
Ladin is a Romance language of the Rhaeto-Romance subgroup, mainly spoken in the Dolomite Mountains in Northern Italy in the provinces of South Tyrol, Trentino, and Belluno, by the Ladin people. It exhibits similarities to Romansh, spoken in Switzerland, as well as Friulian, spoken in north-east Italy.

Tyrol is an Austrian federal state. It comprises the Austrian part of the historical Princely County of Tyrol. It is a constituent part of the present-day Euroregion Tyrol–South Tyrol–Trentino. The capital of Tyrol is Innsbruck.
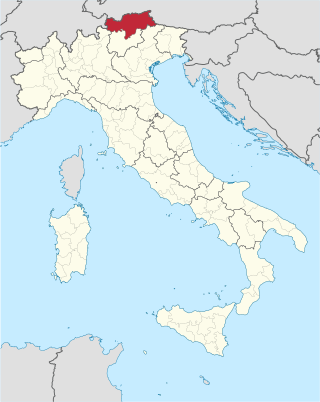
South Tyrol is an autonomous province in northern Italy. An English translation of the official German and Italian names could be the Autonomous Province of Bolzano – South Tyrol, reflecting the multilingualism and different naming conventions in the area. Together with the autonomous province of Trento, South Tyrol forms the autonomous region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol. The province is the northernmost of Italy, the second largest with an area of 7,400 square kilometres (2,857 sq mi), and has a total population of about 534,000 inhabitants as of 2021. Its capital and largest city is Bolzano.

Bolzano is the capital city of the province of South Tyrol, in Northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third largest in historical Tyrol. The greater metro area has about 250,000 inhabitants and is one of the urban centers within the Alps.

Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol is an autonomous region of Italy, located in the northern part of the country. The region has a population of 1.1 million, of whom 62% speak Italian as their mother tongue, 30% speak South Tyrolean German and several foreign languages are spoken by immigrant communities. Since the 1970s, most legislative and administrative powers have been transferred to the two self-governing provinces that make up the region: the province of Trento, commonly known as Trentino, and the province of Bolzano, commonly known as South Tyrol. In South Tyrol, German remains the sizeable majority language.
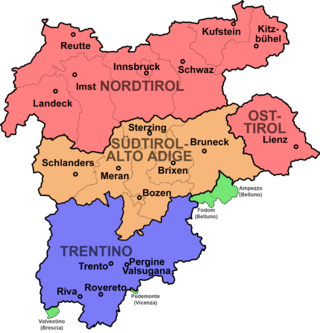
East Tyrol, occasionally East Tirol, is an exclave of the Austrian federal state of Tyrol, separated from North Tyrol by parts of Salzburg State and parts of Italian South Tyrol. It is congruent with the administrative district (Bezirk) of Lienz.

Provincia autonoma di Trento, commonly known as Trentino, is an autonomous province of Italy in the country's far north. Trentino and South Tyrol constitute the region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, an autonomous region under the constitution. The province is composed of 166 comuni. Its capital is the city of Trento (Trent). The province covers an area of more than 6,000 km2 (2,300 sq mi), with a total population of 541,098 in 2019. Trentino is renowned for its mountains, such as the Dolomites, which are part of the Alps.

Kaltern an der Weinstraße, often abbreviated to Kaltern or Caldaro, is a municipality and a village in South Tyrol in northern Italy. It is about 12 kilometres (7 mi) southwest of the city of Bolzano.

Modern-day South Tyrol, an autonomous Italian province created in 1948, was part of the Austro-Hungarian County of Tyrol until 1918. It was annexed by Italy following the defeat of the Central Powers in World War I. It has been part of a cross-border joint entity, the Euroregion Tyrol-South Tyrol-Trentino, since 2001.
A drainage divide, water divide, ridgeline, watershed, water parting or height of land is elevated terrain that separates neighboring drainage basins. On rugged land, the divide lies along topographical ridges, and may be in the form of a single range of hills or mountains, known as a dividing range. On flat terrain, especially where the ground is marshy, the divide may be difficult to discern.

The (Princely) County of Tyrol was an estate of the Holy Roman Empire established about 1140. After 1253, it was ruled by the House of Gorizia and from 1363 by the House of Habsburg. In 1804, the County of Tyrol, unified with the secularised prince-bishoprics of Trent and Brixen, became a crown land of the Austrian Empire. From 1867, it was a Cisleithanian crown land of Austria-Hungary.

Rasen-Antholz is a municipality in South Tyrol in northern Italy.

South Tyrolean Freedom is a regionalist, separatist and national-conservative political party in South Tyrol, Italy. The party, which is part of the South Tyrolean independence movement, seeks to represent the German-speaking population and proposes the secession of South Tyrol from Italy and its reunification with the State of Tyrol within Austria.

In 1919, at the time of its annexation, the middle part of the County of Tyrol which is today called South Tyrol was inhabited by almost 90% German speakers. Under the 1939 South Tyrol Option Agreement, Adolf Hitler and Benito Mussolini determined the status of the German and Ladin (Rhaeto-Romanic) ethnic groups living in the region. They could emigrate to Germany, or stay in Italy and accept their complete Italianization. As a consequence of this, the society of South Tyrol was deeply riven. Those who wanted to stay, the so-called Dableiber, were condemned as traitors while those who left (Optanten) were defamed as Nazis. Because of the outbreak of World War II, this agreement was never fully implemented. Illegal Katakombenschulen were set up to teach children the German language.

The South Tyrol Alpine Club, abbreviated AVS, is an association of German and Ladin-speaking mountain climbers in South Tyrol, northern Italy. Founded in 1946, it is subdivided into 32 sections and 58 local divisions. The AVS is based in Bolzano and has more than 60,000 members.

Tyrol is a historical region in the Alps of Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Empire and Austria-Hungary, from its formation in the 12th century until 1919. In 1919, following World War I and the dissolution of Austria-Hungary, it was divided into two modern administrative parts through the Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye:

The South Tyrolean independence movement is a political movement in the Italian autonomous province of South Tyrol that calls for the secession of the region from Italy and its reunification with the State of Tyrol, Austria. Concurrently, some groups favor the establishment of an interim Free State of South Tyrol as a sovereign nation while reintegration is organized.
South Tyrolean German or Tyrolese is a dialect spoken in the northern Italian province of South Tyrol. It is generally considered to be a sub-variety of Southern Bavarian, and has many similarities with other South German languages, in particular with varieties of Austrian German. It may develop its own standard variety of German, though currently is linguistically heteronomous to German German.















