Savoy is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps. Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south and west and to the Aosta Valley in the east.

The War of the Polish Succession was a major European conflict sparked by a civil war in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth over the succession to Augustus II the Strong, which the other European powers widened in pursuit of their own national interests. France and Spain, the two Bourbon powers, tested the power of the Austrian Habsburgs in Western Europe, as did the Kingdom of Prussia, whilst Saxony and Russia mobilized to support the eventual victor. The fighting in Poland–Lithuania resulted in the accession of Augustus III, who in addition to Russia and Saxony, was politically supported by the Habsburgs.

Victor Amadeus I was the Duke of Savoy and ruler of the Savoyard states from 26 July 1630 until his death in 1637. He was also known as the Lion of Susa.

Victor Amadeus II was the head of the House of Savoy and ruler of the Savoyard states from 12 June 1675 until his abdication in 1730. He was the first of his house to acquire a royal crown, ruling first as King of Sicily (1713–1720) and then as King of Sardinia (1720–1730). Among his other titles were Duke of Savoy, Duke of Montferrat, Prince of Piedmont, Marquis of Saluzzo and Count of Aosta, Maurienne and Nice.

Charles Emmanuel III was Duke of Savoy, King of Sardinia and ruler of the Savoyard states from 3 September 1730 until his death in 1773. He was the paternal grandfather of the last three mainline Kings of Sardinia.

The House of Savoy is an Italian royal house that was established in 1003 in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, the family grew in power from ruling a small Alpine county north-west of Italy to absolute rule of the Kingdom of Sicily from 1713 to 1720, when they were handed the island of Sardinia, over which they would exercise direct rule from then onward.

The Duchy of Savoy was a territorial entity of the Savoyard state that existed from 1416 until 1847 and was a possession of the House of Savoy.

Emmanuel Philibert, known as Testa di ferro, was Duke of Savoy and ruler of the Savoyard states from 17 August 1553 until his death in 1580. He is remembered for the recovery of the Savoyard state following the Battle of St. Quentin (1557), and for moving its capital to Turin.

The 1748 Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle, sometimes called the Treaty of Aachen, ended the War of the Austrian Succession, following a congress assembled on 24 April 1748 at the Free Imperial City of Aachen.

The United Provinces of Central Italy, also known as the Confederation of Central Italy or General Government of Central Italy, was a short-lived military government established by the Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia. It was formed by a union of the former Grand Duchy of Tuscany, Duchy of Parma, Duchy of Modena, and the Papal Legations, after the Second Italian War of Independence.

The War of the Mantuan Succession (1628–1631) was a conflict related to the Thirty Years' War and was caused by the death in December 1627 of Vincenzo II, the last male heir in the direct line of the House of Gonzaga and the ruler of the duchies of Mantua and Montferrat. Those territories were key to control of the Spanish Road, an overland route that allowed Habsburg Spain to move recruits and supplies from Italy to their army in Flanders. The result was a proxy war between France, which supported the French-born Duke of Nevers, and Spain, which backed a distant cousin, the Duke of Guastalla.

Marie Jeanne Baptiste of Savoy-Nemours was born a Princess of Savoy and became the Duchess of Savoy by marriage. First married by proxy to Charles of Lorraine in 1662, Lorraine soon refused to recognise the union and it was annulled. She married Charles Emmanuel II, Duke of Savoy in 1665 who was her kinsman. The mother of the future Victor Amadeus II of Sardinia who saw the elevation of the House of Savoy to kings, she styled herself as Madama Reale or Madame Royale. She acted as Regent of Savoy from 1675 in the name of her son Victor Amadeus II, who was her husband's successor. Her regency officially ended in 1680, but she maintained power until her son banished her from further influence in the state in 1684. She left a considerable architectural legacy in Turin, and was responsible for the remodelling of the Palazzo Madama, which was her private residence. At the time of her death she was the mother of the King of Sardinia as well as great grandmother of two other kings, Louis I of Spain and Louis XV of France.

The Royal Palace of Turin is a historic palace of the House of Savoy in the city of Turin in Northern Italy. It was originally built in the 16th century and was later modernized by Christine Marie of France (1606–1663) in the 17th century, with designs by the Baroque architect Filippo Juvarra. The palace also includes the Palazzo Chiablese and the Chapel of the Holy Shroud, the latter of which was built to house the famous Shroud of Turin.
The Treaty of Susa refers to two separate peace treaties signed in 1629 at Susa in the Duchy of Savoy, recently occupied by France during the Thirty Years' War.
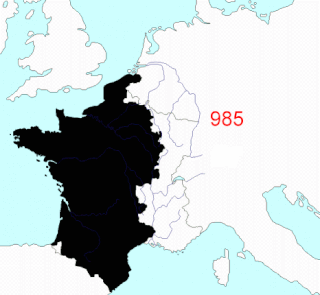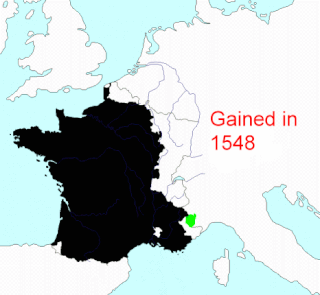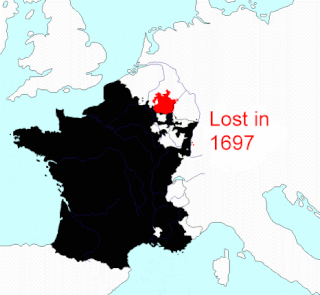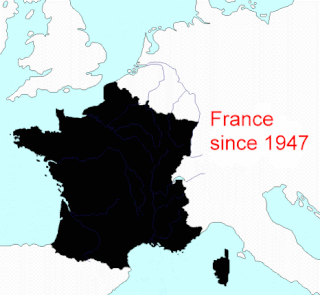
This article describes the process by which metropolitan France - that part of France that is located in Europe, excluding its various overseas territories - came to consist of the territory it does today. Its current borders date from 1947.

Victor Amadeus of Savoy was the eldest son of Victor Amadeus II, Duke of Savoy and his French wife Anne Marie d'Orléans. He was the heir apparent of Savoy from his birth and as such was styled as the Prince of Piedmont. He acted as Regent of Savoy from September 1713 till September 1714 in the absences of his father. He died of smallpox at the age of 15.

Prince Benedetto, Duke of Chablais was an Italian nobleman and military leader. He was the youngest child of King Charles Emmanuel III of Sardinia. He married his niece Maria Anna of Savoy; they had no children. Benedetto was the owner of the Palazzo Chiablese in Turin.

Emmanuel Philibert of Savoy, 2nd Prince of Carignano, Prince of Carignano, was the son and heir of Thomas Francis, Prince of Carignano. He constructed the Palazzo Carignano in Turin.

The Treaty of Turin, signed on 29 August 1696 by the French King and the Duchy of Savoy, ended the latter's involvement in the Nine Years' War.

The Piedmontese Republic was a revolutionary, provisional and internationally unrecognized government established in Turin between 1798 and 1799 on the territory of Piedmont during its military rule by the French First Republic.

















