The Pere Marquette Railway operated in the Great Lakes region of the United States and southern parts of Ontario in Canada. It had trackage in the states of Michigan, Ohio, Indiana and the Canadian province of Ontario. Its primary connections included Buffalo; Toledo; and Chicago. The company was named after Père Jacques Marquette S.J. (1637–1675), a French Jesuit missionary who founded Michigan's first European settlement, Sault Ste Marie.
The Lake Shore and Michigan Southern Railway, established in 1833 and sometimes referred to as the Lake Shore, was a major part of the New York Central Railroad's Water Level Route from Buffalo, New York, to Chicago, Illinois, primarily along the south shore of Lake Erie and across northern Indiana. The line's trackage is still used as a major rail transportation corridor and hosts Amtrak passenger trains, with the ownership in 1998 split at Cleveland between CSX to the east, and Norfolk Southern in the west.

The Grand Trunk Western Railroad Company is an American subsidiary of the Canadian National Railway operating in Michigan, Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio. Since a corporate restructuring in 1971, the railroad has been under CN's subsidiary holding company, the Grand Trunk Corporation. Grand Trunk Western's routes are part of CN's Michigan Division. Its primary mainline between Chicago and Port Huron, Michigan serves as a connection between railroad interchanges in Chicago and rail lines in eastern Canada and the Northeastern United States. The railroad's extensive trackage in Detroit and across southern Michigan has made it an essential link for the automotive industry as a hauler of parts and automobiles from manufacturing plants.

Michigan Services are three Amtrak passenger rail routes connecting Chicago, Illinois with the Michigan cities of Grand Rapids, Port Huron, and Detroit, and stations en route. The group is a component of the Midwest Regional Rail Initiative.
The Porter Subdivision is a railroad line owned by CSX Transportation in the Chicago, Illinois, area. Formerly a part of the main line of the Michigan Central Railroad, it now connects CSX's former Baltimore and Ohio Railroad line and the Chicago Fort Wayne and Eastern Railroad from the east with the Indiana Harbor Belt Railroad towards Blue Island, Illinois.

The Detroit and Toledo Shore Line Railroad is a historic railroad that operated in northwestern Ohio and southeastern Michigan.

The Pere Marquette Rail-Trail (PMRT) is a rail trail in Michigan occupying an 28-mile (45 km) abandoned CSX railroad corridor in Midland County and Isabella County that was once part of the Flint and Pere Marquette Railroad. In 1874, the tracks stretched from Ludington to Flint, transporting supplies to the timber industry and lumber/timber to southern Michigan's mills. It is a Michigan Rails to Trails Conservancy Hall of Fame trail.

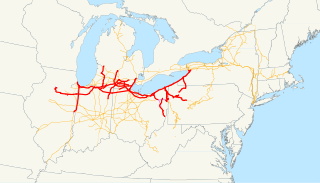
The Pere Marquette is a passenger train operated by Amtrak as part of its Michigan Services on the 176-mile (283 km) route between Grand Rapids, Michigan, and Chicago, Illinois. It is funded in part by the Michigan Department of Transportation and is train 370 eastbound and train 371 westbound. The westbound train leaves Grand Rapids during the morning rush, with the eastbound train leaving Chicago after the afternoon rush, enabling same-day business travel between the two cities.
The Sarnia Subdivision is a railroad line owned by the Lake Erie and Detroit River Railway and operated by CSX Transportation in the Canadian province of Ontario. The line runs from Chatham north to Sarnia along a former Pere Marquette Railway line. From its north end, CSX has trackage rights west over the Canadian National Railway's Strathroy Subdivision and the Grand Trunk Western Railroad's Flint Subdivision to the CSX Port Huron Subdivision near Port Huron, Michigan, and the Saginaw Subdivision in Flint.
The Lincoln Secondary is a railroad line owned and operated by Conrail in the U.S. state of Michigan as part of its Conrail Shared Assets Operations.
The Flint and Pere Marquette Railroad (F&PM) is a defunct railroad which operated in the U.S. state of Michigan between 1857 and 1899. It was one of the three companies which merged to become the Pere Marquette Railway.
The Flint and Holly Railroad (F&H) is a defunct railroad that operated in eastern Michigan from 1863 to 1868. It was founded by Henry H. Crapo, a Massachusetts-born lumber merchant who served as Governor of Michigan (1865–1869). The line was originally chartered as the Flint and Fentonville Railroad on January 3, 1863, and was amended on October 16, 1863. On November 1, 1864, the F&H completed a railway line from Flint, Michigan to Holly, Michigan. Via an agreement with the Detroit and Milwaukee Railway (D&M), F&H ran into Detroit's Brush Street Station over D&M tracks.
The Detroit, Lansing and Northern Railroad (DL&N) is a defunct railroad which was formed on December 27, 1876 as a reorganization of the foreclosed Detroit, Lansing and Lake Michigan Rail Road. The segment of its main line from Detroit to Lansing became an important component of the Pere Marquette Railroad, organized in 1900, and is still in use by CSX.
The Grand Rapids, Belding and Saginaw Railroad is a defunct railroad which operated in the state of Michigan at the turn of the 20th century.
The following is a brief history of the North American rail system, mainly through major changes to Class I railroads, the largest class by operating revenue.

Lake State Railway is a railroad operating in the Saginaw Valley and northeastern quadrant of the Lower Peninsula of Michigan. The railroad moves large quantities of aggregate and limestone, as well as coal, grain, and chemical products. Some of the company's largest customers include Dow Chemical Company, S. C. Johnson & Son, Lafarge, ConAgra Foods, Archer Daniels Midland, Conrad Yelvington Distributors, and Consumers Energy.
The CSX Saginaw Subdivision is a railroad line in the U.S. state of Michigan. The line runs 105 miles from Toledo, Ohio, to Saginaw, Michigan; although since 2006, the section from Mt. Morris to Saginaw has been leased to the Lake State Railway, but is still occasionally used by CSX. The Plymouth to Mt. Morris line was also leased to LSRC starting in March 2019.
The CSX Plymouth Subdivision is a freight railroad line in the U.S. state of Michigan. It connects the Plymouth Diamond at milepost CH 24.5 to Grand Rapids at CH 148.1, passing through the Lansing metropolitan area en route. Other towns served include Brighton, Howell, Williamston, Grand Ledge, and Lake Odessa. Operationally, it is part of the CSX Chicago Division, dispatched from Calumet City, Illinois.

The Flint & Pere Marquette Union Station, commonly known as the Potter Street Station, is a railroad station built in 1881 and located at 501 Potter Street in Saginaw, Michigan, United States. It was designed by New York City architect Bradford Lee Gilbert. The station is 285 feet by 40 feet with 2½ stories, and is Michigan's second largest depot.







