
Dog tag is an informal but common term for a specific type of identification tag worn by military personnel. The tags' primary use is for the identification of casualties; they have information about the individual written on them, including identification and essential basic medical information such as blood type and history of inoculations. They often indicate religious preference as well.
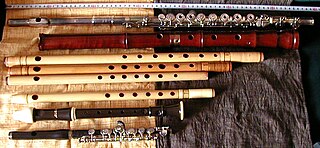
The flute is a family of classical music instrument in the woodwind group. Like all woodwinds, flutes are aerophones, i.e. they make sound by vibrating a column of air. However, unlike woodwind instruments with reeds, a flute is a reedless wind instrument that produces its sound from the flow of air across an opening. According to the instrument classification of Hornbostel–Sachs, flutes are categorized as edge-blown aerophones. A musician who plays the flute is called a flautist or flutist.

Stationery refers to commercially manufactured writing materials, including cut paper, envelopes, writing implements, continuous form paper, and other office supplies. Stationery includes materials to be written on by hand or by equipment such as computer printers.

A bracelet is an article of jewellery that is worn around the wrist. Bracelets may serve different uses, such as being worn as an ornament. When worn as ornaments, bracelets may have a supportive function to hold other items of decoration, such as charms. Medical and identity information are marked on some bracelets, such as allergy bracelets, hospital patient-identification tags, and bracelet tags for newborn babies. Bracelets may be worn to signify a certain phenomenon, such as breast cancer awareness, or for religious/cultural purposes.
The Office of Public Sector Information (OPSI) is the body responsible for the operation of His/Her Majesty's Stationery Office (HMSO) and of other public information services of the United Kingdom. The OPSI is part of the National Archives of the United Kingdom and is responsible for Crown copyright.

A stapler is a mechanical device that joins pages of paper or similar material by driving a thin metal staple through the sheets and folding the ends. Staplers are widely used in government, business, offices, work places, homes and schools.

A hole punch, also known as hole puncher, or paper puncher, is an office tool that is used to create holes in sheets of paper, often for the purpose of collecting the sheets in a binder or folder. A hole punch can also refer to similar tools for other materials, such as leather, cloth, or plastic or metal sheets.

A mandrel, mandril, or arbor is a gently tapered cylinder against which material can be forged or shaped, or a flanged or tapered or threaded bar that grips a workpiece to be machined in a lathe. A flanged mandrel is a parallel bar of a specific diameter with an integral flange towards one end, and threaded at the opposite end. Work is gripped between the flange and a nut on the thread. A tapered mandrel has a taper of approximately 0.005 inches per foot and is designed to hold work by being driven into an accurate hole on the work, gripping the work by friction. A threaded mandrel may have a male or female thread, and work which has an identical thread is screwed onto the mandrel.

Swaging is a forging process in which the dimensions of an item are altered using dies into which the item is forced. Swaging is usually a cold working process, but also may be hot worked.

Filigree is a form of intricate metalwork used in jewellery and other small forms of metalwork.

Deubré is a generic term, originating at Nike, Inc. and dating from the mid 1990s, for an ornamental shoelace tag, most commonly seen on sneakers. Typically, a deubré will have two holes through which a shoelace is threaded, like a bead on string. When the shoe is laced, the deubré is centered between the first two eyelets, with the shoelace passing through and behind the deubré.

A heddle is an integral part of a loom. Each thread in the warp passes through a heddle, which is used to separate the warp threads for the passage of the weft. The typical heddle is made of cord or wire and is suspended on a shaft of a loom. Each heddle has an eye in the center where the warp is threaded through. As there is one heddle for each thread of the warp, there can be near a thousand heddles used for fine or wide warps. A handwoven tea-towel will generally have between 300 and 400 warp threads and thus use that many heddles.

Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, rags, grasses or other vegetable sources in water, draining the water through fine mesh leaving the fibre evenly distributed on the surface, followed by pressing and drying. Although paper was originally made in single sheets by hand, almost all is now made on large machines—some making reels 10 metres wide, running at 2,000 metres per minute and up to 600,000 tonnes a year. It is a versatile material with many uses, including printing, packaging, decorating, writing, cleaning, filter paper, wallpaper, book endpaper, conservation paper, laminated worktops, toilet tissue, currency and security paper and a number of industrial and construction processes.
Banns is a hamlet in west Cornwall, England, United Kingdom situated between Mount Hawke and Porthtowan at grid reference SW 710 480 in the civil parish of St Agnes. The South West Coast Path is 2 km (1.2 mi) to the west of the hamlet. Banns is included in the Mount Hawke and Portreath division of Cornwall Council.

A barrel nut is a specialized forged nut, and is commonly used in aerospace and ready-to-assemble furniture applications.

Bookbinding is the process of physically assembling a book of codex format from an ordered stack of paper sheets that are folded together into sections called signatures or sometimes left as a stack of individual sheets. Several signatures are then bound together along one edge with a thick needle and sturdy thread. Alternative methods of binding that are cheaper but less permanent include loose-leaf rings, individual screw posts or binding posts, twin loop spine coils, plastic spiral coils, and plastic spine combs. For protection, the bound stack is either wrapped in a flexible cover or attached to stiff boards. Finally, an attractive cover is adhered to the boards, including identifying information and decoration. Book artists or specialists in book decoration can also greatly enhance a book's content by creating book-like objects with artistic merit of exceptional quality.
Challan or Chalan is a common Hindi word that has become an Indian English technical word used officially in many professional, especially financial transactions. It usually means an official form or receipt of acknowledgement or other kind of proof document, piece of paperwork, police citation, etc. According to American Merriam-Webster Dictionary "Chalan" means voucher or invoice, comes from Hindi word of same sound and used in India. Similarly, British-English Dictionary Lexico also defines Challan as noun, "an official form or document, such as a receipt, invoice, or summons," and verb, "issue (someone) with an official notice of a traffic offence" and gives several examples of their applications, which are also paralleled by the Oxford Learner's Dictionary's two separate entries on the same. Wiktionary also gives examples of application the word Challan in southeast Asia including its use as a verb with challaning and challaned used similar in context and meaning to police ticketing or someone being ticketed. While most of the dictionaries talk about the meaning representing a monetary penalty which is true in most real cases, Collins English Dictionary goes one step further and defines the verb part of the meaning of Chalan as "verb (transitive), to cause to appear before a magistrate," which in reality happens only in a subset of cases of Challan when a person misses paying the Challan and the matter moves to the next step of receiving a summon from a court.
Sewing is the craft of fastening or attaching objects using stitches made with needle and thread. Sewing is one of the oldest of the textile arts, arising in the Paleolithic Era. Although usually associated with clothing and household linens, sewing is used in a variety of crafts and industries, including shoemaking, upholstery, sailmaking, bookbinding and the manufacturing of some kinds of sporting goods. Sewing is the fundamental process underlying a variety of textile arts and crafts, including embroidery, tapestry, quilting, appliqué and patchwork.
A lawyers bodkin or ribbon threader is a tool used in work with stationery. It is used to bore holes in paper documents so that a connector such as legal tape, a treasury tag or a brass fastener can be threaded through the hole in the documents to bind them together. A lawyers bodkin is similar to a stitching awl: it consists of a pointed metal shaft with an eyelet near the pointed end connected to a bulb-shaped wooden handle; the shaft is kept attached to the handle by a ferrule.
Arthur Blaikie Purvis, PC was a British-born Canadian industrialist who coordinated British war purchases in North America during the Second World War.














