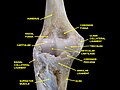
| Radial tuberosity | |
|---|---|
 Left elbow-joint, showing anterior and ulnar collateral ligaments. (Radial tuberosity visible at center right.) | |
 Bones of left forearm. Anterior aspect. (Radius is bone on right. Radial tuberosity is visible at upper left of radius.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | tuberositas radii |
| TA98 | A02.4.05.007 |
| TA2 | 1216 |
| FMA | 23489 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
Beneath the neck of the radius, on the medial side, is an eminence, the radial tuberosity; its surface is divided into:
Contents
- a posterior, rough portion, for the insertion of the tendon of the biceps brachii. [1] [2] [3] [4]
- an anterior, smooth portion, on which a bursa is interposed between the tendon and the bone.
Ligaments that support the elbow joint also attach to the radial tuberosity. [5]