Related Research Articles

A landscape is the visible features of an area of land, its landforms, and how they integrate with natural or human-made features, often considered in terms of their aesthetic appeal. A landscape includes the physical elements of geophysically defined landforms such as mountains, hills, water bodies such as rivers, lakes, ponds and the sea, living elements of land cover including indigenous vegetation, human elements including different forms of land use, buildings, and structures, and transitory elements such as lighting and weather conditions. Combining both their physical origins and the cultural overlay of human presence, often created over millennia, landscapes reflect a living synthesis of people and place that is vital to local and national identity.

Shifting cultivation is an agricultural system in which plots of land are cultivated temporarily, then abandoned while post-disturbance fallow vegetation is allowed to freely grow while the cultivator moves on to another plot. The period of cultivation is usually terminated when the soil shows signs of exhaustion or, more commonly, when the field is overrun by weeds. The period of time during which the field is cultivated is usually shorter than the period over which the land is allowed to regenerate by lying fallow.

The Duwamish River is the name of the lower 12 miles (19 km) of Washington state's Green River. Its industrialized estuary is known as the Duwamish Waterway. Although heavily polluted, it is an important habitat for the wildlife. Important to the Duwamish people, the Duwamish Longhouse and Cultural Center is on the west bank of the river and several parks have indigenous Lushootseed names.
Landscape archaeology, previously known as total archaeology is a sub-discipline of archaeology and archaeological theory. It studies the ways in which people in the past constructed and used the environment around them. It is also known as archaeogeography. Landscape archaeology is inherently multidisciplinary in its approach to the study of culture, and is used by pre-historical, classic, and historic archaeologists. The key feature that distinguishes landscape archaeology from other archaeological approaches to sites is that there is an explicit emphasis on the sites' relationships between material culture, human alteration of land/cultural modifications to landscape, and the natural environment. The study of landscape archaeology has evolved to include how landscapes were used to create and reinforce social inequality and to announce one's social status to the community at large. The field includes with the dynamics of geohistorical objects, such as roads, walls, boundaries, trees, and land divisions.

The IDF Caterpillar D9 — nicknamed Doobi — is a Caterpillar D9 armored bulldozer used by the Israel Defense Forces (IDF). It is supplied by Caterpillar Inc. and modified by the Israel Defense Forces, Israeli Military Industries and Israel Aerospace Industries to increase the survivability of the bulldozer in hostile environments and enable it to withstand attack.

Environmental degradation is the deterioration of the environment through depletion of resources such as quality of air, water and soil; the destruction of ecosystems; habitat destruction; the extinction of wildlife; and pollution. It is defined as any change or disturbance to the environment perceived to be deleterious or undesirable. The environmental degradation process amplifies the impact of environmental issues which leave lasting impacts on the environment.
Productive forces, productive powers, or forces of production is a central idea in Marxism and historical materialism.

Land degradation is a process where land becomes less healthy and productive due to a combination of human activities or natural conditions. The causes for land degradation are numerous and complex. Human activities are often the main cause, such as unsustainable land management practices. Natural hazards are excluded as a cause; however human activities can indirectly affect phenomena such as floods and wildfires.

Ribbon development refers to the building of houses along the routes of communications radiating from a human settlement. The resulting linear settlements are clearly visible on land use maps and aerial photographs, giving cities and the countryside a particular character. Such development generated great concern in the United Kingdom during the 1920s and the 1930s as well as in numerous other countries during the decades since.
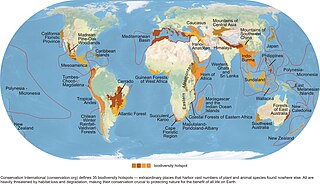
Habitat destruction occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved to elsewhere or are dead, leading to a decrease in biodiversity and species numbers. Habitat destruction is in fact the leading cause of biodiversity loss and species extinction worldwide.

Human impact on the environment refers to changes to biophysical environments and to ecosystems, biodiversity, and natural resources caused directly or indirectly by humans. Modifying the environment to fit the needs of society is causing severe effects including global warming, environmental degradation, mass extinction and biodiversity loss, ecological crisis, and ecological collapse. Some human activities that cause damage to the environment on a global scale include population growth, neoliberal economic policies and rapid economic growth, overconsumption, overexploitation, pollution, and deforestation. Some of the problems, including global warming and biodiversity loss, have been proposed as representing catastrophic risks to the survival of the human species.

Historical ecology is a research program that focuses on the interactions between humans and their environment over long-term periods of time, typically over the course of centuries. In order to carry out this work, historical ecologists synthesize long-series data collected by practitioners in diverse fields. Rather than concentrating on one specific event, historical ecology aims to study and understand this interaction across both time and space in order to gain a full understanding of its cumulative effects. Through this interplay, humans both adapt to and shape the environment, continuously contributing to landscape transformation. Historical ecologists recognize that humans have had world-wide influences, impact landscape in dissimilar ways which increase or decrease species diversity, and that a holistic perspective is critical to be able to understand that system.

Urbicide is a term which describes the deliberate wrecking or "killing" of a city, by direct or indirect means. It literally translates as "city-killing". The term was first coined by the science fiction author Michael Moorcock in 1963 and later used by urban planners and architects to describe 20th century practices of urban restructuring in the United States. Ada Louise Huxtable in 1968 and Marshall Berman in 1996 have written about urban restructuring in areas like the Bronx, and highlight the impacts of aggressive redevelopment on the urban social experience. The term has come into being in an age of rapid globalization and urbanization. Though urbanization trends in the last century have led to a focus on violence and destruction in the context of the city, the practice of urbicide is thousands of years old.

Culture is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, attitude, and habits of the individuals in these groups. Culture is often originated from or attributed to a specific region or location.
Deep ecology is an environmental philosophy that promotes the inherent worth of all living beings regardless of their instrumental utility to human needs, and argues that modern human societies should be restructured in accordance with such ideas.

In the archaeology of Neolithic Europe, the burned house horizon is the geographical extent of the phenomenon of presumably intentionally burned settlements.

Technology, society and life or technology and culture refers to the inter-dependency, co-dependence, co-influence, and co-production of technology and society upon one another. Evidence for this synergy has been found since humanity first started using simple tools. The inter-relationship has continued as modern technologies such as the printing press and computers have helped shape society. The first scientific approach to this relationship occurred with the development of tektology, the "science of organization", in early twentieth century Imperial Russia. In modern academia, the interdisciplinary study of the mutual impacts of science, technology, and society, is called science and technology studies.

Domicide, is the destruction of housing for corporate, political, strategic or bureaucratic reasoning. It can also encompass the widespread destruction of a living environment, forcing the incumbent humans to move elsewhere. In a human rights context, domicide is the deliberate and systematic destruction of housing and basic infrastructure, making an area uninhabitable. The concept of domicide originated in the 1970s, but only assumed its present meaning in 2022, after a report by the UN Special Rapporteur on the Right to Adequate Housing.
Identicide is the deliberate, systematic and targeted destruction of the places, symbols, objects, including ideas, values and aesthetica, and other cultural property that represent the identity of a people, with the intent to erase the cultural narrative and memory of that people, demoralize a population, absorb it into another cultural/political entity, or to rid an area of that people altogether.

The environmental history of Latin America has become the focus of a number of scholars, starting in the later years of the twentieth century. But historians earlier than that recognized that the environment played a major role in the region's history. Environmental history more generally has developed as a specialized, yet broad and diverse field. According to one assessment of the field, scholars have mainly been concerned with "three categories of research: colonialism, capitalism, and conservation" and the analysis focuses on narratives of environmental decline. There are several currents within the field. One examines humans within particular ecosystems; another concerns humans’ cultural relationship with nature; and environmental politics and policy. General topics that scholars examine are forestry and deforestation; rural landscapes, especially agro-export industries and ranching; conservation of the environment through protected zones, such as parks and preserves; water issues including irrigation, drought, flooding and its control through dams, urban water supply, use, and waste water. The field often classifies research by geographically, temporally, and thematically. Much of the environmental history of Latin America focuses on the nineteenth and twentieth centuries, but there is a growing body of research on the first three centuries (1500-1800) of European impact. As the field established itself as a more defined academic pursuit, the journal Environmental History was founded in 1996, as a joint venture of the Forest History Society and the American Society for Environmental History (ASEH). The Latin American and Caribbean Society for Environmental History (SOLCHA) formed in 2004. Standard reference works for Latin American now include a section on environmental history.
References
- ↑ Swanson, Kelly (2009). AP Human Geography 2009. Kaplan. p. 153.
- ↑ Topocide. The Encyclopedia of World Problems and Human Potential, update 24 Jan 2017 (Retrieved Nov 2024)
- ↑ Porteous, Douglas; Sandra E. Smith (2001). Domicide: The Global Destruction Of Home. McGill-Queen's Press - MQUP. p. 12. ISBN 9780773569614.