
Cambridge is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, in the United States. It is a suburb in the Greater Boston metropolitan area, located directly across the Charles River from Boston. The city's population as of the 2020 U.S. census was 118,403, making it the most populous city in the county, the fourth-largest in Massachusetts, behind Boston, Worcester, and Springfield, and ninth-largest in New England. The city was named in honor of the University of Cambridge in Cambridge, England, which was an important center of the Puritan theology that was embraced by the town's founders.

Harvard Square is a triangular plaza at the intersection of Massachusetts Avenue, Brattle Street and John F. Kennedy Street near the center of Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. The term "Harvard Square" is also used to delineate the business district and Harvard University surrounding that intersection, which is the historic center of Cambridge. Adjacent to Harvard Yard, the historic heart of Harvard University, the Square functions as a commercial center for Harvard students, as well as residents of western Cambridge, the western and northern neighborhoods and the inner suburbs of Boston. The Square is served by Harvard station, a major MBTA Red Line subway and a bus transportation hub.
Thomas Oliver was the last royal lieutenant-governor of the Province of Massachusetts Bay.

The Longfellow House–Washington's Headquarters National Historic Site is a historic site located at 105 Brattle Street in Cambridge, Massachusetts. It was the home of noted American poet Henry Wadsworth Longfellow for almost 50 years, and it had previously served as the headquarters of General George Washington (1775–76).

Elmwood, also known as the Oliver-Gerry-Lowell House, is a historic house and centerpiece of a National Historic Landmark District in Cambridge, Massachusetts. It is known for several prominent former residents, including: Thomas Oliver (1734–1815), royal Lieutenant Governor of Massachusetts; Elbridge Gerry (1744–1814), signer of the US Declaration of Independence, Vice President of the United States and eponym of the term "gerrymandering"; and James Russell Lowell (1819–1891), noted American writer, poet, and foreign diplomat.
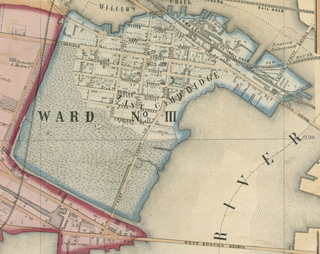
East Cambridge is a neighborhood of Cambridge, Massachusetts. East Cambridge is bounded by the Charles River and the Charlestown neighborhood of Boston on the east, the Somerville border on the north, Broadway and Main Street on the south, and the railroad tracks on the west. Most of the streets form a grid aligned with Cambridge Street, which was laid out to directly connect what is now the Charles River Dam Bridge with what in 1809 was the heart of Cambridge, Harvard Square. The northern part of the grid is a roughly six by eight block residential area. Cambridge Street itself is retail commercial, along with Monsignor O'Brien Highway, the Twin Cities Plaza strip mall, and the enclosed Cambridgeside Galleria. Lechmere Square is the transportation hub for the northern side. The southern half of the grid is largely office and laboratory space for hundreds of dot-com companies, research labs and startups associated with MIT, biotechnology firms including Genzyme, Biogen and Moderna, the Athenaeum Press Building, light industry, an NRG Energy power station, and various small businesses. This half of the neighborhood is generally identified with Kendall Square. Along the waterfront are several hotels and taller apartment buildings.

The Brattle Theatre is a repertory movie theater located in Brattle Hall at 40 Brattle Street near Harvard Square in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The theatre is a small movie house with one screen. It is one of the few remaining movie theaters, if not the only one, to use a rear-projection system; the projector is located behind the screen rather than behind the audience.

Alexander Wadsworth Longfellow Jr. was an American architect and nephew of poet Henry Wadsworth Longfellow.

The William Brattle House is an historic house in Cambridge, Massachusetts. It is one of the seven Colonial mansions described by historian Samuel Atkins Eliot as making up Tory Row, housing several prominent figures in early colonial history. It remains in use by the Cambridge Center for Adult Education.

Fresh Pond Parkway is a historic park and parkway on the western end of Cambridge, Massachusetts, part of the Metropolitan Park System of Greater Boston. The parkway was built in 1899 and added to the National Register of Historic Places in 2005.

The Old Cambridge Historic District is a historic district encompassing a residential neighborhood of Cambridge, Massachusetts that dates to colonial times. It is located just west of Harvard Square, and includes all of the properties on Brattle Street west of Mason Street to Fresh Pond Parkway, all of the properties on Mason Street and Elmwood Avenue, and nearby properties on Craigie Street. The district includes five National Historic Landmarks: Elmwood, the Reginald A. Daly House, the Oliver Hastings House, the Mary Fiske Stoughton House, and the Longfellow House–Washington's Headquarters National Historic Site, as well as several other houses listed separately on the National Register. The district follows the general route of the Watertown Path, an early colonial road that supposedly followed a Native American trail. This portion of the way became known as Tory Row during the American Revolution, because many of the fine mansions lining it were owned by Loyalists. In the 19th and early 20th centuries it continued by a fashionable location, and now features a number of architecturally significant buildings. It includes 215 contributing buildings and one other contributing sites over an area of 52 acres (21 ha). One included building is the Cambridge Historical Society's offices, which are in the NRHP-listed Hooper-Lee Nichols House, located at 159 Brattle Street.

The Brattle Street Church (1698–1876) was a Congregational and Unitarian church on Brattle Street in Boston, Massachusetts.

Samuel Cooper was a Congregational minister in Boston, Massachusetts, affiliated with the Brattle Street Church. He was born in Boston to William Cooper and Judith Sewall, attended the Boston Latin School, and was graduated from Harvard College in 1743. He was ordained as a minister on May 21, 1746, and served as pastor of the Brattle Street Church, 1747-1783. Members of his parish at the Brattle St. Church included some of the most influential people of the American Revolution: John Hancock, Samuel Adams, Joseph Warren, John Adams, and others. He corresponded with Benjamin Franklin, Charles Hector d'Estaing, Gideon Hawley, Charles Gravier de Vergennes; and was associated with Phillis Wheatley. In 1780, he co-founded the American Academy of Arts and Sciences. He served as "chaplain to the General Court" 1758-1770 and 1777-1783. Around 1783 Harvard College offered Cooper the position of college president, but Cooper declined. In September 1746 he married Judith Bulfinch; they had two daughters. A portrait of Cooper by John Singleton Copley now resides in the collection of the Massachusetts Historical Society.

Gardiner Greene (1753–1832) was a cotton planter and merchant from Boston, Massachusetts who conducted business from his plantation, Greenfield, in Demerara (Guyana) in the late 18th and early 19th centuries. Socially prominent in the town of Boston, he owned a house, greenhouse, and garden filled with fruit trees and peacocks on Cotton Hill, opposite Scollay Square. He was also the son-in-law of painter John Singleton Copley.

Brattle Street in Cambridge, Massachusetts, called the "King's Highway" or "Tory Row" before the American Revolutionary War, is the site of many buildings of historical interest, including the modernist glass-and-concrete building that housed the Design Research store, and a Georgian mansion where George Washington and Henry Wadsworth Longfellow both lived, as well as John Vassall and his seven slaves including Darby Vassall. Samuel Atkins Eliot, writing in 1913 about the seven Colonial mansions of Brattle Street's "Tory Row," called the area "not only one of the most beautiful but also one of the most historic streets in America." "As a fashionable address it is doubtful if any other residential street in this country has enjoyed such long and uninterrupted prestige."

The Cambridge Center for Adult Education (CCAE), a non-profit corporation in Cambridge, Massachusetts, has been teaching adult education courses at 42 Brattle Street since taking over the building from the Cambridge Social Union in 1938.
English colonist William Vassall (1592–1656) is remembered both for promoting religious freedom in New England and commencing his family's ownership of slave plantations in the Caribbean. A patentee of the Massachusetts Bay Company, Vassall was among the merchants who petitioned Puritan courts for greater civil liberties and religious tolerance. In 1647, he and John Child published New-England’s Jonas cast up in London, a tract describing the efforts of colonial petitioners. By early 1648, Vassall moved to Barbados to establish a slave-labor sugar plantation. He and his descendants were among the Caribbean's leading planters, enslaving more than 3,865 people before Britain abolished slavery in 1833.

Alice Mary Longfellow was a philanthropist, preservationist, and the eldest surviving daughter of the American poet Henry Wadsworth Longfellow. She is best known as "grave Alice" from her father's poem "The Children's Hour".

Andrew Craigie (1754–1819) is best known for serving as the first Apothecary General of the Continental Army during the American Revolution. The one-time owner of the Longfellow House–Washington's Headquarters National Historic Site, Craigie developed much of East Cambridge, Massachusetts and was responsible for the construction of the Canal Bridge connecting East Cambridge and Boston, which later became known as the Craigie Bridge and later was rebuilt as the Charles River Dam Bridge, but which is still also referred to as Craigie's Bridge.

Major-General William Brattle was an American politician, lawyer, cleric, physician and military officer who served as the Attorney General of Massachusetts from 1736 to 1738. Brattle is best known for his actions during the American Revolution, in which he initially aligned himself with the Patriot cause before transferring his allegiances towards the Loyalist camp, which led to the eventual downfall of his fortunes.

















