

The tricolor hat (Spanish : Gorra tricolor) is a cap popularized in Venezuela by opposition presidential candidate Henrique Capriles Radonsky. [1] [2] Its design replicates the yellow, blue and red colors and stars shown on the Venezuelan flag. [1]


The tricolor hat (Spanish : Gorra tricolor) is a cap popularized in Venezuela by opposition presidential candidate Henrique Capriles Radonsky. [1] [2] Its design replicates the yellow, blue and red colors and stars shown on the Venezuelan flag. [1]
Although Hugo Chávez often wore the colors of the flag and ignored rules governing campaigning, chavistas attempted to sanction Capriles for violating election rules; [3] popular backlash propelled the cap to a symbol of the opposition. [1] [2] Nicolás Maduro later in 2013 co-opted the cap as a symbol of the Bolivarian Revolution [1] [4] with Maduro claiming the cap's design was the idea of Diosdado Cabello. [4]

The politics of Venezuela are conducted under what is nominally a federal presidential republic, but is in practice an authoritarian system of government. Prior to the early 1990s, Venezuela was considered an unusually long-standing and stable liberal democracy in Latin America, having transitioned to democracy in 1958. According to the V-Dem Democracy indices Venezuela was in 2023 the third least electoral democratic country in Latin America.

The national flag of the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, adopted on 15 August 2021 following the Taliban's victory in the 2001–2021 war, features a white field with a black Shahada inscribed. Since the 20th century, Afghanistan has changed its national flag several times. The national flag had black, red and green colors most of the time during the period.

Henrique Capriles Radonski is a Venezuelan politician and lawyer, who served as the 36th Governor of Miranda from 2008 to 2017.

Nicolás Maduro Moros is a Venezuelan politician and the 53rd president of Venezuela since 2013. Previously, he was the 24th vice president of Venezuela from 2012 to 2013, the minister of foreign affairs from 2006 to 2012, and the 3rd president of the National Assembly of Venezuela from 2005 to 2006.

The Democratic Unity Roundtable was a catch-all electoral coalition of Venezuelan political parties formed in January 2008 to unify the opposition to President Hugo Chávez's United Socialist Party of Venezuela in the 2010 Venezuelan parliamentary election. A previous opposition umbrella group, the Coordinadora Democrática, had collapsed after the failure of the 2004 Venezuelan recall referendum.

Tibisay Lucena Ramírez was a Venezuelan politician, president of the National Electoral Council (CNE) between 2006 and 2020, one of the five branches of government of Venezuela. Since 2017, Lucena was sanctioned by several countries for her role in undermining democracy and human rights in the country.

Juan José Rendón Delgado, known professionally as J. J. Rendón, is a Venezuelan political consultant, psychologist, and political activist, known for being the one who has directed and won the most electoral campaigns. He specializes in crisis resolution and is a human rights activist. He is a political asylee in the United States.

Presidential elections were held in Venezuela on 14 April 2013 following the death of President Hugo Chávez on 5 March 2013. Nicolás Maduro—who had assumed the role of acting president since Chávez's death—was declared winner with a narrow victory over his opponent Henrique Capriles, the Governor of Miranda. Capriles had run in the previous election less than a year before, losing to Chávez by an 11-point margin. This time the margin of victory was much smaller, and thus became the closest presidential election of the country since the 1968 election.

In 2014, a series of protests, political demonstrations, and civil insurrection began in Venezuela due to the country's high levels of urban violence, inflation, and chronic shortages of basic goods attributed to economic policies such as strict price controls. Mass protesting began in earnest in February following the attempted rape of a student on a university campus in San Cristóbal. Subsequent arrests and killings of student protesters spurred their expansion to neighboring cities and the involvement of opposition leaders. The year's early months were characterized by large demonstrations and violent clashes between protesters and government forces that resulted in nearly 4,000 arrests and 43 deaths, including both supporters and opponents of the government.

Parliamentary elections were held in Venezuela on 6 December 2015 to elect the 164 deputies and three indigenous representatives of the National Assembly. They were the fourth parliamentary elections to take place after the 1999 constitution, which abolished the bicameral system in favour of a unicameral parliament, and the first to take place after the death of President Hugo Chávez. Despite predictions from the opposition of a possible last-minute cancellation, the elections took place as scheduled, with the majority of polls showing the Democratic Unity Roundtable (MUD) holding a wide lead over the ruling United Socialist Party of Venezuela (PSUV) and its wider alliance, the Great Patriotic Pole (GPP).

2016 protests in Venezuela began in early January following controversy surrounding the 2015 Venezuelan parliamentary elections and the increasing hardships felt by Venezuelans. The series of protests originally began in February 2014 when hundreds of thousands of Venezuelans protested due to high levels of criminal violence, inflation, and chronic scarcity of basic goods because of policies created by the Venezuelan government though the size of protests had decreased since 2014.

On 14 April 2013, Nicolás Maduro was elected President of Venezuela, narrowly defeating opposition candidate Henrique Capriles with just 1.5% of the vote separating the two candidates. Capriles immediately demanded a recount, refusing to recognize the outcome as valid. Maduro was later formally inaugurated as President on 19 April, after the election commission had promised a full audit of the election results. On 24 October 2013, he announced the creation of a new agency, the Vice Ministry of Supreme Happiness, to coordinate all the social programmes.

Presidential elections were held in Venezuela on 20 May 2018, with incumbent Nicolás Maduro being declared re-elected for a second six-year term. The original electoral date was scheduled for December 2018 but was subsequently pulled ahead to 22 April before being pushed back to 20 May. Some analysts described the poll as a sham election, as many prominent opposition parties had been barred from participating in it. The elections had the lowest voter turnout in Venezuela's democratic era.

On 29 March 2017, the Supreme Tribunal of Justice (TSJ) of Venezuela took over legislative powers of the National Assembly. The Tribunal, mainly supporters of President Nicolás Maduro, also restricted the immunity granted to the Assembly's members, who mostly belonged to the opposition.
The Lima Group is a multilateral body that was established following the Lima Declaration on 8 August 2017 in the Peruvian capital of Lima, where representatives of 12 countries met in order to establish a peaceful exit to the ongoing crisis in Venezuela.
Parliamentary elections were held in Venezuela on 6 December 2020. Aside from the 167 deputies of the National Assembly who are eligible to be re-elected, the new National Electoral Council president announced that the assembly would increase by 110 seats, for a total of 277 deputies to be elected.
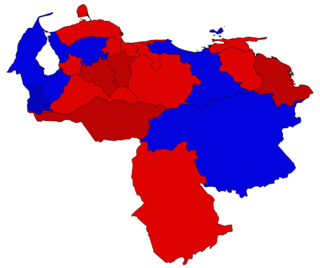
The 2013 Venezuelan political crisis refers to the events that occurred after the presidential elections of the same year, mostly protests in response of the electoral result in which Nicolás Maduro of the Great Patriotic Pole (GPP) was elected as President of Venezuela.

Venezuelan opposition to the Chavista governments of former President Hugo Chávez and current President Nicolás Maduro, commonly referred to as the Venezuelan opposition, or sometimes, anti-Chavismo, is a political umbrella term used to describe political, social and religious movements that have opposed Chavismo, and the associated Bolivarian Revolution political process since 2 February 1999.

A brawl in the National Assembly of Venezuela took place on 30 April 2013 at the Federal Legislative Palace, in Caracas, after opposition deputies who did not recognize the results of the 2013 presidential elections and the ruling party's candidate Nicolás Maduro as president were denied the right to speak for the second consecutive ordinary session. The brawl resulted in at least 11 deputies injured.