Related Research Articles

Tripura is a state in Northeast India. The third-smallest state in the country, it covers 10,491 km2 (4,051 sq mi); and the seventh-least populous state with a population of 3.67 million. It is bordered by Assam and Mizoram to the east and by Bangladesh to the north, south and west. Tripura is divided into 8 districts and 23 sub-divisions, where Agartala is the capital and the largest city in the state. Tripura has 19 different tribal communities with a majority Bengali population. Bengali, English and Kokborok are the state's official languages.

The All India Forward Bloc is a left-wing nationalist political party in India. It emerged as a faction within the Indian National Congress in 1939, led by Subhas Chandra Bose. The party re-established as an independent political party after the independence of India. It has its main stronghold in West Bengal. The party's current Secretary-General is G. Devarajan. Veteran Indian politicians Sarat Chandra Bose and Chitta Basu had been the stalwarts of the party in independent India.

Amra Bangali (AMB) is a political party in India, based on the socio-economic and political philosophy Progressive Utilization Theory given by Prabhat Ranjan Sarkar; the party was sparked off in reaction against anti-Bengali rhetoric in Northeast India. Amra Bangali enjoyed a short stint in the spotlight in the mid-1980s when it even won some gram panchayat seats in border districts. Today, AMB is involved in various movements and protests including those against the Darjeeling Gorkhas calling for the creation of new state of Gorkhaland. It protested National Register of Citizens for Assam and Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019.

The Indigenous Nationalist Party of Twipra was a political party in the Indian state of Tripura. Bijoy Kumar Hrangkhawl was the President of the party. It merged with the Tipraha Indigenous Progressive Alliance (TIPRA) party on 11 June 2021.
The Partition of Bengal in 1947, part of the Partition of India, divided the British Indian Bengal Province along the Radcliffe Line between the Dominion of India and the Dominion of Pakistan. The Bengali Hindu-majority West Bengal became a state of India, and the Bengali Muslim-majority East Bengal became a province of Pakistan.

The Manikya dynasty was the ruling house of the Twipra Kingdom and later the princely Tripura State, what is now the Indian state of Tripura. Ruling since the early 15th century, the dynasty at its height controlled a large swathe of the north-east of the Indian subcontinent. After coming under British influence, in 1761 they transitioned from feudal monarchs into rulers of a princely state, though the Manikyas maintain control of the region until 1949, when it ascended in union with India.
Kirit Pradyot Manikya DebBarma Bahadur is an Indian politician. He is the King of Tripura. He was born in New Delhi, and now resides in Agartala, Tripura. He also served as the editor of TNT-The Northeast Today. He is the current chairman of The Indigenous Progressive Regional Alliance also known as TIPRA Motha. He is known as 'Bubagra' among his people and is one of the active voices for the rights of Indigenous Tripuri people of Tripura.
The Swatantra Tripura Committee was a coordination of political forces in Tripura, India, that struggled against the integration of Tripura into the state of Assam. The campaign was active 1955-1956.

The Indigenous Peoples Front of Tripura (IPFT) is a regional political party in Tripura, India. It is a member of the National Democratic Alliance and North-East Democratic Alliance. The party was merged into the Indigenous Nationalist Party of Tripura (INPT) in 2001, However diverged out in 2009. The party is allied with BJP in the 2018 Tripura Legislative Assembly election and won 8 seats out of 9 contested seats. The party got 7.5% of the total votes polled. The BJP got 36 seats and with a total of 44 seats the BJP-IPFT coalition have two-thirds majority at the Legislative Assembly.
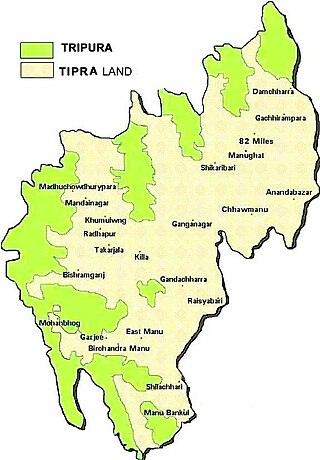
Tipraland is the name of a proposed state in India for the indigenous Tripuri people in the tribal areas of the Tripura state. They demand the Tripura Tribal Areas Autonomous District Council and some surrounding areas to be made into a separate state from Tripura. The proposed state covers 68% of the total geographical area of the Tripura and is home to over one-third of the total population of Tripura.
The politics of Tripura, a state in Northeast India, has been dominated by the Bharatiya Janata Party, the Communist Party of India (Marxist), the Indian National Congress, the Tipra Motha Party, the Indigenous People's Front of Tripura and the Trinamool Congress. As of 2020, the Bharatiya Janata Party is the ruling party in the states's legislative assembly and also won the two parliamentary constituencies in 2019 Indian general election.
The Bengali Hindu diaspora is the worldwide population of the Bengali Hindus of Indian and Bangladeshi origin.

Legislative Assembly elections were held in the Indian state of West Bengal in 1991. The election took place simultaneously with the 1991 Indian general election. The term of the assembly elected in 1987 lasted until February 1992, but the West Bengal government asked the Election Commission of India to arrange the election at an earlier date.
The Left Front is a political alliance in the Indian state of Tripura. The Left Front governed Tripura 1978–1988, and again from 1993 to 2018. The Communist Party of India (Marxist) is the dominant party in the coalition. The other members of the Left Front are the Communist Party of India, the Revolutionary Socialist Party, and the All India Forward Bloc.
The following is a list of political parties in the Indian state of Tripura, on the national, state and regional levels.
Boxanagar is one of the 60 Legislative Assembly constituencies of Tripura state in India. It is in Sipahijala district and is a part of West Tripura Lok Sabha constituency.
Tippera Krishak Samiti is a specially organized peasant organization comprising Greater Comilla, Comilla, Chandpur, Lakshmipur, Noakhali and Brahmanbaria districts. It was founded by Maulvi Emdadul Haque, a member of the Bengal Legislative Council in 1919.

The Tipra Motha Party (TMP), also known as the Tipraha Indigenous Progressive Regional Alliance, is a regional political party and previously a social organisation in Tripura, India. The TIPRA is led by Pradyot Bikram Manikya Deb Barma. It is currently the largest opposition party in Tripura Legislative Assembly

Bangla Pokkho is a pro-Bangla advocacy organization that focuses on rights for Bengalis in the Republic of India based on Bengali Nationalism, and works against the Hindi–Urdu cultural and linguistic imperialism and forced domination of Hindustani speakers in West Bengal. It is organized along linguistic lines and aimed at protecting Bengali culture. It uses the Bengali slogan Joy Bangla.
Discrimination against Bengalis in India comprises negative attitudes and views on Bengalis in India. Though Bengalis have lived in different parts of India for centuries, they are subject to widespread discrimination. This can be either by any other community or in any particular place, due to reasons like inhabitation, discriminating sentiments, political reasons, Government actions, anti-Bangladeshi sentiment etc. The discriminative condition of Bengalis can be traced from Khoirabari massacre, Nellie massacre, Silapathar massacre, North Kamrup massacre, Goreswar massacre, Bongal Kheda etc. This has led to emergence of Bengali sub-nationalism in India as a form of protest and formation of many pro-Bengali organisations in India.