
Rail transport is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of land transport, next to road transport. It is used for about 8% of passenger and freight transport globally, thanks to its energy efficiency and potentially high speed.

America's first transcontinental railroad was a 1,911-mile (3,075 km) continuous railroad line built between 1863 and 1869 that connected the existing eastern U.S. rail network at Council Bluffs, Iowa, with the Pacific coast at the Oakland Long Wharf on San Francisco Bay. The rail line was built by three private companies over public lands provided by extensive U.S. land grants. Building was financed by both state and U.S. government subsidy bonds as well as by company-issued mortgage bonds. The Western Pacific Railroad Company built 132 miles (212 km) of track from the road's western terminus at Alameda/Oakland to Sacramento, California. The Central Pacific Railroad Company of California (CPRR) constructed 690 miles (1,110 km) east from Sacramento to Promontory Summit, Utah Territory. The Union Pacific Railroad (UPRR) built 1,085 miles (1,746 km) from the road's eastern terminus at the Missouri River settlements of Council Bluffs and Omaha, Nebraska, westward to Promontory Summit.

The Union Pacific Railroad is a Class I freight-hauling railroad that operates 8,300 locomotives over 32,200 miles (51,800 km) routes in 23 U.S. states west of Chicago and New Orleans. Union Pacific is the second largest railroad in the United States after BNSF, with which it shares a duopoly on transcontinental freight rail lines in the Western, Midwestern and West South Central United States.

The Liverpool and Manchester Railway (L&MR) was the first inter-city railway in the world. It opened on 15 September 1830 between the Lancashire towns of Liverpool and Manchester in England. It was also the first railway to rely exclusively on locomotives driven by steam power, with no horse-drawn traffic permitted at any time; the first to be entirely double track throughout its length; the first to have a true signalling system; the first to be fully timetabled; and the first to carry mail.
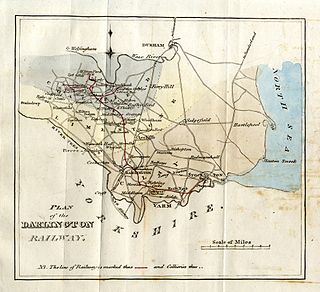
The Stockton and Darlington Railway (S&DR) was a railway company that operated in north-east England from 1825 to 1863. The world's first public railway to use steam locomotives, its first line connected collieries near Shildon with Darlington and Stockton in County Durham, and was officially opened on 27 September 1825. The movement of coal to ships rapidly became a lucrative business, and the line was soon extended to a new port at Middlesbrough. While coal waggons were hauled by steam locomotives from the start, passengers were carried in coaches drawn by horses until carriages hauled by steam locomotives were introduced in 1833.

The Southwest Chief is a long-distance passenger train operated by Amtrak on a 2,265-mile (3,645 km) route between Chicago and Los Angeles through the Midwest and Southwest via Kansas City, Albuquerque, and Flagstaff. Amtrak bills the route as one of its most scenic, with views of the Painted Desert and the Red Cliffs of Sedona, as well as the plains of Illinois, Missouri, Kansas, and Colorado.

The Texas Eagle is a long-distance passenger train operated daily by Amtrak on a 1,306-mile (2,102 km) route between Chicago, Illinois, and San Antonio, Texas, with major stops in St. Louis, Little Rock, Dallas, Fort Worth, and Austin. Three days per week, the train joins the Sunset Limited in San Antonio and continues to Los Angeles via El Paso and Tucson. The combined 2,728-mile (4,390 km) route is the longest in the United States and the second-longest in the Americas, after the Canadian.

The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway, often referred to as the Santa Fe or AT&SF, was one of the largest Class 1 railroads in the United States.
The Norton Fitzwarren rail crash occurred on 4 November 1940 between Taunton and Norton Fitzwarren in the English county of Somerset, when the driver of a train misunderstood the signalling and track layout, causing him to drive the train through a set of points and off the rails at approximately 40 miles per hour (64 km/h). 27 people were killed. The locomotive involved was GWR King Class GWR 6028 King Class King George VI which was subsequently repaired and returned to service. A previous significant accident occurred here on 10 November 1890 and the Taunton train fire of 1978 was also within 2 metres.
The Lancaster and Preston Junction Railway opened its twenty-mile line in 1840 in Lancashire, England. The company was not commercially successful. When the Lancaster and Carlisle Railway opened in 1846, the L&PJR became part of a busy trunk railway. It had never had the money to provide substantial track equipment or proper signalling arrangements. Most of the line is in use today as part of the West Coast Main Line railway and has been electrified. None of the L&PJR stations are still in use.

Tough Guys is a 1986 American action comedy film directed by Jeff Kanew and starring Burt Lancaster, Kirk Douglas, Eli Wallach, Charles Durning, Dana Carvey, and Darlanne Fluegel. It is the eighth film of Touchstone Pictures, and the final film to be released from Douglas's Bryna Productions.
William Jones (1884–1968), a seasoned veteran of the steam era who established the Wildcat Railroad in Los Gatos, California, was born the son of a teamster in the town of Ben Lomond, California, USA.
The Rosstown Railway was a private railway in the south-eastern suburbs of Melbourne, Australia, running between the current railway stations of Elsternwick, on the Sandringham line, and Oakleigh, on the Pakenham line. The line was built in the late 19th century by William Murray Ross, with the intention of transporting sugar beet to his sugar beet mill, and the refined product to the Port of Melbourne. When the mill failed to begin production, the line fell into disrepair without being used, and it was eventually dismantled, with the land being sold.

The Lost Boys are characters from J. M. Barrie's 1904 play Peter Pan, or The Boy Who Wouldn't Grow Up and later adaptations and extensions to the story. They are boys "who fall out of their prams when the nurse is looking the other way and if they are not claimed in seven days, they are sent far away to the Neverland," where Peter Pan is their captain.

Cotton Belt 819 is a class "L-1" 4-8-4 "Northern" type steam locomotive and is also the official state locomotive of Arkansas. It was completed in 1943 and was the last engine built by the St. Louis Southwestern Railway, which was affectionately known as "The Cotton Belt Route" or simply "Cotton Belt". It was also the last locomotive built in Arkansas. It was restored to operating condition in 1986 and operated in excursion service until October 1993. As of 2023, the locomotive is now located at the Arkansas Railroad Museum, currently being cosmetically restored.

Newman railway station was a station on the Wairarapa Line in the Tararua District area of the Manawatū-Whanganui region of New Zealand’s North Island. It served the small rural community of Newman, 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) north of Eketāhuna. It is accessed via Cliff Road, but is now located on private property.

The Liverpool and Manchester Railway (L&M) opened on 15 September 1830. Work on the L&M had begun in the 1820s, to connect the textile mills of the city of Manchester with the nearest deep water port at the Port of Liverpool, 35 miles (56 km) away. Although horse-drawn railways already existed elsewhere, the Stockton and Darlington Railway had been running for five years, and a few industrial sites already used primitive steam locomotives for bulk haulage, the L&M was the first locomotive-hauled railway to connect two major cities, and the first to provide a scheduled passenger service. The opening day was a major public event. Arthur Wellesley, Duke of Wellington, the prime minister, rode on one of the eight inaugural trains, as did many other dignitaries and notable figures of the day. Huge crowds lined the track at Liverpool to watch the trains depart for Manchester.

The Reuben Wells is a steam locomotive in the permanent collection of The Children's Museum of Indianapolis located in Indianapolis, Indiana, United States. Beginning in 1868, it operated for 30 years in Madison, Indiana, pushing train cars up the steepest "standard-gauge main-track grade" in the United States.

Play Safe is a 1936 animated short film produced by Fleischer Studios and released by Paramount Pictures. This film was part of Max Fleischer's Color Classics series. The film follows the story of a boy who has a dream about being on a real train.















