Chapter 11 of the United States Bankruptcy Code permits reorganization under the bankruptcy laws of the United States. Such reorganization, known as Chapter 11 bankruptcy, is available to every business, whether organized as a corporation, partnership or sole proprietorship, and to individuals, although it is most prominently used by corporate entities. In contrast, Chapter 7 governs the process of a liquidation bankruptcy, though liquidation may also occur under Chapter 11; while Chapter 13 provides a reorganization process for the majority of private individuals.

The Bank of America Corporation is an American multinational investment bank and financial services holding company headquartered at the Bank of America Corporate Center in Charlotte, North Carolina, with investment banking and auxiliary headquarters in Manhattan. The bank was founded in San Francisco, California. It is the second-largest banking institution in the United States, after JPMorgan Chase, and the second-largest bank in the world by market capitalization. Bank of America is one of the Big Four banking institutions of the United States. It serves approximately 10.73% of all American bank deposits, in direct competition with JPMorgan Chase, Citigroup, and Wells Fargo. Its primary financial services revolve around commercial banking, wealth management, and investment banking.
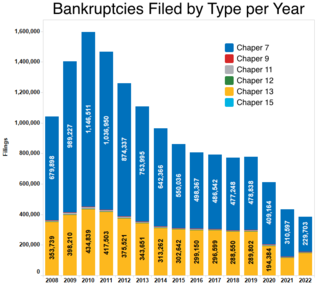
In the United States, bankruptcy is largely governed by federal law, commonly referred to as the "Bankruptcy Code" ("Code"). The United States Constitution authorizes Congress to enact "uniform Laws on the subject of Bankruptcies throughout the United States". Congress has exercised this authority several times since 1801, including through adoption of the Bankruptcy Reform Act of 1978, as amended, codified in Title 11 of the United States Code and the Bankruptcy Abuse Prevention and Consumer Protection Act of 2005 (BAPCPA).
Bank of America Home Loans is the mortgage unit of Bank of America. In 2008, Bank of America purchased the failing Countrywide Financial for $4.1 billion. In 2006, Countrywide financed 20% of all mortgages in the United States, at a value of about 3.5% of the United States GDP, a proportion greater than any other single mortgage lender.

Belk, Inc. is an American department store chain founded in 1888 by William Henry Belk in Monroe, North Carolina, with nearly 300 locations in 16 states. Belk stores and Belk.com offer apparel, shoes, accessories, cosmetics, home furnishings, and a wedding registry.

Piper Sandler Companies is an American multinational investment bank and financial services company, focused on mergers and acquisitions, financial restructuring, public offerings, public finance, institutional brokerage, investment management and securities research. Through its principal subsidiary, Piper Sandler & Co., the company targets corporations, institutional investors, and public entities.
Ditech Financial LLC was a provider of home loan, loan servicing and refinance products to consumers and institutional partners in the U.S.
Banc of America Securities LLC (BAS), was the investment banking subsidiary of Bank of America until it was merged with Merrill Lynch after that firm's acquisition in 2008 to become Bank of America Merrill Lynch. Headquartered in New York City, the company competed in both the domestic and international equity and investment banking markets.

CIT Group (CIT), a subsidiary of First Citizens BancShares, is an American financial services company. It provides financing, including factoring, cash management, treasury management, mortgage loans, Small Business Administration loans, leasing, and advisory services principally to individuals, middle-market companies and small businesses, primarily in North America. Under the reporting mark CEFX, it leases locomotives and railroad cars to rail transport and shipping companies in North America. It also operates a direct bank. In January 2022, CIT was acquired by First Citizens BancShares.
Peer-to-peer lending, also abbreviated as P2P lending, is the practice of lending money to individuals or businesses through online services that match lenders with borrowers. Peer-to-peer lending companies often offer their services online, and attempt to operate with lower overhead and provide their services more cheaply than traditional financial institutions. As a result, lenders can earn higher returns compared to savings and investment products offered by banks, while borrowers can borrow money at lower interest rates, even after the P2P lending company has taken a fee for providing the match-making platform and credit checking the borrower. There is the risk of the borrower defaulting on the loans taken out from peer-lending websites.
Sentinel Management Group was a cash-management firm based in Northbrook, Illinois.
The subprime mortgage crisis impact timeline lists dates relevant to the creation of a United States housing bubble and the 2005 housing bubble burst and the subprime mortgage crisis which developed during 2007 and 2008. It includes United States enactment of government laws and regulations, as well as public and private actions which affected the housing industry and related banking and investment activity. It also notes details of important incidents in the United States, such as bankruptcies and takeovers, and information and statistics about relevant trends. For more information on reverberations of this crisis throughout the global financial system see 2007–2008 financial crisis.
LendingClub is a financial services company headquartered in San Francisco, California. It was the first peer-to-peer lender to register its offerings as securities with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), and to offer loan trading on a secondary market. At its height, LendingClub was the world's largest peer-to-peer lending platform. The company reported that $15.98 billion in loans had been originated through its platform up to December 31, 2015.
Delta Funding Corporation (abbreviated to DFC) was a specialty consumer finance company that originated, securitized and sold non-conforming mortgage loans.

Lynn G. Tilton is an American businesswoman and collateralized loan obligation (CLO) creator, owner and manager. She is the chief executive officer and sole principal of Patriarch Partners, LLC and its affiliated entities, a holding company managing 75 companies. She worked for Goldman Sachs and Merrill Lynch as an investment banker.
First Franklin Financial Corp., not to be confused with 1st Franklin Financial Corporation, was a San Jose, California-based home mortgage lender that specialized in subprime loans. It had been owned by two of the biggest casualties of the subprime mortgage crisis, National City Corp. in Cleveland and Merrill Lynch.
Merrill, previously branded Merrill Lynch, is an American investment management and wealth management division of Bank of America. Along with BofA Securities, the investment banking arm, both firms engage in prime brokerage and broker-dealer activities. The firm is headquartered in New York City, and once occupied the entire 34 stories of 250 Vesey Street, part of the Brookfield Place complex in Manhattan. Merrill employs over 14,000 financial advisors and manages $2.8 trillion in client assets. The company also operates Merrill Edge, a division for investment and related services, including call center counsultancy.
TMX Finance is the parent company to the brands TitleMax, TitleBucks, EquityAuto Loan, and InstaLoan. The company holds more than 900 stores in over fourteen states including Alabama, Arizona, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Mississippi, Missouri, Nevada, New Mexico, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Utah, and Wisconsin, and an online presence in Idaho. TMX Finance’s brands serve individuals who generally have limited access to consumer credit from banks, thrift institutions, credit card lenders, and other traditional sources of consumer credit.
Jeffrey Peek is a finance industry executive. He headed CIT Group from 2003 until it was reorganized following the 2008 financial crisis.
Genesis is a cryptocurrency brokerage for institutional investors. It is a subsidiary of Digital Currency Group (DCG).







