
Aromatic compounds or arenes usually refers to organic compounds "with a chemistry typified by benzene" and "cyclically conjugated." The word "aromatic" originates from the past grouping of molecules based on odor, before their general chemical properties were understood. The current definition of aromatic compounds does not have any relation to their odor. Aromatic compounds are now defined as cyclic compounds satisfying Hückel's Rule. Aromatic compounds have the following general properties:
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic; their odor is usually faint, and may be similar to that of gasoline or lighter fluid. They occur in a diverse range of molecular structures and phases: they can be gases, liquids, low melting solids or polymers.
In chemistry, a structural isomer of a compound is another compound whose molecule has the same number of atoms of each element, but with logically distinct bonds between them. The term metamer was formerly used for the same concept.
In chemistry, halogenation is a chemical reaction which introduces one or more halogens into a chemical compound. Halide-containing compounds are pervasive, making this type of transformation important, e.g. in the production of polymers, drugs. This kind of conversion is in fact so common that a comprehensive overview is challenging. This article mainly deals with halogenation using elemental halogens. Halides are also commonly introduced using salts of the halides and halogen acids. Many specialized reagents exist for and introducing halogens into diverse substrates, e.g. thionyl chloride.
In organic chemistry, an aryl halide is an aromatic compound in which one or more hydrogen atoms, directly bonded to an aromatic ring are replaced by a halide. Haloarenes are different from haloalkanes because they exhibit many differences in methods of preparation and properties. The most important members are the aryl chlorides, but the class of compounds is so broad that there are many derivatives and applications.
In organic chemistry, free-radical halogenation is a type of halogenation. This chemical reaction is typical of alkanes and alkyl-substituted aromatics under application of UV light. The reaction is used for the industrial synthesis of chloroform (CHCl3), dichloromethane (CH2Cl2), and hexachlorobutadiene. It proceeds by a free-radical chain mechanism.
In organic chemistry, an electrophilic aromatic halogenation is a type of electrophilic aromatic substitution. This organic reaction is typical of aromatic compounds and a very useful method for adding substituents to an aromatic system.

Triazines are a class of nitrogen-containing heterocycles. The parent molecules' molecular formula is C3H3N3. They exist in three isomeric forms, 1,3,5-triazines being common.

Chlorobenzene (abbreviated PhCl) is an aryl chloride and the simplest of the chlorobenzenes, consisting of a benzene ring substituted with one chlorine atom. Its chemical formula is C6H5Cl. This colorless, flammable liquid is a common solvent and a widely used intermediate in the manufacture of other chemicals.
Arene substitution patterns are part of organic chemistry IUPAC nomenclature and pinpoint the position of substituents other than hydrogen in relation to each other on an aromatic hydrocarbon.
Chlorotoluenes are aryl chlorides based on toluene in which at least one aromatic hydrogen atom is replaced with a chlorine atom. They have the general formula C7H8–nCln, where n = 1–5 is the number of chlorine atoms.
Hexachlorobenzene, or perchlorobenzene, is an aryl chloride and a six-substituted chlorobenzene with the molecular formula C6Cl6. It is a fungicide formerly used as a seed treatment, especially on wheat to control the fungal disease bunt. It has been banned globally under the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants.
A chlorophenol is any organochloride of phenol that contains one or more covalently bonded chlorine atoms. There are five basic types of chlorophenols and 19 different chlorophenols in total when positional isomerism is taken into account. Chlorophenols are produced by electrophilic halogenation of phenol with chlorine.
1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene is an organochlorine compound, one of three isomers of trichlorobenzene. It is a derivative of benzene with three chloride substituents. It is a colorless liquid used as a solvent for a variety of compounds and materials.

Hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH), C
6H
6Cl
6, is any of several polyhalogenated organic compounds consisting of a six-carbon ring with one chlorine and one hydrogen attached to each carbon. This structure has nine stereoisomers, which differ by the stereochemistry of the individual chlorine substituents on the cyclohexane. It is sometimes erroneously called "benzene hexachloride" (BHC). They have been used as models for analyzing the effects of different geometric positions of the large atoms with dipolar bonds on the stability of the cyclohexane conformation. The isomers are poisonous, pesticidal, and persistent organic pollutants, to varying degrees.
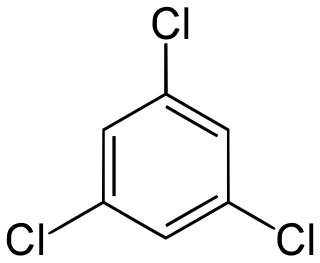
1,3,5-Trichlorobenzene is an organochlorine compound. It is one of the three isomers of trichlorobenzene. Being more symmetrical than the other isomers, it exists as colourless crystals whereas the other isomers are liquids at room temperature.
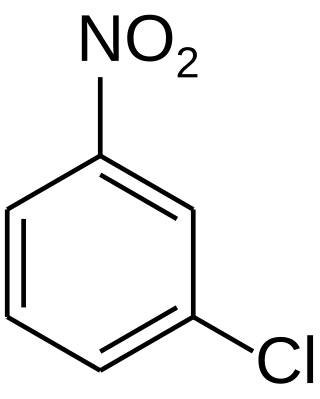
3-Nitrochlorobenzene is an organic compound with the formula C6H4ClNO2. It is a yellow crystalline solid that is important as a precursor to other compounds due to the two reactive sites present on the molecule.

1,3-Dichlorobenzene (also known as meta-dichlorobenzene) is an aryl chloride and isomer of dichlorobenzene with the formula C6H4Cl2. It is the least common of the three isomers of dichlorobenzene, and it is a colorless liquid that is insoluble in water. It is produced as a minor byproduct of the chlorination of benzene, but can also be prepared in a directed manner by the Sandmeyer reaction of 3-chloroaniline. It also arises from the isomerization of the other dichlorobenzenes at high temperature.
1,2,3-Trichlorobenzene is an organochlorine compound with the chemical formula C6H3Cl3. This is one of three isomers of trichlorobenzene; the two others are 1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene and 1,3,5-Trichlorobenzene.
Dichlorotoluenes are organochlorine compounds, in particular aryl chlorides, with the formula CH3C6H3Cl2. Six constitutional isomers exist, differing in the relative position of the two chlorine substituents around the ring. They are all colorless and lipophilic. The 3,5 isomer is a solid at room temperature, whereas the others are liquids.













