
The Royal Proclamation of 1763 was issued by King George III on 7 October 1763. It followed the Treaty of Paris (1763), which formally ended the Seven Years' War and transferred French territory in North America to Great Britain. The Proclamation forbade all settlements west of a line drawn along the Appalachian Mountains, which was delineated as an Indian Reserve. Exclusion from the vast region of Trans-Appalachia created discontent between Britain and colonial land speculators and potential settlers. The proclamation and access to western lands was one of the first significant areas of dispute between Britain and the colonies and would become a contributing factor leading to the American Revolution. The 1763 proclamation line is more or less similar to the Eastern Continental Divide, extending from Georgia in the south to the divide's northern terminus near the middle of the northern border of Pennsylvania, where it intersects the northeasterly St. Lawrence Divide, and extends further through New England.
The State of Franklin was an unrecognized proposed state located in present-day East Tennessee, in the United States. Franklin was created in 1784 from part of the territory west of the Appalachian Mountains that had been offered by North Carolina as a cession to Congress to help pay off debts related to the American War for Independence. It was founded with the intent of becoming the 14th state of the new United States.

The Transylvania Colony, also referred to as the Transylvania Purchase or the Henderson Purchase, was a short-lived, extra-legal colony founded in early 1775 by North Carolina land speculator Richard Henderson, who formed and controlled the Transylvania Company. Henderson and his investors had reached an agreement to purchase a vast tract of Cherokee lands west of the southern and central Appalachian Mountains through the acceptance of the Treaty of Sycamore Shoals with most leading Cherokee chieftains then controlling these lands. In exchange for the land the tribes received goods worth, according to the estimates of some scholars, about 10,000 British pounds. To further complicate matters, this frontier land was also claimed by the Virginia Colony and a southern portion by Province of North Carolina.

The Treaty of Fort Stanwix was a treaty signed between representatives from the Iroquois and Great Britain in 1768 at Fort Stanwix. It was negotiated between Sir William Johnson, his deputy George Croghan, and representatives of the Iroquois.
Thomas Walker was a physician, planter and explorer in colonial Virginia who served multiple terms in the Virginia General Assembly, and whose descendants also had political careers. Walker explored the Western Colony of Virginia in 1750, a full 19 years before the arrival of famed frontiersman Daniel Boone.

Three agreements, each known as a Treaty of Hopewell, were signed between representatives of the Congress of the United States and the Cherokee, Choctaw, and Chickasaw peoples. They were negotiated and signed at the Hopewell plantation in South Carolina over 45 days during the winter of 1785–86.

The Overmountain Men were American frontiersmen from west of the Blue Ridge Mountains which are the leading edge of the Appalachian Mountains, who took part in the American Revolutionary War. While they were present at multiple engagements in the war's southern campaign, they are best known for their role in the American victory at the Battle of Kings Mountain in 1780. The term "overmountain" arose because their settlements were west of, or "over", the Blue Ridge, which was the primary geographical boundary dividing several of the 13 American states from the Native American lands to the west. The Overmountain Men hailed from parts of Virginia, North Carolina, and what is now Tennessee and Kentucky.

The Watauga Association was a semi-autonomous government created in 1772 by frontier settlers living along the Watauga River in what is now Elizabethton, Tennessee. Although it lasted only a few years, the Watauga Association provided a basis for what later developed into the state of Tennessee and likely influenced other western frontier governments in the trans-Appalachian region. North Carolina annexed the Watauga settlement area, by then known as the Washington District, in November 1776. Within a year, the area was placed under a county government, becoming Washington County, North Carolina, in November 1777. This area covers the present day Washington County, Carter County, and other areas now located in the northeast part of the state of Tennessee.

The Sycamore Shoals of the Watauga River, usually shortened to Sycamore Shoals, is a rocky stretch of river rapids along the Watauga River in Elizabethton, Tennessee. Archeological excavations have found Native Americans lived near the shoals since prehistoric times, and Cherokees gathered there. As Europeans began settling the Trans-Appalachian frontier, the shoals proved strategic militarily, as well as shaped the economies of Tennessee and Kentucky. Today, the shoals are protected as a National Historic Landmark and are maintained as part of Sycamore Shoals State Historic Park.

A longhunter was an 18th-century explorer and hunter who made expeditions into the American frontier for as much as six months at a time.

The Cherokee–American wars, also known as the Chickamauga Wars, were a series of raids, campaigns, ambushes, minor skirmishes, and several full-scale frontier battles in the Old Southwest from 1776 to 1794 between the Cherokee and American settlers on the frontier. Most of the events took place in the Upper South region. While the fighting stretched across the entire period, there were extended periods with little or no action.

Fort Watauga, also known as Fort Caswell, was a fortification located in the Watauga River's Sycamore Shoals near modern-day Elizabethton, Tennessee. It was constructed from 1775 to 1776 by the Watauga Association, a semi-autonomous government founded by American settlers living near the river, to defend the settlers against attacks from British-allied Indians. The fort was originally named Fort Caswell after the governor of North Carolina, Richard Caswell.

Long Island, also known as Long Island of the Holston, is an island in the Holston River at Kingsport in East Tennessee. Important in regional history since pre-colonial times, the island is listed on the National Register of Historic Places and is designated as a U.S. National Historic Landmark District.
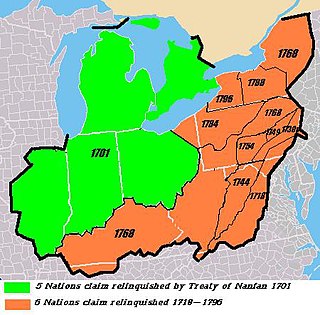
The Six Nations land cessions were a series of land cessions by the Haudenosaunee and Lenape which ceded large amounts of land, including both recently conquered territories acquired from other indigenous peoples in the Beaver Wars, and ancestral lands to the Thirteen Colonies and the United States. The land ceded covered, partially or in the entire, the U.S. states of New York, Pennsylvania, Maryland, Virginia, West Virginia, Kentucky, Ohio, Tennessee and North Carolina. They were bordered to the west by the Algonquian lands in the Ohio Country, Cherokee lands to the south, and Muscogee and Choctaw lands to the southeast.
The Cherokee have participated in over forty treaties in the past three hundred years.
In an effort to resolve concerns of settlers and land speculators following the western boundary established by the Royal Proclamation of 1763 by King George III, it was desired to move the boundary farther west to encompass more settlers who were outside of the boundary. The two treaties that resulted to address this issue were the Treaty of Hard Labour and the Treaty of Fort Stanwix. On October 17, 1768, British representative John Stuart signed the Treaty of Hard Labour with the Cherokee tribe, relinquishing all Cherokee claims to the property west of the Allegheny Mountains and east of the Ohio River, comprising all of present-day West Virginia except the extreme southwestern part of the state. The resulting boundary line ran from the confluence of the Ohio and Kanawha Rivers, to the headwaters of the Kanawha River, then south to East Florida.

The Path Grant Deed is a document regarded as a first step toward the American westward migration across the Appalachian Mountains, resulting from negotiations at Sycamore Shoals in March 1775. The land acquired within the boundaries of the Path Grant allowed Daniel Boone to develop the Wilderness Road free from attack or claims by the Cherokee. The Path Grant was recorded on November 15, 1794, by the Hawkins County, Tennessee registrar in Deed Book #1, pages 147-151
The Jacob Brown Grant Deeds, also known more simply as the Nolichucky Grants, were transactions for the sale of land by the Cherokee Nation to Jacob Brown. The transaction occurred at Sycamore Shoals on the Watauga River on March 25, 1775. The Jacob Brown grants were for two large tracts along the Nolichucky River some of which had been previously leased from the Cherokee.

The Charles Robertson Grant, also known more simply as the Watauga Grant, was a transaction for the sale of land by the Cherokee Nation to Charles Robertson. The transaction occurred at Sycamore Shoals on the Watauga River on March 19, 1775. The Charles Robertson Grant was for a large tract in what is now East Tennessee and Western North Carolina, some of which had been previously leased from the Cherokee.
The Treaty of Dewitts Corner ended the initial Overhill Cherokee targeted attacks on colonial settlements that took place at the beginning of the American Revolution. A peace document signed by the Cherokee and South Carolina, the treaty instead laid the foundation for the decades long Cherokee–American wars fought between the European-Americans and the Chickamauga Cherokee people.















