
A mind map is a diagram used to visually organize information into a hierarchy, showing relationships among pieces of the whole. It is often created around a single concept, drawn as an image in the center of a blank page, to which associated representations of ideas such as images, words and parts of words are added. Major ideas are connected directly to the central concept, and other ideas branch out from those major ideas.
Usability engineering is a field that is concerned generally with human–computer interaction and specifically with devising human–computer interfaces that have high usability or user friendliness. It provides structured methods for achieving efficiency and elegance in interface design.
Usability can be described as the capacity of a system to provide a condition for its users to perform the tasks safely, effectively, and efficiently while enjoying the experience. In software engineering, usability is the degree to which a software can be used by specified consumers to achieve quantified objectives with effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction in a quantified context of use.

Graph drawing is an area of mathematics and computer science combining methods from geometric graph theory and information visualization to derive two-dimensional depictions of graphs arising from applications such as social network analysis, cartography, linguistics, and bioinformatics.
A technical writer is a professional information communicator whose task is to transfer information between two or more parties, through any medium that best facilitates the transfer and comprehension of the information. Technical writers research and create information through a variety of delivery media. Example types of information include online help, manuals, white papers, design specifications, project plans, and software test plans. With the rise of e-learning, technical writers are increasingly becoming involved with creating online training material.
In computer science, a software agent is a computer program that acts for a user or other program in a relationship of agency, which derives from the Latin agere : an agreement to act on one's behalf. Such "action on behalf of" implies the authority to decide which, if any, action is appropriate. Agents are colloquially known as bots, from robot. They may be embodied, as when execution is paired with a robot body, or as software such as a chatbot executing on a phone or other computing device. Software agents may be autonomous or work together with other agents or people. Software agents interacting with people may possess human-like qualities such as natural language understanding and speech, personality or embody humanoid form.

Apache Ant is a software tool for automating software build processes which originated from the Apache Tomcat project in early 2000 as a replacement for the Make build tool of Unix. It is similar to Make, but is implemented using the Java language and requires the Java platform. Unlike Make, which uses the Makefile format, Ant uses XML to describe the code build process and its dependencies.
User-centered design (UCD) or user-driven development (UDD) is a framework of process in which usability goals, user characteristics, environment, tasks and workflow of a product, service or process are given extensive attention at each stage of the design process. These tests are conducted with/without actual users during each stage of the process from requirements, pre-production models and post production, completing a circle of proof back to and ensuring that "development proceeds with the user as the center of focus." Such testing is necessary as it is often very difficult for the designers of a product to understand intuitively the first-time users of their design experiences, and what each user's learning curve may look like. User-centered design is based on the understanding of a user, their demands, priorities and experiences and when used, is known to lead to an increased product usefulness and usability as it delivers satisfaction to the user.
Technical communication is used to convey scientific, engineering, or other technical information. Individuals in a variety of contexts and with varied professional credentials engage in technical communication. Some individuals are designated as technical communicators or technical writers. These individuals use a set of methods to research, document, and present technical processes or products. Technical communicators may put the information they capture into paper documents, web pages, computer-based training, digitally stored text, audio, video, and other media. The Society for Technical Communication defines the field as any form of communication that focuses on technical or specialized topics, communicates specifically by using technology, or provides instructions on how to do something. More succinctly, the Institute of Scientific and Technical Communicators defines technical communication as factual communication, usually about products and services. The European Association for Technical Communication briefly defines technical communication as "the process of defining, creating and delivering information products for the safe, efficient and effective use of products ".
Web usability of a website are broad goals of usability and presentation of information and choices in a clear and concise way, a lack of ambiguity and the placement of important items in appropriate areas as well as ensuring that the content works on various devices and browsers. The end-goal a website creator wants to achieve is to provide the users of the website a better experience.
User interface (UI) design or user interface engineering is the design of user interfaces for machines and software, such as computers, home appliances, mobile devices, and other electronic devices, with the focus on maximizing usability and the user experience. In computer or software design, user interface (UI) design primarily focuses on information architecture. It is the process of building interfaces that clearly communicates to the user what's important. UI design refers to graphical user interfaces and other forms of interface design. The goal of user interface design is to make the user's interaction as simple and efficient as possible, in terms of accomplishing user goals.
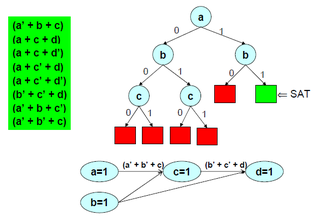
In logic and computer science, the Davis–Putnam–Logemann–Loveland (DPLL) algorithm is a complete, backtracking-based search algorithm for deciding the satisfiability of propositional logic formulae in conjunctive normal form, i.e. for solving the CNF-SAT problem.
User experience design is the process of defining the experience a user would go through when interacting with a digital product or website. Design decisions in UX design are often driven by research, data analysis, and test results rather than aesthetic preferences and opinions. Unlike user interface design, which focuses solely on the design of a computer interface, UX design encompasses all aspects of a user's perceived experience with a product or website, such as its usability, usefulness, desirability, brand perception, and overall performance. UX design is also an element of the customer experience (CX), which encompasses all aspects and stages of a customer's experience and interaction with a company.
MEDCIN, a system of standardized medical terminology, is a proprietary medical vocabulary and was developed by Medicomp Systems, Inc. MEDCIN is a point-of-care terminology, intended for use in Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems, and it includes over 280,000 clinical data elements encompassing symptoms, history, physical examination, tests, diagnoses and therapy. This clinical vocabulary contains over 38 years of research and development as well as the capability to cross map to leading codification systems such as SNOMED CT, CPT, ICD-9-CM/ICD-10-CM, DSM, LOINC, CDT, CVX, and the Clinical Care Classification (CCC) System for nursing and allied health.
Card sorting is a technique in user experience design in which a person tests a group of subject experts or users to generate a dendrogram or folksonomy. It is a useful approach for designing information architecture, workflows, menu structure, or web site navigation paths.
User experience evaluation (UXE) or user experience assessment (UXA) refers to a collection of methods, skills and tools utilized to uncover how a person perceives a system before, during and after interacting with it. It is non-trivial to assess user experience since user experience is subjective, context-dependent and dynamic over time. For a UXA study to be successful, the researcher has to select the right dimensions, constructs, and methods and target the research for the specific area of interest such as game, transportation, mobile, etc.

Content curation is the process of gathering information relevant to a particular topic or area of interest, usually with the intention of adding value through the process of selecting, organizing, and looking after the items in a collection or exhibition. Services or people that implement content curation are called curators. Curation services can be used by businesses as well as end users.
The Classification Tree Method is a method for test design, as it is used in different areas of software development. It was developed by Grimm and Grochtmann in 1993. Classification Trees in terms of the Classification Tree Method must not be confused with decision trees.
User research focuses on understanding user behaviors, needs, and motivations through interviews, surveys, usability evaluations and other forms of feedback methodologies. It is used to understand how people interact with products and evaluate whether design solutions meet their needs. This field of research aims at improving the user experience (UX) of products, services, or processes by incorporating experimental and observational research methods to guide the design, development, and refinement of a product. User research is used to improve a multitude of products like websites, mobile phones, medical devices, banking, government services and many more. It is an iterative process that can be used at anytime during product development and is a core part of user-centered design.
This glossary of computer science is a list of definitions of terms and concepts used in computer science, its sub-disciplines, and related fields, including terms relevant to software, data science, and computer programming.






