Tecumseh and his brother Tenskwatawa, leaders of a confederacy of various tribes who opposed European-American settlement of the American frontier. As tensions and violence increased, Governor Harrison marched with an army of about 1,000 men to attack the confederacy's headquarters at Prophetstown, near the confluence of the Tippecanoe River and the Wabash River.

Tecumseh was a Shawnee chief and warrior who promoted resistance to the expansion of the United States onto Native American lands. A persuasive orator, Tecumseh traveled widely, forming a Native American confederacy and promoting intertribal unity. Even though his efforts to unite Native Americans ended with his death in the War of 1812, he became an iconic folk hero in American, Indigenous, and Canadian popular history.

The Potawatomi, also spelled Pottawatomi and Pottawatomie, are a Native American people of the Great Plains, upper Mississippi River, and western Great Lakes region. They traditionally speak the Potawatomi language, a member of the Algonquian family. The Potawatomi call themselves Neshnabé, a cognate of the word Anishinaabe. The Potawatomi are part of a long-term alliance, called the Council of Three Fires, with the Ojibway and Odawa (Ottawa). In the Council of Three Fires, the Potawatomi are considered the "youngest brother". Their people are referred to in this context as Bodéwadmi, a name that means "keepers of the fire" and refers to the council fire of three peoples.

The Battle of Fallen Timbers was the final battle of the Northwest Indian War, a struggle between Native American tribes affiliated with the Northwestern Confederacy and their British allies, against the nascent United States for control of the Northwest Territory. The battle took place amid trees toppled by a tornado near the Maumee River in northwestern Ohio at the site of the present-day city of Maumee, Ohio.

Tecumseh's War or Tecumseh's Rebellion was a conflict between the United States and Tecumseh's Confederacy, led by the Shawnee leader Tecumseh in the Indiana Territory. Although the war is often considered to have climaxed with William Henry Harrison's victory at the Battle of Tippecanoe in 1811, Tecumseh's War essentially continued into the War of 1812 and is frequently considered a part of that larger struggle. The war lasted for two more years, until 1813, when Tecumseh and his second-in-command, Roundhead, died fighting Harrison's Army of the Northwest at the Battle of Moraviantown in Upper Canada, near present-day Chatham, Ontario, and his confederacy disintegrated. Tecumseh's War is viewed by some academic historians as the final conflict of a longer-term military struggle for control of the Great Lakes region of North America, encompassing a number of wars over several generations, referred to as the Sixty Years' War.

Tenskwatawa was a Native American religious and political leader of the Shawnee tribe, known as the Prophet or the Shawnee Prophet. He was a younger brother of Tecumseh, a leader of the Shawnee. In his early years Tenskwatawa was given the name Lalawethika, but he changed it around 1805 and transformed himself from a hapless, alcoholic youth into an influential spiritual leader. Tenskwatawa denounced the Americans, calling them the offspring of the Evil Spirit, and led a purification movement that promoted unity among the Indigenous peoples of North America, rejected acculturation to the American way of life, and encouraged his followers to pursue traditional ways.

The Northwest Indian War (1785–1795), also known by other names, was an armed conflict for control of the Northwest Territory fought between the United States and a united group of Native American nations known today as the Northwestern Confederacy. The United States Army considers it the first of the American Indian Wars.

The Siege of Fort Wayne took place from September 5 – September 12, 1812, during the War of 1812. The stand-off occurred in the modern city of Fort Wayne, Indiana between the U.S. military garrison at Fort Wayne and a combined force of Potawatomi and Miami forces. The conflict began when warriors under the Potawatomi Native American Chiefs Winamac, and Five Medals killed two members of the U.S. garrison. Over the next several days, the Potawatomi burned the buildings and crops of the fort's adjacent village, and launched assaults from outside the fort. Winamac withdrew on 12 September, ahead of reinforcements led by Major General William Henry Harrison.

Fort Harrison was a War of 1812 era stockade constructed in Oct. 1811 on high ground overlooking the Wabash River on a portion of what is today the modern city of Terre Haute, Indiana, by forces under command of Gen. William Henry Harrison. It was a staging point for Harrison to encamp his forces just prior to the Battle of Tippecanoe a month later. The fort was the site of a famous battle in the War of 1812, the siege of Fort Harrison in Sept. 1812 that was the first significant victory for the U.S. in the war. The fort was abandoned in 1818 as the frontier moved westward.

William Wells, also known as Apekonit, was the son-in-law of Chief Little Turtle of the Miami. He fought for the Miami in the Northwest Indian War. During the course of that war, he became a United States Army officer, and also served in the War of 1812.
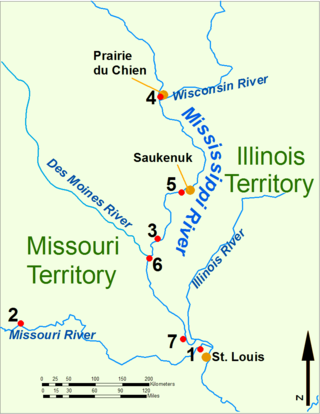
During the War of 1812, the Illinois Territory was the scene of fighting between Native Americans and United States soldiers and settlers. The Illinois Territory at that time included the areas of modern Illinois, Wisconsin and parts of Minnesota and Michigan.
Winamac was the name of a number of Potawatomi leaders and warriors beginning in the late 17th century. The name derives from a man named Wilamet, a Native American from an eastern tribe who in 1681 was appointed to serve as a liaison between New France and the natives of the Lake Michigan region. Wilamet was adopted by the Potawatomis, and his name, which meant "Catfish" in his native Eastern Algonquian language, was soon transformed into "Winamac", which means the same thing in the Potawatomi language. The Potawatomi version of the name has been spelled in a variety of ways, including Winnemac, Winamek, and Winnemeg.

Waubonsie was a leader of the Potawatomi Native American people. His name has been spelled in a variety of ways, including Wabaunsee, Wah-bahn-se, Waubonsee, Waabaanizii in the contemporary Ojibwe language, and Wabanzi in the contemporary Potawatomi language.

Brave Warrior is a 1952 Technicolor American Western film, directed by Spencer Gordon Bennet. It stars Jon Hall and Christine Larsen. The story is based on events during the War of 1812 and the Battle of Tippecanoe, but contains historical inaccuracies, mainly in that Tecumseh is depicted as siding with the Americans and not the British.

Shabbona or Shab-eh-nay, sometimes referred to as Shabonee and Shaubena, was an Ottawa tribe member who became a chief within the Potawatomi tribe in Illinois during the 19th century.
Five Medals was a leader of the Elkhart River Potawatomi. He led his people in defense of their homelands and was a proponent of agriculture. Five Medals first appeared in eastern records after the Battle of Fallen Timbers, but disappears from those records shortly after the end of the War of 1812.
Stone Eater (Sanemamitch) was a Wea war chief in the 18th century, after the abandonment of Ouiantanon, in the present day U.S. state Indiana.

During the War of 1812, the Indiana Territory was the scene of numerous engagements which occurred as part of the conflict's western theater. Prior to the war's outbreak in 1812, settlers from the United States had been gradually colonizing the region, which led to increased tensions with local Native Americans and the outbreak of Tecumseh's War. In 1811, Tecumseh's confederacy, formed in response to encroachment by white American settlers, was defeated by U.S. forces at the Battle of Tippecanoe. After the conflict broke out, most Native Americans in the region joined forces with the British Empire and attacked American forces and settlers in concert with their British allies.

Tecumseh's confederacy was a confederation of Native Americans in the Great Lakes region of North America which formed during the early 19th century around the teaching of Shawnee leader Tenskwatawa. The confederation grew over several years and came to include several thousand Native American warriors. Shawnee leader Tecumseh, the brother of Tenskwatawa, became the leader of the confederation as early as 1808. Together, they worked to unite the various tribes against colonizers from the United States who had been crossing the Appalachian Mountains and occupying their traditional homelands.
White Loon, Michikinikwa's son-in law, was a Miami leader during Tecumseh's War and the War of 1812. He may also have been active in raids against the United States in years following the 1791 St. Clair's Defeat, repeatedly fighting against General "Mad" Anthony Wayne's troops, and, as "Wapamangwa", he signed the Greenville Treaty on August 3, 1795. He led warriors at the Battle of Tippecanoe, along with Wea chief Stone Eater and Potawatomi chief Winamac.
References
- ↑ Tunnell, Appendix B
- ↑ Colonel Boyd served as second-in-command of the expedition with the rank of "acting brigadier general". He also acted as brigade commander of all field units and commander of all regular army units (Tunnell, Appendix B)
- ↑ Tunnel p.127
- ↑ Pirtle p.36
- ↑ In the absence of Tecumseh command of the Confederacy fell to his brother, Tenskwatawa, who was not a war chief but a spiritual leader. Tenskwatawa nevertheless authorized the attack at Prophetstown (Tunnell). The attacking force was led by White Loon, Winamac and Stone Eater (Pirtle p.56)
- ↑ Winkler (2015), p. 34
- ↑ Winkler (2015), p. 32