| Trapezoid bone | |
|---|---|
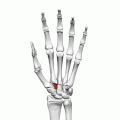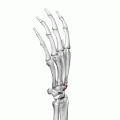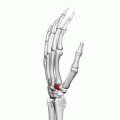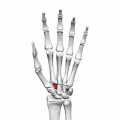
 Left hand anterior view (palmar view). Trapezoid bone shown in red. | |
 The left trapezoid bone. | |
| Details | |
| Articulations | Articulates with four bones: scaphoid proximally second metacarpal distally trapezium bone laterally capitate medially |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | os trapezoideum, os multangulum minus |
| MeSH | D051223 |
| TA98 | A02.4.08.010 |
| TA2 | 1257 |
| FMA | 23724 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The trapezoid bone (lesser multangular bone) is a carpal bone in tetrapods, including humans. It is the smallest bone in the distal row of carpal bones that give structure to the palm of the hand. It may be known by its wedge-shaped form, the broad end of the wedge constituting the dorsal, the narrow end the palmar surface; and by its having four articular facets touching each other, and separated by sharp edges. It is homologous with the "second distal carpal" of reptiles and amphibians.