Related Research Articles

Desertification is a type of gradual land degradation of fertile land into arid desert due to a combination of natural processes and human activities. This spread of arid areas is caused by a variety of factors, such as overexploitation of soil as a result of human activity and the effects of climate change. Geographic areas most affected are located in Africa, Asia and parts of South America. Drylands occupy approximately 40–41% of Earth's land area and are home to more than 2 billion people. Effects of desertification include sand and dust storms, food insecurity, and poverty.

Political ecology is the study of the relationships between political, economic and social factors with environmental issues and changes. Political ecology differs from apolitical ecological studies by politicizing environmental issues and phenomena.

The Sahel region or Sahelian acacia savanna is a biogeographical region in Africa. It is the transition zone between the more humid Sudanian savannas to its south and the drier Sahara to the north. The Sahel has a hot semi-arid climate and stretches across the southernmost latitudes of North Africa between the Atlantic Ocean and the Red Sea. Although geographically located in the tropics, the Sahel does not have a tropical climate.
The Uppsala Conflict Data Program (UCDP) is a data collection program on organized violence, based at Uppsala University in Sweden. The UCDP is a leading provider of data on organized violence and armed conflict, and it is the oldest ongoing data collection project for civil war, with a history of almost 40 years. UCDP data are systematically collected and have global coverage, comparability across cases and countries, and long time series. Data are updated annually and are publicly available, free of charge. Furthermore, preliminary data on events of organized violence in Africa is released on a monthly basis.
Philippe Le Billon is a researcher known for his work in political ecology and on the political economy of war. A Fulbright Research Chair at UC Berkeley and Scholar at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, Le Billon is a professor at the University of British Columbia (UBC) with the Department of Geography and the School of Public Policy and Global Affairs. He earned an MBA at the Pantheon-Sorbonne University in Paris and a doctorate at the University of Oxford. Prior to joining UBC he collaborated with the International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS) and the Overseas Development Institute (ODI).
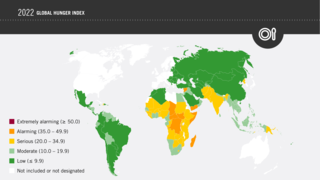
The Global Hunger Index (GHI) is a tool that attempts to measure and track hunger globally as well as by region and by country, prepared by European NGOs of Concern Worldwide and Welthungerhilfe. The GHI is calculated annually, and its results appear in a report issued in October each year.
The Journal of Agrarian Change is a peer-reviewed academic journal established in 2001 covering agrarian political economy. The journal publishes historical and contemporary studies of the social relations and dynamics of production, power relations in agrarian formations and ownership structures and their processes of change.
Michael Mortimore was a British geographer and a prolific researcher of issues in the African drylands. He was an academic in Nigerian universities for over 25 years. He ran a British research consultancy, Drylands Research. He is best known for an anti-Malthusian account of population-environment relationships, More People, Less Erosion, and field-based studies of adaptation to drought.

Margunn Bjørnholt is a Norwegian sociologist and economist. She is a research professor at the Norwegian Centre for Violence and Traumatic Stress Studies (NKVTS) and a professor of sociology at the University of Bergen. Her research has focused on financial institutions, management and working life and later on gender equality, migration and violence. She has also worked as a consultant, a civil servant, served as an expert to the European Commission and been president of the Norwegian Association for Women's Rights.

Henrik Urdal is a Norwegian political scientist and the current director of the Peace Research Institute Oslo (PRIO). Before his appointment as director in 2017 he was a research professor and research director at the institute. He was editor-in-chief of the Journal of Peace Research, the premier journal in the field, from 2010 to 2017.

Katherine Jane Willis, Baroness Willis of Summertown, is a British biologist, academic and life peer, who studies the relationship between long-term ecosystem dynamics and environmental change. She is Professor of Biodiversity in the Department of Biology and Pro-Vice-Chancellor at the University of Oxford, and an adjunct professor in biology at the University of Bergen. In 2018 she was elected Principal of St Edmund Hall, and took up the position from 1 October. She held the Tasso Leventis Chair of Biodiversity at Oxford and was founding Director, now Associate Director, of the Biodiversity Institute Oxford. Willis was Director of Science at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew from 2013 to 2018. Her nomination by the House of Lords Appointments Commission as a crossbench life peer was announced on 17 May 2022.
The Armed Conflict Location & Event Data Project (ACLED) is a non-governmental organization specializing in disaggregated conflict data collection, analysis, and crisis mapping. ACLED codes the dates, actors, locations, fatalities, and types of all reported political violence and demonstration events around the world in real time. As of 2022, ACLED has recorded more than 1.3 million individual events globally. In addition to data collection, the ACLED team conducts analysis to describe, explore, and test conflict scenarios, with analysis made freely available to the public for non-commercial use.

Climate security is a political and policy framework that looks at the impacts of climate on security. Climate security often refers to the national and international security risks induced, directly or indirectly, by changes in climate patterns. It is a concept that summons the idea that climate-related change amplifies existing risks in society that endangers the security of humans, ecosystems, economy, infrastructure and societies. Climate-related security risks have far-reaching implications for the way the world manages peace and security. Climate actions to adapt and mitigate impacts can also have a negative effect on human security if mishandled.
Herder–farmer conflicts in Nigeria are a series of disputes over arable land resources across Nigeria between the mostly-Muslim Fulani herders and the mostly-Christian non-Fulani farmers. The conflicts have been especially prominent in the Middle Belt since the return of democracy in 1999. More recently, they have deteriorated into attacks on farmers by Fulani herdsmen.

Ashok Swain is an Indian-born Swedish academic and public intellectual. He is a professor of peace and conflict research at the Department of Peace and Conflict Research at Uppsala University in Uppsala, Sweden. In 2017, he was appointed as the UNESCO Chair on International Water Cooperation and became the first UNESCO Chair of Uppsala University.

Florian Krampe is a German/Swedish political scientist and international relations scholar at the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI).[2] He is best known for his work on climate-related security risks, Environmental Peacebuilding, and the governance of natural resources after armed conflict. He also serves as Affiliated Researcher at the Research School for International Water Cooperation at the Department of Peace and Conflict Research at Uppsala University. Between 2020 and 2022 Krampe was cross appointed Specially Appointed Professor at the Network for Education and Research on Peace and Sustainability at Hiroshima University, Japan.
Nancy Lee Peluso is an American rural sociologist. She is the Henry J. Vaux Distinguished Professor of Forest Policy at the University of California, Berkeley. In 2006, she was awarded a Guggenheim Fellowship.
The Fulani refers to an ethnic group, the Fulani are group of people whose neighboring farmers are against them in various ethnicities. Nigeria is considered a “melting pot” of different cultural and ethnic groups. Ethnic identification in the country is a complicated amalgamation of primordial and constructivist approaches.
Climate migration is a subset of climate-related mobility that refers to movement driven by the impact of sudden or gradual climate-exacerbated disasters, such as "abnormally heavy rainfalls, prolonged droughts, desertification, environmental degradation, or sea-level rise and cyclones". Gradual shifts in the environment tend to impact more people than sudden disasters. The majority of climate migrants move internally within their own countries, though a smaller number of climate-displaced people also move across national borders.
On 18 and 19 June 2022, 132 civilians were killed by Islamist insurgents in Bankass Cercle, Mopti Region, Mali.
References
- 1 2 Tor A. Benjaminsen
- ↑ "Tor A. Benjaminsen". Google Scholar . Retrieved 22 August 2022.
- ↑ "Årets tidsskriftartikkel". Universitetsforlaget . Retrieved 6 June 2022.
- ↑ "New project to determine the causes of violent conflict and migration in the Sahel". 21 July 2022. Retrieved 22 August 2022.