The Research Triangle Regional Public Transportation Authority, known as GoTriangle, provides regional bus service to the Research Triangle region of North Carolina in Wake, Durham, and Orange counties. The GoTriangle name was adopted in 2015 as part of the consolidated GoTransit branding scheme for the Triangle.
The Metropolitan Transportation Commission (MTC) is the government agency responsible for regional transportation planning and financing in the San Francisco Bay Area. It was created in 1970 by the State of California, with support from the Bay Area Council, to coordinate transportation services in the Bay Area's nine counties: Alameda, Contra Costa, Marin, Napa, San Francisco, San Mateo, Santa Clara, Solano, and Sonoma. The MTC is fourth most populous metropolitan planning organization in the United States.

The New Hampshire Department of Transportation (NHDOT) is a government agency of the U.S. state of New Hampshire. The Commissioner of NHDOT is Victoria Sheehan. The main office of the NHDOT is located in the J.O. Morton Building in Concord.
The Lexington Area Metropolitan Planning Organization (MPO) has been involved with transportation planning in Lexington, Kentucky, USA, and its immediate area since being established in 1974. It is responsible, in cooperation with the Kentucky Transportation Cabinet, for planning and coordinating all aspects of transportation planning on behalf of local governments within its region, which includes the Lexington-Fayette Urban County Government and Jessamine County.
The Massachusetts Department of Transportation (MassDOT) oversees roads, public transit, aeronautics, and transportation licensing and registration in the US state of Massachusetts. It was created on November 1, 2009 by the 186th Session of the Massachusetts General Court upon enactment of the 2009 Transportation Reform Act.
The Capital Area Metropolitan Planning Organization (CAMPO) is the federally mandated metropolitan planning organization (MPO) responsible for comprehensive transportation planning in the Austin, Texas, USA area, including Williamson, Travis, Hays, Bastrop, Burnet and Caldwell counties. CAMPO is one of 25 Texas MPOs.
The North Carolina Capital Area Metropolitan Planning Organization is the federally required Metropolitan Planning Organization responsible for the continuous and comprehensive transportation planning process in Wake County and parts of Franklin County, Granville County, Harnett County and Johnston County Counties. NC CAMPO is responsible for carrying out an annual work program that includes updating the Metropolitan Transportation Improvement Program and the Long-Range Transportation Plan.
The Regional Transportation Plan (RTP) is a long-term blueprint of a region’s transportation system. Usually RTPs are conducted every five years and are plans for thirty years into the future, with the participation of dozens of transportation and infrastructure specialists. The plan identifies and analyzes transportation needs of the metropolitan region and creates a framework for project priorities.
The H-GAC 2035 Regional Transportation Plan is the long range transportation plan for the Houston-Galveston Area and serves as blueprint for further planning to be undertaken in the region over the next 30 years. The plan which was developed in a joint cooperation with Cities, Counties, Texas Department of Transportation (TxDOT) and METRO. The RTP combines research, plans and programs by various organizations into one comprehensive plan which is updated every four years. The RTP's main aim is to identify long-range transportation needs, prioritize programs and projects and to provide a forum for dialogue and regional problem solving.
The Hampton Roads Transportation Accountability Commission (HRTAC) is a political subdivision of the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States that has the responsibility for funding several major traffic projects in the Hampton Roads area. It was created by the Virginia General Assembly in 2014 to maintain & administer the Hampton Roads Transportation Fund, a trust fund established by the Virginia General Assembly through a 0.7% increase in the state sales and use tax and a 2.1% increase in the fuel tax region-wide. The organization previously existed as the Hampton Roads Transportation Authority (HRTA) but was disbanded in 2008 after the Virginia Supreme Court invalidated its authority to raise and levy taxes.
The Puget Sound Regional Council (PSRC) is a metropolitan planning organization that develops policies and makes decisions about transportation planning, economic development, and growth management throughout the four-county Seattle metropolitan area surrounding Puget Sound. It is a forum for cities, towns, counties, transit agencies, port districts, Native American tribes, and state agencies to address regional issues.

The Tampa Bay Area Regional Transit Authority, or TBARTA, is a regional transportation agency of the U.S. state of Florida which was created on July 1, 2007. The purpose of the agency is "to plan, develop, finance, construct, own, purchase, operate, maintain, relocate, equip, repair, and manage multimodal systems in Hernando, Hillsborough, Manatee, Pasco, and Pinellas Counties." The agency coordinates its efforts with the Florida Department of Transportation to improve transportation in the Tampa Bay Area.
The New York Metropolitan Transportation Council (NYMTC) is the metropolitan planning organization for New York City, Long Island, and the lower Hudson Valley. It is a federally mandated planning forum to allow the ten counties it represents to coordinate the use of federal transportation funds. NYMTC was created in 1982 after the disbanding of the Tri-State Regional Planning Commission, a metropolitan planning organization for the states of New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut. Unlike most other Metropolitan Planning Organizations (MPOs) in the United States, NYMTC's staff are all employees of the New York State Department of Transportation.
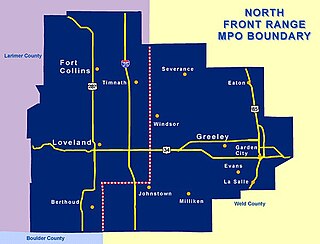
The North Front Range Metropolitan Planning Organization (NFRMPO) is an association of 15 local governments working together to improve regional transportation and air quality. The NFRMPO does long-range and short-range planning, and prioritizes which projects in those plans will receive state and federal funding. The goal of the NFRMPO is to enhance air quality and mobility among northern Colorado communities, and between the North Front Range and the Denver Metro area, by developing cooperative working relationships and financial partnerships among our member governments: Berthoud, Eaton, Evans, Fort Collins, Garden City, Greeley, Johnstown, Larimer County, LaSalle, Loveland, Milliken, Severance, Timnath, Weld County, and Windsor, the Colorado Department of Transportation (CDOT), Federal Highway Administration, the Federal Transit Administration (FTA), and the private sector, giving local governments a voice in regional transportation planning.

Transportation Investment Generating Economic Recovery (TIGER) is a supplementary discretionary grant program included in the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009. The legislation provided $1.5 billion for a National Surface Transportation System through September 30, 2011, "to be awarded on a competitive basis for capital investments in surface transportation projects".
The North Jersey Transportation Planning Authority (NJTPA) is the federally authorized metropolitan planning organization (MPO) for the 13-county northern New Jersey region, one of three MPOs in the state. NJTPA's annual budget is more than $2 billion for transportation improvement projects. The Authority also participates in inter-agency cooperation and receives public input into funding decisions. The NJTPA sponsors and conducts studies, assists county planning agencies and monitors compliance with national air quality goals. The Authority provides federal funding to support the planning work of its 15 subregions. The funds are matched by a local contribution. As vital partners in regional planning work, the subregions help bring a local perspective to all aspects of NJTPA's work to improve the northern New Jersey transportation network.
There are three metropolitan planning organizations (MPO) in New Jersey. The organizations are the main decision-making forums for selecting projects for the Statewide Transportation Improvement Program (STIP) in deliberations involving the New Jersey Department of Transportation (NJDOT), the New Jersey Transit Corporation (NJT), county and municipal transportation planners and engineers, other transportation implementing agencies, the public and elected officials at the state, county, and municipal levels.
Section 165 of the Surface Transportation Assistance Act of 1982 is a section of the larger STAA that deals with purchases related to rail or road transportation. Unlike the similarly titled Buy American Act (1933), the Buy America Act applies only to purchases related to rail or road transportation, such as the construction of highways, railways, or rapid transit systems. The 1982 provisions also apply to purchases made by third-party agencies, using funds granted by agencies within the United States Department of Transportation.






