Related Research Articles

Year 1514 (MDXIV) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar.

Charles VIII, called the Affable, was King of France from 1483 to his death in 1498. He succeeded his father Louis XI at the age of 13. His elder sister Anne acted as regent jointly with her husband Peter II, Duke of Bourbon until 1491, when the young king turned 21 years of age. During Anne's regency, the great lords rebelled against royal centralisation efforts in a conflict known as the Mad War (1485–1488), which resulted in a victory for the royal government.

The Duchy of Brittany was a medieval feudal state that existed between approximately 939 and 1547. Its territory covered the northwestern peninsula of Europe, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and the English Channel to the north. It was also less definitively bordered by the river Loire to the south, and Normandy, and other French provinces, to the east. The Duchy was established after the expulsion of Viking armies from the region around 939. The Duchy, in the 10th and 11th centuries, was politically unstable, with the dukes holding only limited power outside their own personal lands. The Duchy had mixed relationships with the neighbouring Duchy of Normandy, sometimes allying itself with Normandy, and at other times, such as the Breton–Norman War, entering into open conflict.

Francis II was Duke of Brittany from 1458 to his death. He was the grandson of John IV, Duke of Brittany. A recurring theme in Francis' life would be his quest to maintain the quasi-independence of Brittany from France. As such, his reign was characterized by conflicts with King Louis XI of France and with his daughter, Anne of France, who served as regent during the minority of her brother, King Charles VIII. The armed and unarmed conflicts from 1465 to 1477 and 1484–1488 have been called the "War of the Public Weal" and the Mad War, respectively.

Anne of Brittany was reigning Duchess of Brittany from 1488 until her death, and Queen of France from 1491 to 1498 and from 1499 to her death. She was the only woman to have been queen consort of France twice. During the Italian Wars, Anne also became Queen of Naples, from 1501 to 1504, and Duchess of Milan, in 1499–1500 and from 1500 to 1512.

The Peace of Étaples was signed on 3 November 1492 in Étaples between Charles VIII of France and Henry VII of England. Charles agreed to end his support for the Yorkist Pretender Perkin Warbeck, in return for being recognised as ruler of the Duchy of Brittany.

The Treaty of Arras was signed at Arras on 23 December 1482 by King Louis XI of France and Archduke Maximilian I of Habsburg as heir of the Burgundian Netherlands in the course of the Burgundian succession crisis.

The House of Montfort-Brittany was a Breton-French noble family, which reigned in the Duchy of Brittany from 1365 to 1514. It was a cadet branch of the House of Dreux; it was thus ultimately part of the Capetian dynasty. It should not be confused with the older House of Montfort which ruled as Counts of Montfort.
The Treaty of Frankfurt may refer to one of three treaties signed at Frankfurt, as follows:

The Treaty of Senlis concerning the Burgundian succession was signed at Senlis, Oise on 23 May 1493 between Maximilian I of Habsburg and his son Philip "the Handsome", Archduke of Austria, and King Charles VIII of France.
The Treaty of Redon was signed in February 1489 in Redon, Ille-et-Vilaine between Henry VII of England and representatives of Brittany. Based on the terms of the accord, Henry sent 6000 English troops to fight under the command of Lord Daubeney. The purpose of the agreement was to prevent France from annexing Brittany. Despite the military support Henry provided, the Bretons were divided and had unreliable allies. It marked a transition from the policy pursued by the Plantagenets, of acquiring and holding territories in France, to a more defensive, Anglo-centric policy. According to Currin, the treaty redefined Anglo-Breton relations, Henry started a new policy to recover Guyenne and other lost Plantagenet claims in France. The treaty marks a shift from neutrality over the French invasion of Brittany to active intervention against it.

The Battle of Saint-Aubin-du-Cormier took place on 28 July 1488, between the forces of King Charles VIII of France, and those of Francis II, Duke of Brittany, and his allies. The defeat of the latter signalled the end to the "guerre folle", a feudal conflict in which French aristocrats revolted against royal power during the regency of Anne de Beaujeu. It also effectively precipitated the end of the independence of Brittany from France.

The Mad War was a late medieval conflict between a coalition of feudal lords and the French monarchy. It occurred during the regency of Anne of Beaujeu in the period after the death of Louis XI and before the majority of Charles VIII. The war began in 1485 and ended in 1488.

Giles Daubeney, 1st Baron Daubeney, KG PC was an English soldier, diplomat, courtier and politician.

John IV of Chalon-Arlay or John of Chalon was a prince of Orange and lord of Arlay. He played an important role in the Mad War, a series of conflicts in which aristocrats sought to resist the expansion and centralisation of power under the French monarch.

The union of the Duchy of Brittany with the Crown of France was the culmination of a political process begun at the end of the 15th century in the wake of the Mad War. It resulted in the Edict of Union of 13 August 1532 and the incorporation of the duchy into the Crown lands of France, a critical step in the formation of modern-day France.

Anne of Brittany was the object of representations very early on. The royal propaganda of Charles VIII and, later on, of Louis XII idealized her as a symbol of the perfect queen, on the union between the kingdom and the duchy, and of the return to peace. Maximilian's Austria having been evicted from the marriage, had a different perspective on the events. Throughout the centuries, historians and popular imagery forged a very different Anne of Brittany, attributing her physical or psychological characteristics or actions that are not necessarily verifiable through historical data.

In the period 1482–1492, the cities of the County of Flanders revolted twice against Maximilian of Austria, who ruled the county as regent for his son, Philip the Handsome. Both revolts were ultimately unsuccessful.
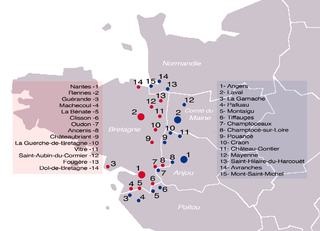
The French–Breton War lasted from 1487 to 1491. The cause of this war was the approaching death of the Breton Duke Francis II of Brittany, who had no clear successor. If not resolved, this meant a resumption of issues from a previous War of the Breton Succession (1341–1364), which had rival claimants allying with England or France, resulting in an ambiguous peace treaty that failed to prevent future succession disputes.

The War of the Burgundian Succession took place from 1477 to 1482, immediately following the Burgundian Wars. At stake was the partition of the Burgundian hereditary lands between the Kingdom of France and the House of Habsburg, after Duke Charles the Bold had perished in the Battle of Nancy on 5 January 1477.
References
- ↑ Currin, p. 888. At Frankfurt on 22 July Maximilian thus concluded a treaty of peace with the envoys of Charles VIII, in which the King of France, among other things, agreed to promote reconciliation between Maximilian and the Flemish rebels and to surrender the French-occupied towns in Brittany to Duchess Anne as soon as she had expelled all English troops from the duchy.