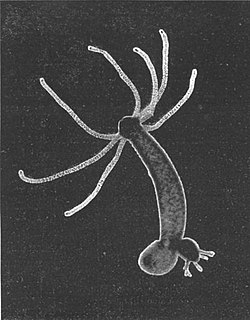
Hydra is a genus of small, freshwater organisms of the phylum Cnidaria and class Hydrozoa. They are native to the temperate and tropical regions. Biologists are especially interested in Hydra because of their regenerative ability; they do not appear to die of old age, or to age at all.

Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is a genetic disorder of the eyes that causes loss of vision. Symptoms include trouble seeing at night and decreasing peripheral vision. As peripheral vision worsens, people may experience "tunnel vision". Complete blindness is uncommon. Onset of symptoms is generally gradual and often begins in childhood.
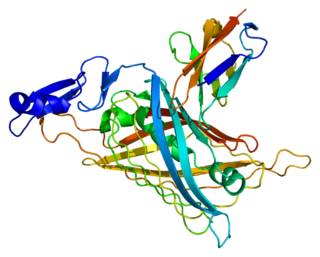
Perlecan (PLC) also known as basement membrane-specific heparan sulfate proteoglycan core protein (HSPG) or heparan sulfate proteoglycan 2 (HSPG2), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HSPG2 gene.

Protein c-Fos is a proto-oncogene that is the human homolog of the retroviral oncogene v-fos. It is encoded in humans by the FOS gene. It was first discovered in rat fibroblasts as the transforming gene of the FBJ MSV. It is a part of a bigger Fos family of transcription factors which includes c-Fos, FosB, Fra-1 and Fra-2. It has been mapped to chromosome region 14q21→q31. c-Fos encodes a 62 kDa protein, which forms heterodimer with c-jun, resulting in the formation of AP-1 complex which binds DNA at AP-1 specific sites at the promoter and enhancer regions of target genes and converts extracellular signals into changes of gene expression. It plays an important role in many cellular functions and has been found to be overexpressed in a variety of cancers.

Ralph Lawrence Brinster is an American geneticist, National Medal of Science laureate, and Richard King Mellon Professor of Reproductive Physiology at the School of Veterinary Medicine, University of Pennsylvania.

Forkhead box protein M1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FOXM1 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the FOX family of transcription factors. Its potential as a target for future cancer treatments led to it being designated the 2010 Molecule of the Year.

Microtubule-associated serine/threonine-protein kinase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAST2 gene. The protein encoded by this gene controls TRAF6 and NF-kappaB activity.

Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase kappa is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTPRK gene. PTPRK is also known as PTPkappa and PTPκ.
In molecular cloning and biology, a gene knock-in refers to a genetic engineering method that involves the one-for-one substitution of DNA sequence information in a genetic locus or the insertion of sequence information not found within the locus. Typically, this is done in mice since the technology for this process is more refined and there is a high degree of shared sequence complexity between mice and humans. The difference between knock-in technology and traditional transgenic techniques is that a knock-in involves a gene inserted into a specific locus, and is thus a "targeted" insertion. It is the opposite of gene knockout.

Forkhead box protein K1 is a transcription factor of the forkhead box family that in humans is encoded by the FOXK1 gene.

A knockout rat is a genetically engineered rat with a single gene turned off through a targeted mutation used for academic and pharmaceutical research. Knockout rats can mimic human diseases and are important tools for studying gene function and for drug discovery and development. The production of knockout rats was not economically or technically feasible until 2008.

Hydramacin-1 is a type of antimicrobial protein. It was first isolated and reproduced in 2008 from cells of the freshwater hydroid Hydra. Only around 60 amino acids long, the protein is unique both in amino acid sequence and tertiary structure, prompting its classification in a new family of proteins, the macins. The protein's unusual structure is most likely a reason for the compound's potent antimicrobial qualities.

Genetically modified animals are animals that have been genetically modified for a variety of purposes including producing drugs, enhancing yields, increasing resistance to disease, etc. The vast majority of genetically modified animals are at the research stage while the number close to entering the market remains small.

Intravital microscopy is a form of microscopy that allows observing biological processes in live animals at a high resolution that makes distinguishing between individual cells of a tissue possible.

Genetically modified mammals are mammals that have been genetically engineered. They are an important category of genetically modified organisms. The majority of research involving genetically modified mammals involves mice with attempts to produce knockout animals in other mammalian species limited by the inability to derive and stably culture embryonic stem cells.
Gliogenesis is the generation of non-neuronal glia populations derived from multipotent neural stem cells.

Genetic engineering techniques allow the modification of animal and plant genomes. Techniques have been devised to insert, delete, and modify DNA at multiple levels, ranging from a specific base pair in a specific gene to entire genes. There are a number of steps that are followed before a genetically modified organism (GMO) is created. Genetic engineers must first choose what gene they wish to insert, modify, or delete. The gene must then be isolated and incorporated, along with other genetic elements, into a suitable vector. This vector is then used to insert the gene into the host genome, creating a transgenic or edited organism.
Breast cancer metastatic mouse models are experimental approaches in which mice are genetically manipulated to develop a mammary tumor leading to distant focal lesions of mammary epithelium created by metastasis. Mammary cancers in mice can be caused by genetic mutations that have been identified in human cancer. This means models can be generated based upon molecular lesions consistent with the human disease.
Research on amyotrophic lateral sclerosis has focused on animal models of the disease, its mechanisms, ways to diagnose and track it, and treatments.













