
Córdoba, or sometimes Cordova, is a city in Andalusia, Spain, and the capital of the province of Córdoba. It is the third most populated municipality in Andalusia and the 11th overall in the country.

An alcázar, from Arabic al-Qasr, is a type of Islamic castle or palace in the Iberian Peninsula built during Muslim rule between the 8th and 15th centuries. They functioned as homes and regional capitals for governmental figures throughout the Umayyad caliphate and later, for Christian rulers following the Spanish Reconquista. The term alcázar is also used for many medieval castles built by Christians on earlier Roman, Visigothic or Islamic fortifications and is frequently used as a synonym for castillo or castle.

The Mosque–Cathedral of Córdoba, officially known by its ecclesiastical name of Cathedral of Our Lady of the Assumption, is the cathedral of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Córdoba dedicated to the Assumption of Mary and located in the Spanish region of Andalusia. Due to its status as a former mosque, it is also known as the Mezquita and as the Great Mosque of Córdoba.

The Puerta del Sol is a public square in Madrid, one of the best known and busiest places in the city. This is the centre of the radial network of Spanish roads. The square also contains the famous clock whose bells mark the traditional eating of the Twelve Grapes and the beginning of a new year. The New Year's celebration has been broadcast live since 31 December 1962 on major radio and television networks including Atresmedia and RTVE.

Arcos de la Frontera is a town and municipality in the Sierra de Cádiz comarca, province of Cádiz, in Andalusia, Spain. It is located on the northern, western and southern banks of the Guadalete river, which flows around three sides of the city under towering vertical cliffs, to Jerez and on to the Bay of Cádiz. The town commands a fine vista atop a sandstone ridge, from which the peak of San Cristóbal and the Guadalete Valley can be seen. The town gained its name by being the frontier of Spain's 13th-century battle with the Moors.

Los Remedios is a district of Seville, the regional capital of Andalusia, Spain. It is located on the Isla de La Cartuja, south of the district of Triana, between two forks of the Guadalquivir river. It is linked by bridge to the city centre and the districts of Distrito Sur and Bellavista-La Palmera. From the western side of the island, it is linked by road bridge to the city of San Juan de Aznalfarache and shares a boundary in the Guadalquivir with the city of Gelves. The southern tip of La Cartuja is opposite the municipality of Dos Hermanas.

The history of Carmona begins at one of the oldest urban sites in Europe, with nearly five thousand years of continuous occupation on a plateau rising above the vega (plain) of the River Corbones in Andalusia, Spain. The city of Carmona lies thirty kilometres from Seville on the highest elevation of the sloping terrain of the Los Alcores escarpment, about 250 metres above sea level. Since the first appearance of complex agricultural societies in the Guadalquivir valley at the beginning of the Neolithic period, various civilizations have had an historical presence in the region. All the different cultures, peoples, and political entities that developed there have left their mark on the ethnographic mosaic of present-day Carmona. Its historical significance is explained by the advantages of its location. The easily defended plateau on which the city sits, and the fertility of the land around it, made the site an important population center. The town's strategic position overlooking the vega was a natural stronghold, allowing it to control the trails leading to the central plateau of the Guadalquivir valley, and thus access to its resources.

The Walls of Seville are a series of defensive walls surrounding the Old Town of Seville. The city has been surrounded by walls since the Roman period, and they were maintained and modified throughout the subsequent Visigoth, Islamic and finally Castilian periods. The walls remained intact until the 19th century, when they were partially demolished after the revolution of 1868. Some parts of the walls still exist, especially around the Alcázar of Seville and some curtain walls in the barrio de la Macarena.
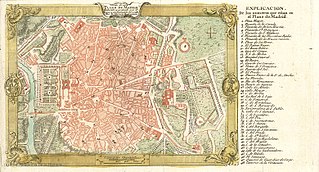
The Walls of Felipe IV surrounded the city of Madrid between 1625 and 1868. Philip IV ordered their construction to replace the earlier Walls of Philip II and the Walls del Arrabal, which had already been surpassed by the growth of population of Madrid. These were not defensive walls, but essentially served fiscal and surveillance purposes: to control the access of goods to the city, ensure the collection of taxes, and to monitor who went in and out of Madrid. The materials used for construction were brick, mortar and compacted earth.

The Walls of Madrid are the five successive sets of walls that surrounded the city of Madrid from the Middle Ages until the end of the 19th century. Some of the walls had a defensive or military function, while others made it easy to tax goods entering the city. Towards the end of the 19th century the demographic explosion that came with the Industrial Revolution prompted urban expansion throughout Spain. Older walls were torn down to enable the expansion of the city under the grid plan of Carlos María de Castro.
The Christian Walls of Madrid, also known as the Medieval Walls, were built in Madrid, Spain between the 11th and 12th centuries, once the city passed to the Crown of Castile. They were built as an extension of the original 9th-century Muslim Walls of Madrid to accommodate the new districts which emerged after the Reconquista.
The Walls del Arrabal were the third in a set of five walls built around Madrid, now the capital of Spain. There are no remaining ruins of the Walls del Arrabal, leaving some debate as to their extent and the period of their construction. It is possible that the walls were built as early as the 12th century, however they were most likely constructed in 1438. The walls may have been intended to protect people against the plagues that ravaged the city at the time. The walls united the urbanized suburbs of the city and prevented entry of the infected.

The Puerta de la Macarena, also known as Arco de la Macarena, stands alongside the Postigo del Aceite and the Puerta de Córdoba the only three city gates that remain today of the original walls of Seville. It is located in the calle Resolana, within of barrio de San Gil, which belongs to the district of Casco Antiguo of the city of Seville, in Andalusia, Spain. The gate faces the Basílica de La Macarena, which houses the image of the Our Lady of la Esperanza Macarena, one of the most characteristic images of the Holy Week in Seville.

.
The Puerta de Triana was the generic name for an Almohad gate and a Christian gate rose in the same place. It was one of the gates of the walled enclosure of Seville (Andalusia).

Puerta del Campo was a city gate in Valladolid, Spain, named after the street that ran through it. Until at least the 18th century, it lent its name to the surrounding area.

Old Town of Cáceres is a historic walled city in Cáceres, Spain.

The Arch of Isabel II was an ephemeral triumphal arch, now disappeared, located in Córdoba, Spain. This commemorative monument was built in front of the old Puerta Nueva in 1862. The reason for its construction was to welcome the arrival of Queen Isabel II to the city of Cordoba, which took place on September 14, 1862. After the Queen's visit, the arch was abandoned and later dismantled.

Avenida de la Constitución is an important avenue in the Casco Antiguo district of Seville, Andalusia, Spain. It starts from the square known as Puerta de Jerez and reaches the Plaza Nueva, considered the center of the city and where the historic building of the Seville City Council is located. It has a length of 600 m (0.37 mi).

The history of the Puerta del Sol represents an essential part of the memory of the Villa de Madrid, not only because the Puerta del Sol is a point of frequent passage, but also because it constitutes the "center of gravity" of Madrid's urban planning. The square has been acquiring its character as a place of historical importance from its uncertain beginnings as a wide and impersonal street in the sixteenth century, to the descriptions of the first romantic travelers, the receptions of kings, popular rebellions, demonstrations, etc. It has been the scene of major events in the life of the city, from the struggle against the French invaders in 1808 to the proclamation of the Second Republic in 1931, and it has also retained its place as the protagonist of the custom of serving twelve grapes on New Year's Eve, to the sound of the chimes struck by the Correos clock. Nowadays it is a communications hub, a meeting point, a place of appointments, a place for celebrations and the beginning of demonstrations in the Capital.



















