
The Wheatbelt is one of nine regions of Western Australia defined as administrative areas for the state's regional development, and a vernacular term for the area converted to agriculture during colonisation. It partially surrounds the Perth metropolitan area, extending north from Perth to the Mid West region, and east to the Goldfields-Esperance region. It is bordered to the south by the South West and Great Southern regions, and to the west by the Indian Ocean, the Perth metropolitan area, and the Peel region. Altogether, it has an area of 154,862 square kilometres (59,793 sq mi).

The Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA) is a biogeographic regionalisation of Australia developed by the Australian Government's Department of Sustainability, Environment, Water, Population and Communities. It was developed for use as a planning tool, for example for the establishment of a National Reserve System.

Southwest Australia is a biogeographic region in Western Australia. It includes the Mediterranean-climate area of southwestern Australia, which is home to a diverse and distinctive flora and fauna.

Esperance Plains, also known as Eyre Botanical District, is a biogeographic region in southern Western Australia on the south coast between the Avon Wheatbelt and Hampton regions, and bordered to the north by the Mallee region. It is a plain punctuated by granite and quartz outcrops and ranges, with a semi-arid Mediterranean climate and vegetation consisting mostly of mallee-heath and proteaceous scrub. About half of the region has been cleared for intensive agriculture. Recognised as a bioregion under the Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA), it was first defined by John Stanley Beard in 1980.

Mallee, also known as Roe Botanical District, is a biogeographic region in southern Western Australia. Located between the Esperance Plains, Avon Wheatbelt and Coolgardie regions, it has a low, gently undulating topography, a semi-arid mediterranean climate, and extensive Eucalyptus mallee vegetation. About half of the region has been cleared for intensive agriculture. Recognised as a region under the Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA), it was first defined by John Stanley Beard in 1980.

Warren, also known as Karri Forest Region and the Jarrah-Karri forest and shrublands ecoregion, is a biogeographic region in southern Western Australia. Located in the southwest corner of Western Australia between Cape Naturaliste and Albany, it is bordered to the north and east by the Jarrah Forest region. Its defining characteristic is an extensive tall forest of Eucalyptus diversicolor (karri). This occurs on dissected, hilly ground, with a moderately wet climate. Karri is a valuable timber and much of the karri forest has been logged over, but less than a third has been cleared for agriculture. Recognised as a region under the Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA), and as a terrestrial ecoregion by the World Wide Fund for Nature, it was first defined by Ludwig Diels in 1906.

The High Rainfall Zone is one of three biogeographic zones into which south west Western Australia is divided, the others being the Transitional Rainfall Zone and the Low Rainfall Zone.
The Low Rainfall Zone (LRZ) is one of three biogeographic zones into which south west Western Australia is divided, the others being the High Rainfall Zone and the Transitional Rainfall Zone. The LRZ is considered marginal to the south west, and extends throughout much of Australia.
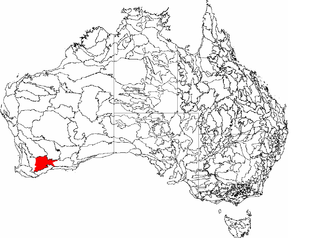
Western Mallee is an Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA) subregion in southern Western Australia. It is a sparsely populated subregion with an area of about 47,000 square kilometres, roughly centred on the town of Newdegate. Largely cleared for intensive agriculture, it still retains patches of native vegetation, but these are under environmental stress from threats such as rising salinity, and are poorly managed.

Eastern Mallee is an Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA) subregion in southern Western Australia.

The Avon Wheatbelt is an Australian bioregion in Western Australia and part of the larger Southwest Australia savanna ecoregion.
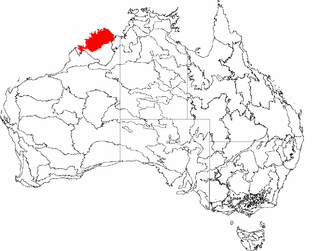
The Northern Kimberley, an interim Australian bioregion, is located in the northern Kimberley region of Western Australia, comprising 8,420,100 hectares.

The Southwest Australia savanna is an ecoregion in Western Australia.
The Eremaean province is a botanical region in Western Australia, characterised by a desert climate. It is sometimes referred to as the dry and arid inland or interior region of Western Australia It is one of John Stanley Beard's phytogeographic regions of WA, based on climate and types of vegetation who, in "Plant Life of Western Australia" (p. 29-37) gives a short history of the various mappings.
Gunniopsis quadrifida, the Sturts pigface, is a plant endemic to Australia that is within the family Aizoaceae. This family consists of a diverse array of species that inhabit arid and/or saline coastal and inland areas, with the plants displaying leaf morphology that is conducive to such harsh environments. Typical features of members of this genus that lie within this family of succulents includes the presence of fleshy-leaves that acts as a water reservoir for the plant with the habit of a smalls shrub.
The botanical provinces of Western Australia delineate "natural" phytogeographic regions of WA, based on climate and types of vegetation. John Stanley Beard, in "Plant Life of Western Australia" (p. 29-37) gives a short history of the various mappings.

Opercularia vaginata (dogweed) is a species of plant within the genus, Opercularia, in the family Rubiaceae. It is endemic to the southwest of Western Australia.

Anigozanthos gabrielae is a species of Anigozanthos in the family Haemodoraceae known as dwarf kangaroo paw. This flowering, rhizomatous, perennial plant is endemic to Southwest Australia and grows on sand in areas which are wet in winter.

Lepidosperma asperatum is a sedge that is endemic to Western Australia. It was first described in 1941 by Georg Kükenthal as Lepidosperma leptostachyum var. asperatum, but was elevated to species status in 2012 by Karen Wilson and Russell Barrett.















