This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist that connects the hand to the forearm. The term "carpus" is derived from the Latin carpus and the Greek καρπός (karpós), meaning "wrist". In human anatomy, the main role of the wrist is to facilitate effective positioning of the hand and powerful use of the extensors and flexors of the forearm, and the mobility of individual carpal bones increase the freedom of movements at the wrist.

Trapezium, describing a geometric shape, has two contradictory meanings:

The trapezius is a large paired surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula. It moves the scapula and supports the arm.

In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as 1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; (2) the wrist joint or radiocarpal joint, the joint between the radius and the carpus and
(3) the anatomical region surrounding the carpus including the distal parts of the bones of the forearm and the proximal parts of the metacarpus or five metacarpal bones and the series of joints between these bones, thus referred to as wrist joints. This region also includes the carpal tunnel, the anatomical snuff box, bracelet lines, the flexor retinaculum, and the extensor retinaculum.

The anatomical snuff box or snuffbox is a triangular deepening on the radial, dorsal aspect of the hand—at the level of the carpal bones, specifically, the scaphoid and trapezium bones forming the floor. The name originates from the use of this surface for placing and then sniffing powdered tobacco, or "snuff." It is sometimes referred to by its French name tabatière.
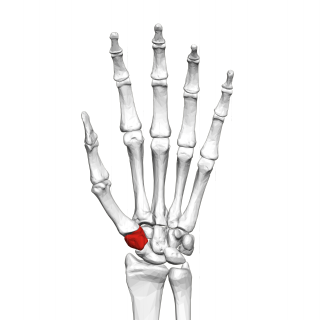
The trapezium bone is a carpal bone in the hand. It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel.

In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus, form the intermediate part of the skeletal hand located between the phalanges of the fingers and the carpal bones of the wrist which forms the connection to the forearm. The metacarpal bones are equivalent to the metatarsal bones in the foot.

The scaphoid bone is one of the carpal bones of the wrist. It is situated between the hand and forearm on the thumb side of the wrist. It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel. The scaphoid bone is the largest bone of the proximal row of wrist bones, its long axis being from above downward, lateralward, and forward. It is approximately the size and shape of a medium cashew.

The flexor pollicis brevis is a muscle in the hand that flexes the thumb. It is one of three thenar muscles. It has both a superficial part and a deep part.
In human anatomy, the abductor pollicis longus (APL) is one of the extrinsic muscles of the hand. As the name implies, its major function is to abduct the thumb at the wrist. Its tendon forms the anterior border of the anatomical snuffbox.

The carpometacarpal (CMC) joints are five joints in the wrist that articulate the distal row of carpal bones and the proximal bases of the five metacarpal bones.
Multangular can refer to one of two bones:
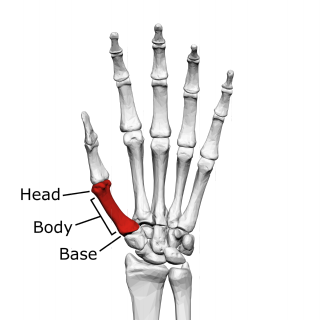
The first metacarpal bone or the metacarpal bone of the thumb is the first bone proximal to the thumb. It is connected to the trapezium of the carpus at the first carpometacarpal joint and to the proximal thumb phalanx at the first metacarpophalangeal joint.

The midcarpal joint is formed by the scaphoid, lunate, and triquetral bones in the proximal row, and the trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate bones in the distal row. The distal pole of the scaphoid articulates with two trapezial bones as a gliding type of joint. The proximal end of the scaphoid combines with the lunate and triquetrum to form a deep concavity that articulates with the convexity of the combined capitate and hamate in a form of diarthrodial, almost condyloid joint.

The Palmar carpometacarpal ligaments are a series of bands on the palmar surface of the carpometacarpal joints that connect the carpal bones to the second through fifth metacarpal bones. The second metacarpal is connected to the trapezium. The third metacarpal is connected to the trapezium, to the capitate, and to the hamate. The fourth and fifth metacarpals are connected to the hamate.
The posterior carpometacarpal ligament consists of a series of bands on the posterior surface of the carpometacarpal joints. They connect the carpal bones to the bases of the second to fifth metacarpals. The second metacarpal bone is connected to the trapezium, trapezoid, and capitate. The third meacarpal is connected to the capitate. The fourth metacarpal is connected to the capitate and hamate, and the fifth metacarpal is connected to the hamate.
Multangular bone may refer to:














