Related Research Articles

DeBary is a city in Volusia County, Florida, United States, on the eastern shore of the St. Johns River near Lake Monroe. According to the 2020 U.S. Census, the city had a population of 20,696. It is part of the Deltona–Daytona Beach–Ormond Beach, FL metropolitan statistical area, which was home to 553,284 people in 2019.

Harriet Elisabeth Beecher Stowe was an American author and abolitionist. She came from the religious Beecher family and wrote the popular novel Uncle Tom's Cabin (1852), which depicts the harsh conditions experienced by enslaved African Americans. The book reached an audience of millions as a novel and play, and became influential in the United States and in Great Britain, energizing anti-slavery forces in the American North, while provoking widespread anger in the South. Stowe wrote 30 books, including novels, three travel memoirs, and collections of articles and letters. She was influential both for her writings as well as for her public stances and debates on social issues of the day.

The St. Johns River is the longest river in the U.S. state of Florida and it is the most significant one for commercial and recreational use. At 310 miles (500 km) long, it flows north and winds through or borders twelve counties. The drop in elevation from headwaters to mouth is less than 30 feet (9 m); like most Florida waterways, the St. Johns has a very slow flow speed of 0.3 mph (0.13 m/s), and is often described as "lazy".

Fort Caroline was an attempted French colonial settlement in Florida, located on the banks of the St. Johns River in present-day Duval County. It was established under the leadership of René Goulaine de Laudonnière on 22 June 1564, following King Charles IX's enlisting of Jean Ribault and his Huguenot settlers to stake a claim in French Florida ahead of Spain. The French colony came into conflict with the Spanish, who established St. Augustine in September 1565, and Fort Caroline was sacked by Spanish troops under Pedro Menéndez de Avilés on 20 September. The Spanish continued to occupy the site as San Mateo until 1569.

San Juan del Puerto was a Spanish Franciscan mission founded before 1587 on Fort George Island, near the mouth of the St. Johns River in what is now Jacksonville, Florida. It was founded to serve the Saturiwa, a Timucua tribe who lived around the mouth of the St. Johns. It was organized by separating them into nine smaller villages. It has an important place in the study of the Timucua, as the place where Francisco Pareja undertook his work on the Timucua language.

The 74-mile-long (119 km) Ocklawaha River flows north from central Florida until it joins the St. Johns River near Palatka. Its name is derived from ak-lowahe, Creek for "muddy".
Mandarin is a neighborhood located in the southernmost portion of Jacksonville, in Duval County, Florida, United States. It is located on the eastern banks of the St. Johns River, across from Orange Park. It's a short drive south of Jacksonville's city center, and is bordered by Beauclerc to the north, Julington Creek to the south and St. John's River to the west.

Volusia is an unincorporated community in Volusia County, Florida, United States, on the eastern shore of the St. Johns River. It is about three miles south of Lake George and across the river from the town of Astor in Lake County. Established by Spanish missionaries, Volusia is one of the oldest European settlements in Florida. The main route through the town is State Road 40, which crosses the St. Johns on the Astor Bridge.

Beginning in the second half of the 16th century, the Kingdom of Spain established a number of missions throughout La Florida in order to convert the Native Americans to Roman Catholicism, to facilitate control of the area, and to obstruct regional colonization by other Protestants, particularly, those from England and France. Spanish Florida originally included much of what is now the Southeastern United States, although Spain never exercised long-term effective control over more than the northern part of what is now the State of Florida from present-day St. Augustine to the area around Tallahassee, southeastern Georgia, and some coastal settlements, such as Pensacola, Florida. A few short-lived missions were established in other locations, including Mission Santa Elena in present-day South Carolina, around the Florida peninsula, and in the interior of Georgia and Alabama.
The World Golf Village (WGV) is a golf resort in St. Johns County, Florida, United States, located between Jacksonville and St. Augustine. It was created by the PGA Tour and showcases the World Golf Hall of Fame. In addition to the resort the World Golf Village features residential and commercial developments. There is also a census-designated place with the same name.
Acuera was the name of both an indigenous town and a province or region in central Florida during the 16th and 17th centuries. The indigenous people of Acuera spoke a dialect of the Timucua language. In 1539 the town first encountered Europeans when it was raided by soldiers of Hernando de Soto's expedition. French colonists also knew this town during their brief tenure (1564–1565) in northern Florida.

St. Johns County School District (SJCSD) is the public school district for St. Johns County, Florida.
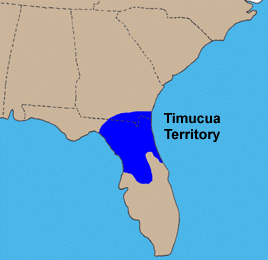
The Timucua were a Native American people who lived in Northeast and North Central Florida and southeast Georgia. They were the largest indigenous group in that area and consisted of about 35 chiefdoms, many leading thousands of people. The various groups of Timucua spoke several dialects of the Timucua language. At the time of European contact, Timucuan speakers occupied about 19,200 square miles (50,000 km2) in the present-day states of Florida and Georgia, with an estimated population of 200,000. Milanich notes that the population density calculated from those figures, 10.4 per square mile (4.0/km2) is close to the population densities calculated by other authors for the Bahamas and for Hispaniola at the time of first European contact. The territory occupied by Timucua speakers stretched from the Altamaha River and Cumberland Island in present-day Georgia as far south as Lake George in central Florida, and from the Atlantic Ocean west to the Aucilla River in the Florida Panhandle, though it reached the Gulf of Mexico at no more than a couple of points.

The Agua Dulce or Agua Fresca (Freshwater) were a Timucua people of northeastern Florida. They lived in the St. Johns River watershed north of Lake George, and spoke a dialect of the Timucua language also known as Agua Dulce.

The Northern Utina, also known as the Timucua or simply Utina, were a Timucua people of northern Florida. They lived north of the Santa Fe River and east of the Suwannee River, and spoke a dialect of the Timucua language known as "Timucua proper". They appear to have been closely associated with the Yustaga people, who lived on the other side of the Suwannee. The Northern Utina represented one of the most powerful tribal units in the region in the 16th and 17th centuries, and may have been organized as a loose chiefdom or confederation of smaller chiefdoms. The Fig Springs archaeological site may be the remains of their principal village, Ayacuto, and the later Spanish mission of San Martín de Timucua.
Pedro Benedit Horruytiner y Catalán was a Spanish soldier who served as interim co-governor of Spanish Florida between 1646 and 1648, and as governor between 1651 and 1654. When governor Benito Ruíz de Salazar Vallecilla was suspended from office in 1646, acting royal contador Horruytiner and Francisco Menendez Marquez served as co-governors until Salazar Vallecilla was returned to office in 1648.
San Buenaventura de Potano was a Spanish mission near Orange Lake in southern Alachua County or northern Marion County, Florida, located on the site where the town of Potano had been located when it was visited by Hernando de Soto in 1539. The Richardson/UF Village Site (8AL100), in southern Alachua County, has been proposed as the location of the town and mission.
Diego de Rebolledo y Suárez de Aponte, was the 21st colonial governor of Spanish Florida, in office from June 18, 1654 to February 20, 1659. He is considered by historians to be one of the more controversial governors of Spanish colonial Florida. Rebolledo showed a marked lack of respect for the status of the Timucua chiefs as hereditary leaders and administrative intermediaries, an attitude that provoked a Timucuan uprising against Spanish rule. Rebolledo was a Knight of the Order of Santiago.

Tocoi is a former settlement along the St. Johns River in St. Johns County, Florida.

Tocoi Creek High School (TCHS) is a new public high school in the World Golf Village census-designated place, in north central area of St. Johns County, Florida near St. Augustine. It is part of the St. Johns County School District and opened to students for the 2021-22 academic year.
References
- ↑ "Paddling Tocoi Creek to old steamship dock". AllTrails.com.
- ↑ "What's in a name?" (PDF). Tocoi Creek High School. No. 2. December 2020.
- ↑ "The Timucua: North Florida's Early People - Timucuan Ecological & Historic Preserve (U.S. National Park Service)". www.nps.gov.
- ↑ "General Acts and Resolutions Adopted by the Legislature of Florida". Office of the Floridian and Journal. July 23, 1879 – via Google Books.
- ↑ Cox, Jeremy. "The ghost towns of Northeast Florida's past". The Florida Times-Union.
- ↑ Delaney, Bill (2020-04-21). "Writers of the First Coast: Harriet Beecher Stowe". The Jaxson.
- ↑ Parker, Susan (2020-12-12). "New high school's name carries centuries of history". The St. Augustine Record.
- ↑ Jones, Colleen Michele. "Tocoi Creek High School name pays homage to St. Johns County geographical, historical ties". St. Augustine Record.
29°51′40″N81°33′10″W / 29.86111°N 81.55278°W