Related Research Articles

The Neoproterozoic Era is the unit of geologic time from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago.
The Precambrian is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of the Phanerozoic Eon, which is named after Cambria, the Latinised name for Wales, where rocks from this age were first studied. The Precambrian accounts for 88% of the Earth's geologic time.

The Snowball Earth is a geohistorical hypothesis that proposes during one or more of Earth's icehouse climates, the planet's surface became entirely or nearly entirely frozen with no liquid oceanic or surface water exposed to the atmosphere. The most academically referred period of such global glaciation is believed to have occurred sometime before 650 mya during the Cryogenian period.
Rodinia was a Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic supercontinent that assembled 1.26–0.90 billion years ago (Ga) and broke up 750–633 million years ago (Ma). Valentine & Moores 1970 were probably the first to recognise a Precambrian supercontinent, which they named "Pangaea I." It was renamed "Rodinia" by McMenamin & McMenamin 1990 who also were the first to produce a reconstruction and propose a temporal framework for the supercontinent.

Banded iron formations are distinctive units of sedimentary rock consisting of alternating layers of iron oxides and iron-poor chert. They can be up to several hundred meters in thickness and extend laterally for several hundred kilometers. Almost all of these formations are of Precambrian age and are thought to record the oxygenation of the Earth's oceans. Some of the Earth's oldest rock formations, which formed about 3,700 million years ago (Ma), are associated with banded iron formations.

The Proterozoic is the third of the four geologic eons of Earth's history, spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8 Mya, the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale. It is preceded by the Archean and followed by the Phanerozoic, and is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon".

The Cryogenian is a geologic period that lasted from 720 to 635 million years ago. It forms the second geologic period of the Neoproterozoic Era, preceded by the Tonian Period and followed by the Ediacaran.

Pannotia, also known as the Vendian supercontinent, Greater Gondwana, and the Pan-African supercontinent, was a relatively short-lived Neoproterozoic supercontinent that formed at the end of the Precambrian during the Pan-African orogeny, during the Cryogenian period and broke apart 560 Ma with the opening of the Iapetus Ocean, in the late Ediacaran and early Cambrian. Pannotia formed when Laurentia was located adjacent to the two major South American cratons, Amazonia and Río de la Plata. The opening of the Iapetus Ocean separated Laurentia from Baltica, Amazonia, and Río de la Plata. A 2022 paper argues that Pannotia never fully existed, reinterpreting the geochronological evidence: "the supposed landmass had begun to break up well before it was fully assembled". However, the assembly of the next supercontinent Pangaea is well established.
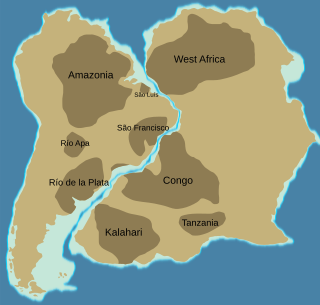
The Congo Craton, covered by the Palaeozoic-to-recent Congo Basin, is an ancient Precambrian craton that with four others makes up the modern continent of Africa. These cratons were formed between about 3.6 and 2.0 billion years ago and have been tectonically stable since that time. All of these cratons are bounded by younger fold belts formed between 2.0 billion and 300 million years ago.

The geology of Australia includes virtually all known rock types, spanning a geological time period of over 3.8 billion years, including some of the oldest rocks on earth. Australia is a continent situated on the Indo-Australian Plate.
The Pan-African orogeny was a series of major Neoproterozoic orogenic events which related to the formation of the supercontinents Gondwana and Pannotia about 600 million years ago. This orogeny is also known as the Pan-Gondwanan or Saldanian Orogeny. The Pan-African orogeny and the Grenville orogeny are the largest known systems of orogenies on Earth. The sum of the continental crust formed in the Pan-African orogeny and the Grenville orogeny makes the Neoproterozoic the period of Earth's history that has produced most continental crust.
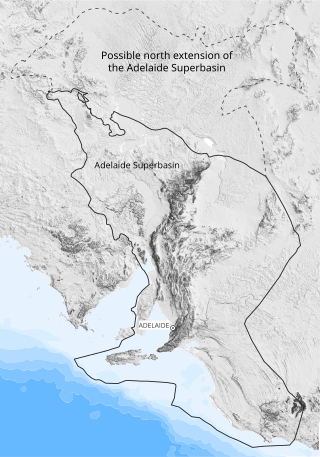
The Adelaide Superbasin is a major Neoproterozoic to middle Cambrian geological province in central and south-east South Australia, western New South Wales, and western Victoria.

The Amazonian Craton is a geologic province located in South America. It occupies a large portion of the central, north and eastern part of the continent and represents one of Earth's largest cratonic regions. The Guiana Shield and Central Brazil Shield constitute respectively the northern and southern exhumed parts of the craton. Between the two shields lies the Amazon Rift, a zone of weakness within the craton. Smaller cratons of Precambrian rocks south of the Amazonian Shield are the Río de la Plata Craton and the São Francisco Craton, which lies to the east.
The Marinoan glaciation, sometimes also known as the Varanger glaciation, was a period of worldwide glaciation. Its beginning is poorly constrained, but occurred no earlier than 654.5 Ma. It ended approximately 632.3 ± 5.9 Ma during the Cryogenian period. This glaciation possibly covered the entire planet, in an event called the Snowball Earth. The end of the glaciation was caused by volcanic release of carbon dioxide and dissolution of gas hydrates and might have been hastened by the release of methane from equatorial permafrost.
The Sturtian glaciation was a worldwide glaciation during the Cryogenian Period when the Earth experienced repeated large-scale glaciations. As of January 2023, the Sturtian glaciation is thought to have lasted from c. 717 Ma to c. 660 Ma, a time span of approximately 57 million years. It is hypothesised to have been a Snowball Earth event, or contrastingly multiple regional glaciations, and is the longest and most severe known glacial event preserved in the geologic record, after the much earlier Huronian glaciation.

The East Antarctic Shield or Craton is a cratonic rock body that covers 10.2 million square kilometers or roughly 73% of the continent of Antarctica. The shield is almost entirely buried by the East Antarctic Ice Sheet that has an average thickness of 2200 meters but reaches up to 4700 meters in some locations. East Antarctica is separated from West Antarctica by the 100–300 kilometer wide Transantarctic Mountains, which span nearly 3,500 kilometers from the Weddell Sea to the Ross Sea. The East Antarctic Shield is then divided into an extensive central craton that occupies most of the continental interior and various other marginal cratons that are exposed along the coast.

The Terra Australis Orogen (TAO) was a late Neoproterozoic- to Paleozoic-age accretionary orogen that ringed the ancient, active southern margin of the supercontinents Rodinia and later Pannotia. This vast orogenic belt stretched for c. 18,000 km (11,000 mi) along-strike and involved, from west to east, landmasses belonging to the modern-day Andean margin of South America, the South African Cape, West Antarctica, Victoria Land in East Antarctica, Eastern Australia, Tasmania, and New Zealand. The formation of the Terra Australis Orogen is associated with the breakup of Rodinia at the end of the Neoproterozoic Era and the creation of Panthalassa, the paleo-Pacific Ocean, and it was succeeded by the Gondwanide orogeny with the formation of the supercontinent Pangea in the middle Paleozoic Era.

The Gondwanide orogeny was an orogeny active in the Permian that affected parts of Gondwana that are by current geography now located in southern South America, South Africa, Antarctica, Australia and New Guinea. The zone of deformation in Argentina extends as a belt south and west of the cratonic nucleus of Río de la Plata–Pampia. The deformation of the orogeny is visible in the Sierra de la Ventana mountains in Argentina and the Cape Fold Belt in South Africa. The Gondwanide orogeny might have been linked with the roughly contemporary San Rafael orogeny of western Argentina.

Brasiliano orogeny or Brasiliano cycle refers to a series of orogenies of Neoproterozoic age exposed chiefly in Brazil but also in other parts of South America. The Brasiliano orogeny is a regional name for the larger Pan-African/Brasiliano orogeny that extended not only in South America but across most of Gondwana. In a wide sense the Brasiliano orogeny includes also the Pampean orogeny. Almeida et al. coined the term Brasiliano Orogenic Cycle in 1973. The orogeny led to the closure of several oceans and aulacogens including the Adamastor Ocean, the Goianides Ocean, the Puncoviscana Ocean and the Peri-Franciscano Ocean.
References
- ↑ Maloof, Adam C.; Rose, Catherine V.; Beach, Robert; Samuels, Bradley M.; Calmet, Claire C.; Erwin, Douglas H.; Poirier, Gerald R.; Yao, Nan; Simons, Frederik J. (17 August 2010). "Possible animal-body fossils in pre-Marinoan limestones from South Australia". Nature Geoscience. 3 (9): 653. Bibcode:2010NatGe...3..653M. doi:10.1038/ngeo934.