A tombstone is a stele or marker, usually stone, that is placed over a grave.

A machinist is a tradesperson or trained professional who not only operates machine tools but also has the knowledge of tooling and materials required to create set ups on machine tools such as milling machines, grinders, lathes, and drilling machines.
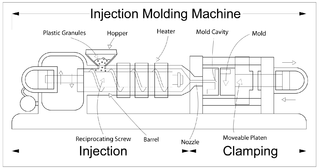
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals, glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed, and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers that do not melt during the injection moulding of some lower-temperature thermoplastics, can be used for some simple injection moulds.

Numerical control is the automated control of machining tools by means of a computer. A CNC machine processes a piece of material to meet specifications by following a coded programmed instruction and without a manual operator directly controlling the machining operation.

Dextre, also known as the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator (SPDM), is a two armed robot, or telemanipulator, which is part of the Mobile Servicing System on the International Space Station (ISS), and does repairs otherwise requiring spacewalks. It was launched March 11, 2008 on mission STS-123.

Metal fabrication is the creation of metal structures by cutting, bending and assembling processes. It is a value-added process involving the creation of machines, parts, and structures from various raw materials.

A grinding machine, often shortened to grinder, is one of power tools or machine tools used for grinding, it is a type of machining using an abrasive wheel as the cutting tool. Each grain of abrasive on the wheel's surface cuts a small chip from the workpiece via shear deformation.
:) Grinding is used to finish workpieces that must show high surface quality and high accuracy of shape and dimension. As the accuracy in dimensions in grinding is of the order of 0.000025 mm, in most applications it tends to be a finishing operation and removes comparatively little metal, about 0.25 to 0.50 mm depth. However, there are some roughing applications in which grinding removes high volumes of metal quite rapidly. Thus, grinding is a diverse field.

A mandrel, mandril, or arbor is a gently tapered cylinder against which material can be forged or shaped, or a flanged or tapered or threaded bar that grips a workpiece to be machined in a lathe. A flanged mandrel is a parallel bar of a specific diameter with an integral flange towards one end, and threaded at the opposite end. Work is gripped between the flange and a nut on the thread. A tapered mandrel has a taper of approximately 0.005 inches per foot and is designed to hold work by being driven into an accurate hole on the work, gripping the work by friction. A threaded mandrel may have a male or female thread, and work which has an identical thread is screwed onto the mandrel.

A tool and cutter grinder is used to sharpen milling cutters and tool bits along with a host of other cutting tools.

Turning is a machining process in which a cutting tool, typically a non-rotary tool bit, describes a helix toolpath by moving more or less linearly while the workpiece rotates.

A rotary table is a precision work positioning device used in metalworking. It enables the operator to drill or cut work at exact intervals around a fixed axis. Some rotary tables allow the use of index plates for indexing operations, and some can also be fitted with dividing plates that enable regular work positioning at divisions for which indexing plates are not available. A rotary fixture used in this fashion is more appropriately called a dividing head.

Design for manufacturability is the general engineering practice of designing products in such a way that they are easy to manufacture. The concept exists in almost all engineering disciplines, but the implementation differs widely depending on the manufacturing technology. DFM describes the process of designing or engineering a product in order to facilitate the manufacturing process in order to reduce its manufacturing costs. DFM will allow potential problems to be fixed in the design phase which is the least expensive place to address them. Other factors may affect the manufacturability such as the type of raw material, the form of the raw material, dimensional tolerances, and secondary processing such as finishing.

Tool and die makers are highly skilled craftsman working in the manufacturing industries. Variations on the name include tool maker,toolmaker, die maker,diemaker, mold maker,moldmaker or tool jig and die-maker depending on which area of concentration or industry an individual works in.

A fixture is a work-holding or support device used in the manufacturing industry. Fixtures are used to securely locate and support the work, ensuring that all parts produced using the fixture will maintain conformity and interchangeability. Using a fixture improves the economy of production by allowing smooth operation and quick transition from part to part, reducing the requirement for skilled labor by simplifying how workpieces are mounted, and increasing conformity across a production run.

An injection molding machine, also known as an injection press, is a machine for manufacturing plastic products by the injection molding process. It consists of two main parts, an injection unit and a clamping unit.

A jig is a type of custom-made tool used to control the location and/or motion of parts or other tools.

A computer numerical control (CNC) router is a computer-controlled cutting machine which typically mounts a hand-held router as a spindle which is used for cutting various materials, such as wood, composites, aluminium, steel, plastics, glass, and foams. CNC routers can perform the tasks of many carpentry shop machines such as the panel saw, the spindle moulder, and the boring machine. They can also cut joinery such as mortises and tenons.

Selective laser melting (SLM) is one of many proprietary names for a metal additive manufacturing technology that uses a bed of powder with a source of heat to create metal parts. Also known as direct metal laser melting (DMLM), the ASTM standard term is powder bed fusion (PBF). PBF is a rapid prototyping, 3D printing, or additive manufacturing (AM) technique designed to use a high power-density laser to melt and fuse metallic powders together.

Milling is the process of machining using rotary cutters to remove material by advancing a cutter into a workpiece. This may be done varying direction on one or several axes, cutter head speed, and pressure. Milling covers a wide variety of different operations and machines, on scales from small individual parts to large, heavy-duty gang milling operations. It is one of the most commonly used processes for machining custom parts to precise tolerances.

A rotary transfer machine is a machine tool, typically for metal working by machining, comprising a large indexing table with machining stations surrounding the table. Such rotary transfer machines are used for producing a large number of parts in fairly short cycle times.



















